Prognose der Verkehrslage in der Region Hannover
Die primäre Anforderung der Verkehrsteilnehmer im Bereich des Straßenverkehrs ist die Kenntnis der aktuellen Verkehrslage. Diese basiert in der Regel auf der wirklich benötigten Reisezeit von sehr vielen Verkehrsteilnehmern, deren Daten häufig im Kontext von Routingdiensten abgegriffen werden.
Im Rahmen von Data4UrbanMobility wurden Werkzeuge entwickelt um eine ganglineinbasierte Prognose der Verkehrslage zu ermöglichen. Die folgende Abbildung zeigt eine Oberfläche auf der typische Ganglinienverläufe und Ausreißer visualisiert werden.
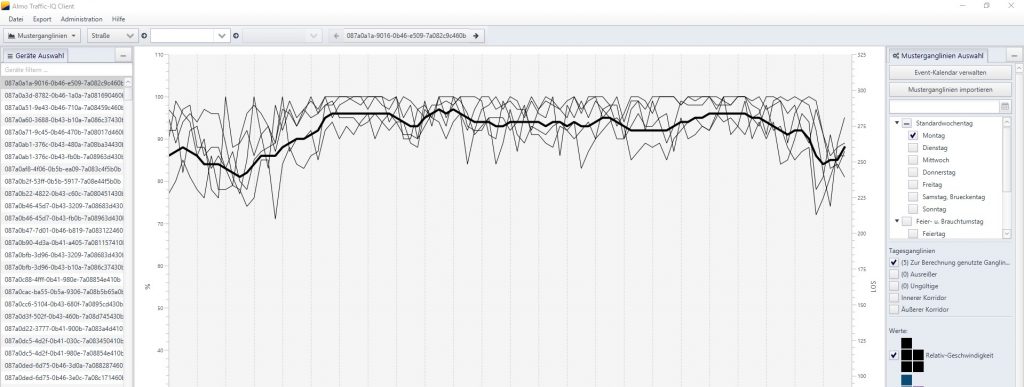
Die Prognose der Verkehrslage kann dann mittels einer Karte für den Endnutzer visualisert werden:
Erste Version der MIC-App bereitgestellt
Eine erste Version der MIC-App (Move in the City) konnte allen Partnerinnen und Partnern des Projekts und einer geschützten Nutzer*innengruppe der Öffentlichkeit zur Verfügung gestellt werden. Die mobile App MiC ist ein Instrument zur Datenerhebung.
Dabei verknüpft MiC – eine Entwicklung des Institute for Sustainable Urbanism ISU der TU Braunschweig und Projektionisten GmbH Hannover – das wachsende Bewusstsein und die Notwendigkeit für digitale Bürger*innenrechte mit den Potentialen mittels der Auswertung großer Datenmengen neue Formen der menschzentrierten Entwicklung von Stadt und Mobilität zu ermöglichen stellt eine Möglichkeit dar, sich aktiv als Bürgerwissenschaftlerin und Bürgerwissenschaftler an der Forschung und Entwicklung der Mobilität für alle in der Stadt der Zukunft zu beteiligen.
MiC erhebt – durch die Nutzerinnen und Nutzer gesteuert – Daten zu Strecken und Art der Fortbewegung. Diese Daten werden pseudonymisiert, so dass ein Rückschluss auf die jeweilige Person nicht mehr möglich ist. Wichtig ist die Vielzahl der Nutzerinnen und Nutzer – nicht die einzelne Bewegung. Die Stadt der Zukunft zeichnet sich aus durch den barrierearmen Zugang zu Mobilität und Erreichbarkeit für alle. Der holistische Ansatz der Forscherinnen und Forscher des Institute for Sustainable Urbanism ISU (TU Braunschweig) sowie der Projektbeteiligten betrachtet Stadt dabei auf verschiedenen Maßstabsebenen und bringt intelligente Planungen – wie z.B. die 5-Minuten Stadt –, Städtebau und innovative Technologien zusammen. Für ein umfassendes Verständnis individueller Mobilität und darauf aufbauende neue Methoden und Werkzeuge für integrierte Verkehrs- und Stadtplanung werden mittels der MiC-App uns umfangreiche und detaillierte Daten darüber geliefert, wie und auf welchem Wege wir uns in der Stadt fortbewegen.
Entwicklungsstand:
In der ersten Version ermöglicht das Stadtforschungstool MiC den Nutzer*innen durch eine einfach Handhabung das Starten und Beenden der „Tracking-Time“ (Bild 1). Wichtig ist, die Nutzer*innen entscheidet selber über den Zeitraum. Als erstes Ergebnis für die Nutzer*innen steht eine Zusammenfassung ihrer bisher aufgezeichneten Routen (Bild2). In den Einstellung (Bild 3) kann der Nutzer sich aktiv an Feedback beteiligen (Bild 4) sowie seinen Account und somit seiner zur Verfügung gestellten Daten löschen (Bild 5).
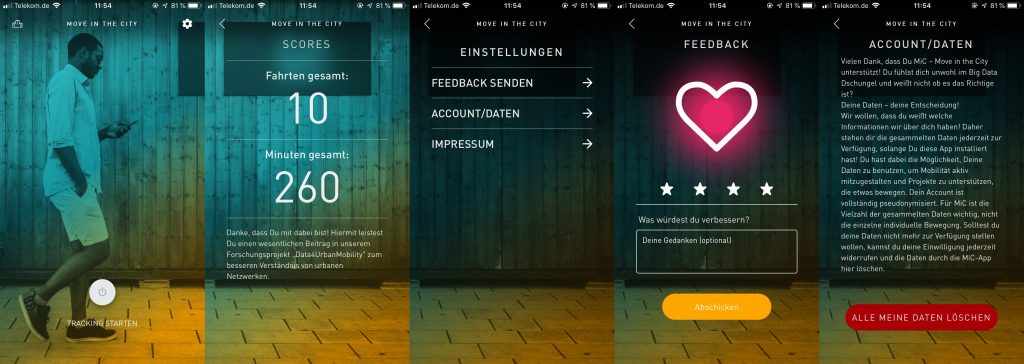
von links nach recht: Bild1-5 MIC App Interface – Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
Die aktuelle Weiterentwicklung sieht eine Visualisierung der Routen für den jeweiligen Nutzer vor.
Um Teil der Testgruppe zu werden ist zur Zeit noch eine Anmeldung unter: www.mic-app.org notwendig. Die Anwendung ist nicht frei im App Store / GooglePlay Store zu erhalten.
Auf der Internetseite www.mic-app.org wird zusätzlich detailliert auf häufige Fragen (FAQ) zur Anwendung sowie über Entwicklungen und Neuheiten informiert
D4UM Plattform und Dashboard V2
Die neue Version der Plattform inklusive des Dashboards gibt noch detailliertere Auskünfte über die Verkehrssituation
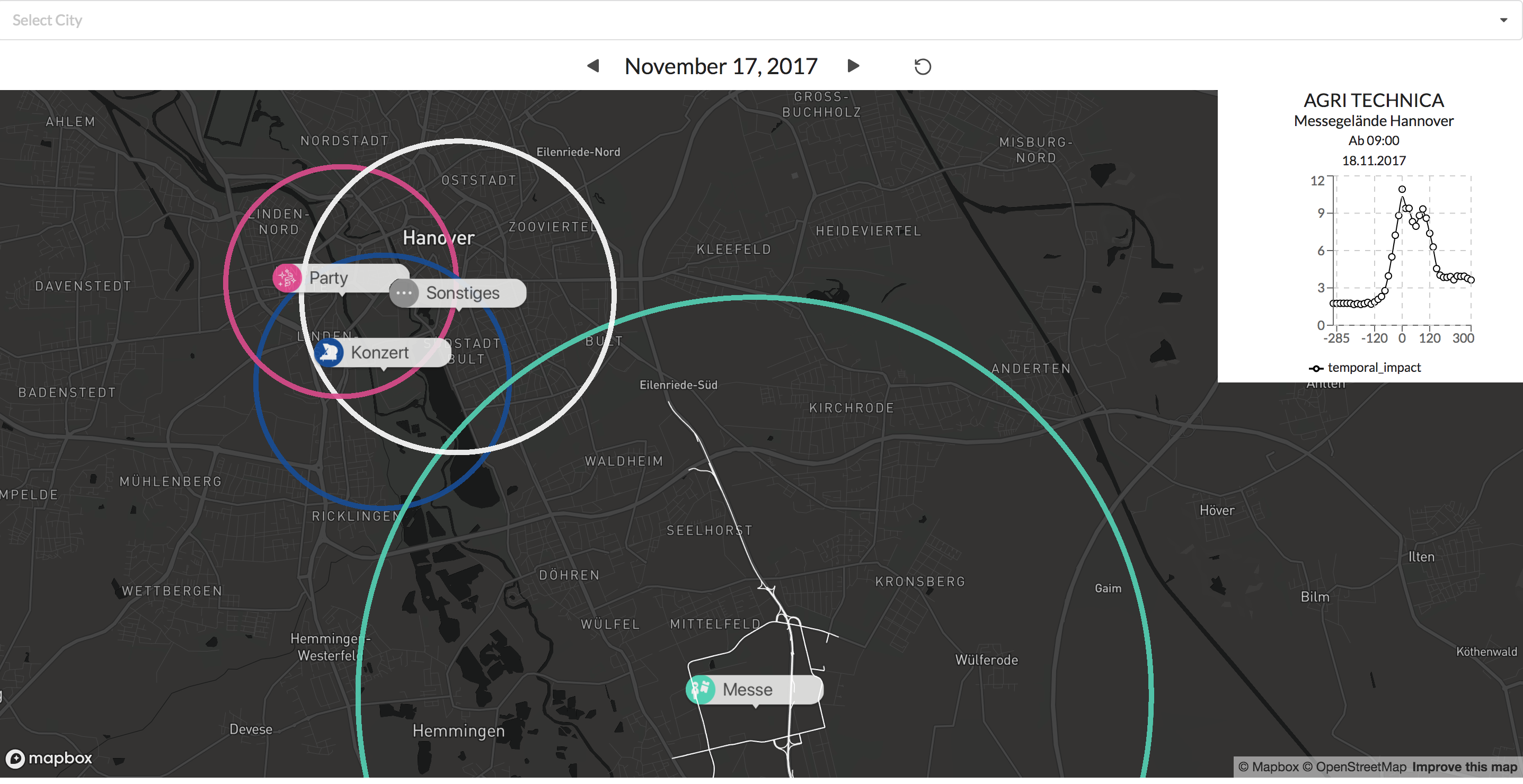
Die farblich unterschiedlichen Label lassen eine schnelle Unterscheidung zwischen den verschiedenen Event typen zu. Durch das klicken auf eines der Events wird der typically affected subgraph angezeigt für diesen Eventtyp.
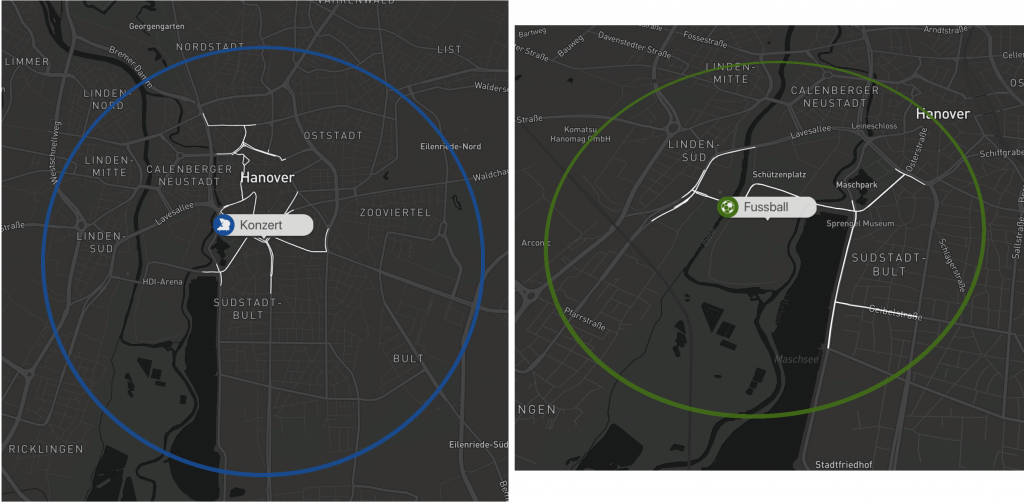
Beispiele: Visualisierungen eines Konzerts und eines Fußballspiels
Zusätzlich gibt der Graph in der oberen rechten Ecke Auskunft über die Verkehrssituation vor und nach dem Eventstart.
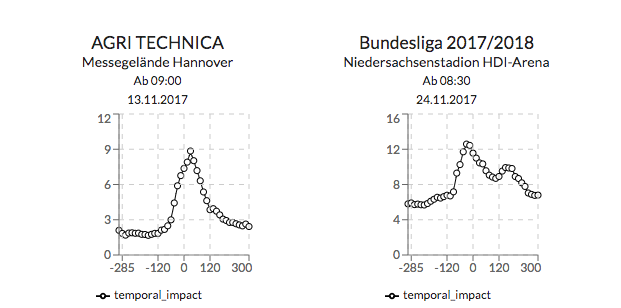
{API}
Es wurden die API Endpunkte mit zusätzlichen Information erweitert.
Diese werden mittels der als Teil der Forschung entwickelten Modellen erstellt.
Erste Version der D4UM-App bereitgestellt
Eine erste Version der D4UM-App konnte allen Partnern des Projekts zur Verfügung gestellt werden. Die App stellt eine Möglichkeit dar, sich Fahrtauskünfte mit dem öffentlichen Personennahverkehr in Niedersachsen und Bremen (Datengrundlage: EFA – elektronische Fahrplanauskunft für Niedersachsen und Bremen) ausgeben zu lassen. Im Fokus stand hierbei, dass der Nutzer schnell und einfach an die für ihn wichtigen Informationen gelangen kann, um so seine Reise möglichst simpel planen zu können.
Folgende Funktionen dienen dabei in der ersten Version der schnellen Auskunft:
Abfahrten und Verbindungen
Über die Funktion Abfahrten lassen sich Abfahrtszeiten an einer bestimmten oder an nahegelegenen Haltestellen ermitteln. Unter Verbindungen können hingegen Fahrtvorschläge von einem Startpunkt (Adresse oder Haltestelle) zu einem Zielpunkt gesucht werden. Zeiten stehen dabei auch in Echtzeit zur Verfügung, sodass auch Verspätungen direkt von dem Nutzer erkannt werden können.
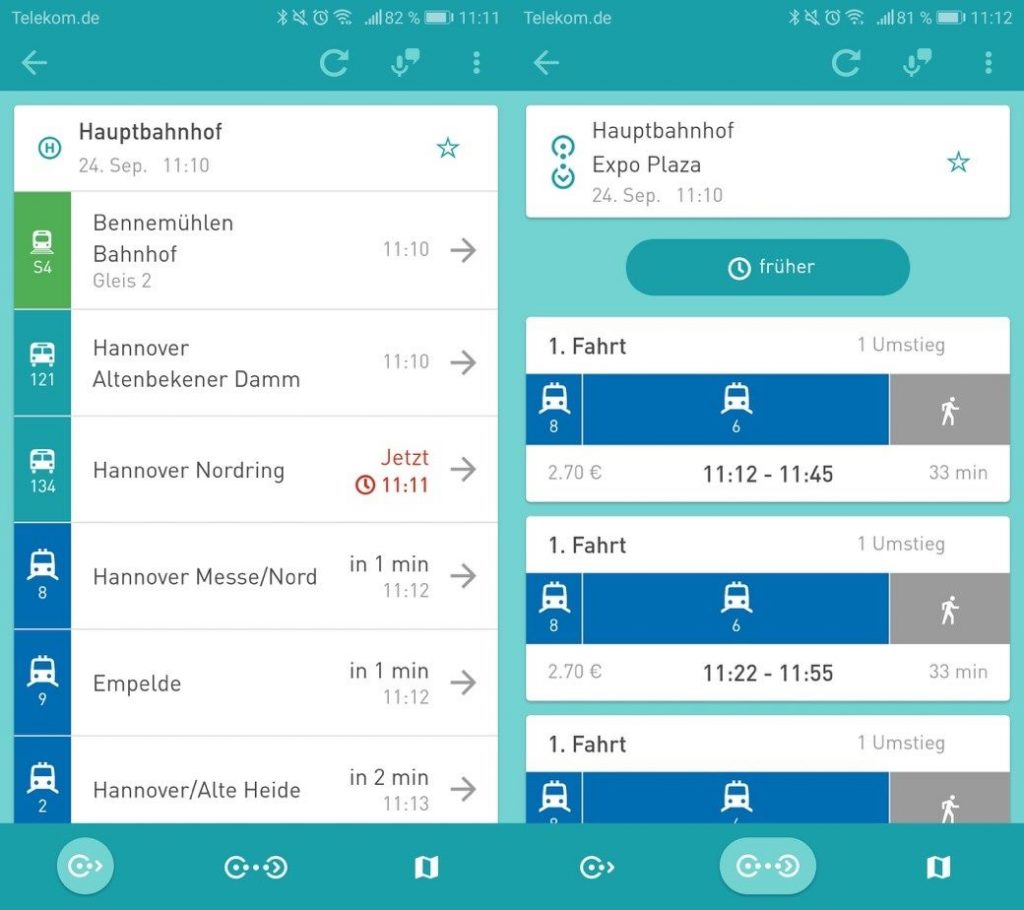
Karte
Über die Karte sind alle Haltestellen zu finden, sodass sich der Nutzer einen Überblick über die nähere Umgebung oder auch den Weg zur Haltestelle oder einem Ziel verschaffen kann.
Wird auf der Karte auf ein Haltestellensymbol oder den zugehörigen Haltestellennamen geklickt, öffnet sich der Abfahrtsmonitor zu dieser Haltestelle. Die nächsten Abfahrten können somit auch über diesen Weg aufgerufen werden.
Darüber hinaus kann sich der Nutzer auch den Verlauf seiner Fahrt anzeigen lassen.
Menü/Einstellungen
Weitere Funktionen und Einstellungen finden sich ergänzend im Menü der App.
Der Nutzer bekommt hier zum einen die Möglichkeit, dass erweiterte Einstellungen zu den Suchanfragen bei Verbindungen oder Abfahrten vorgenommen werden können, und zum anderen, dass er weitere Features verwenden kann. Darunter befindet sich zum Beispiel das Feedbackformular. Hierüber kann unkompliziert Kontakt mit den Entwicklern der D4UM-App per Mail aufgenommen werden. Icons ermöglichen es, dass ein Eindruck zu der App übermittelt werden kann. Ein weiteres Feld für Freitext bietet zudem Platz für individuelle Kritik und einer Meinung zu der App. So kann in Zukunft kundennah an der App weiterentwickelt und einfach auf Wünsche und Meinungen reagiert werden.
Quantifizierungen und Vorhersage von Auswirkungen von Veranstaltungen
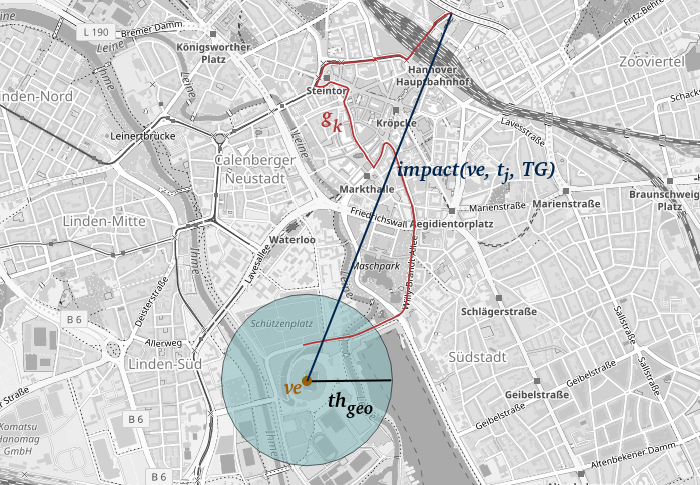
Neue Data4UrbanMobility-Forschungsergebnisse ermöglichen es, die räumlichen Auswirkungen von Veranstaltungen zu quantifizieren und vorherzusagen. Dazu werden zusammenhängende, betroffene Straßenabschnitte in der Nähe von Veranstaltungen identifiziert. Auf dieser Grundlage kann dann die räumliche Auswirkung quantifiziert werden. Das Verfahren ist in der folgenden Grafik dargestellt.
(Karte von https://www.openstreetmap.org)
Hier in Gelb markiert ist eine Veranstaltung, in Rot betroffene Straßenabschnitte und in Dunkelblau die gemessene Auswirkung. Weiterhin wurden Verfahren des Maschinellen Lernens angewandt, um diese Auswirkungen zu prognostizieren. Dabei konnte der Fehler gegenüber bestehenden state-of-the-art Ansätzen um bis zu 40% verringert werden.
D4UM – Plattform V1 fertiggestellt
Die erste Version der Data4UrbanMobility Plattform wurde fertiggestellt. Dazu wurde zunächst eine 3-Schichten Architektur der Plattform konzipiert und implementiert. Die Plattform bietet RESTfull Webservices für Mobilitätsapplikationen wie Dashboard-Anwendungen oder Apps an. Als erste Beispielanwendung wurde dazu eine interaktive Karte entwickelt, die die Auswirkungen von Veranstaltungen visualisiert. Ein Ausschnitt aus der Anwendung ist im folgenden Screenshot zu sehen.
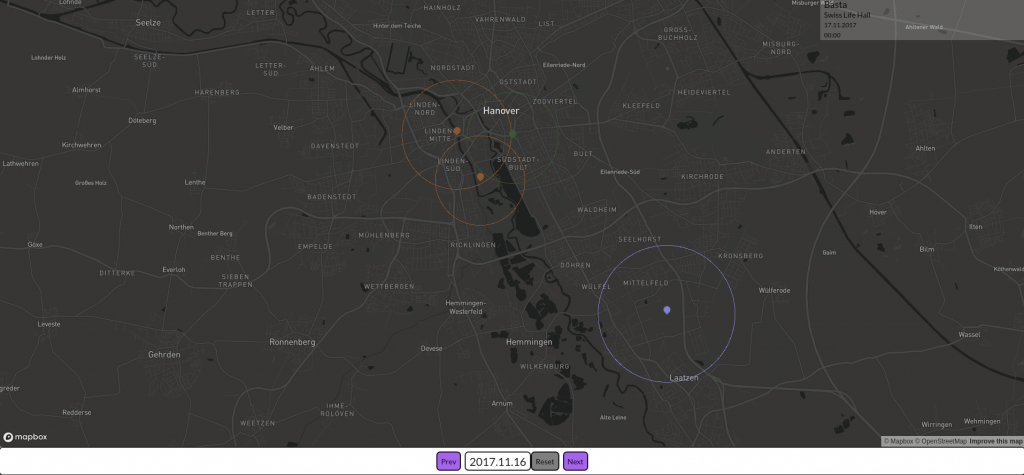
Zu sehen sind 4 Veranstaltungen in Hannover. Die Farben entsprechen dabei unterschiedlichen Veranstaltungsarten (etwa Konzerte, Messen, Fußballspiele). Die Kreise visualisieren die räumlichen Auswirkungen, die diese Veranstaltungen auf den Verkehr hatten.
Umfangreicher Anforderungskatalog
Die Data4UrbanMobility Anforderungsanalyse umfasst die Erfassung der Anforderungen der Anwendungspartner Region Hannover (RH) und Wolfsburg AG (WAG), sowie der nicht-funktionalen Anforderungen. Aus den Anforderungen der AnwendungspartnerInnen (RH und WAG), die von MOMA erhoben wurden, sind von L3S Forschungsfragen für die Datenanalyse abgeleitet worden, die sich speziell auf die Informationsbedürfnisse der AnwenderInnen beziehen und im weiteren Projektverlauf adressiert werden.
Die aktuelle Forschungsfragen adressieren insbesondere:
- Automatische Verifikation von Verkehrswarnmeldungen und Prognose von deren Auswirkungen.
- Identifikation von Veranstaltungen und Prognose verkehrsrelevanter Auswirkungen.
- Korrelation von IV-Reiseflussdaten, EFA-Querylogs, Warnmeldungen und Twitterfeeds.
- Bestimmung von optimalen Reisezeitpunkte.
Wachsende Datensammlung
Das ISU hat einen umfassende Datenmatrix mit potentiellen Quellen für mobilitätsrelevante Daten erstellt. Das von L3S entwickelte Data4UrbanMobility Datenmodell beschreibt alle projektrelevanten Daten und setzt diese in Verbindung um die Daten sowohl für die Analyse als auch für die Anwendungen und Apps einheitlich zur Verfügung zu stellen. Die ausgewählten Datenquellen sind von L3S in das Data4UrbanMobility Datenmodell überführt. Einige der Datenquellen wie EFA-logs, und IV-Daten sind dabei auf deren Qualität geprüft worden.
Um die Datenintegration zu ermöglichen sind Werkzeuge zur Extraktion der relevanten Daten aus Mobilitätsrelevanten Datenquellen entwickelt worden:
- Straßen- und Graphextraktion aus OpenStreetMap
- EFA-Anfragen Bulkloader für die Extraktion der ÖPNV Anfragen aus EFA Logs
- Integration von Daten aus dem Zentralen Haltestellen Verzeichnis (ZHV) inklusive Verknüpfung der Daten mit den EFA-Anfragen
Die aktuelle Datensammlung (Stand: 12 Dezember 2017) umfasst:
EFA-Logs: 17 Mio. Suchanfragen
IV-Daten: 174 Tsd. Straßen, alle 15 Minuten
GTFS-Daten: 90 Tsd. Haltestellen, 2,6 Tsd. Routen
Wetter: Radolan Regenraster
Twitter: 2,5 Mio. Tweets ab Juni 2017
OSM: 440 Tsd. Straßen
Events: 21 Tsd. Veranstaltungen (14.08.2016-17.07.2018)
Warnmeldungen: 13 Tsd. Warnmeldungen (ab 06.2017)
Visualisierungen der ÖPNV Informationen
Zur intuitiven Analyse von mobilitätsrelevanten Informationen, insbesondere von ÖPNV Informationen, wurde von den PROJEKTIONISTEN (PROJ) eine Dashboard-Webapplikation konzipiert. Erste Prototypen visualisieren Anfragen an das regionale Fahrplanauskunftsystem EFA (www.efa.de) und dienen als Ausgangsbasis für explorative Analysen und die Implementierung der produktiven Version des Dashboards. Im Folgenden ist eine im Dashboard integrierte Visualisierung der häufigsten Start- und Ziel-punkte zu sehen.
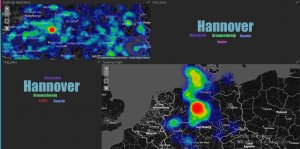
Analysen der EFA-Logs
Als erste Forschungsfrage wird aktuell die Analyse der Auswirkungen der Veranstaltungen auf dem ÖPNV mit Methoden des Maschinellen Lernens analysiert. Hierzu wurden in explorativen Datenanalysen der Einfluss von großen Veranstaltungen wie z.B. Fussballspielen und mittelgroßen Veranstaltungen, etwa Konzerte, auf Anfragen an den ÖPNV betrachtet. Als Grundlage für umfassende Analysen wurden mit Hilfe visueller Methoden exemplarisch Korrelation zwischen ÖPNV-Nachfrage und Veranstaltungszeiträumen detektiert.
Dabei zeichnen sich z.B. für Hannovers Innenstadt klare, sternförmige Muster ab, die zentrale Mobilitätsknoten identifizieren.
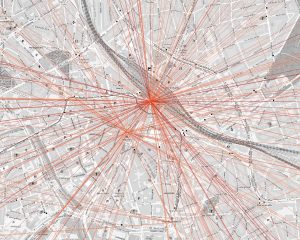
Das Bild stellt die Luftlinie zwischen Start- und Ziel-Ort der Anfragen dar. Dabei entsprechen dunklere Farben häufigeren Strecken. Hier werden deutlich Hannover Hauptbahnhof und Hannover Kröpcke (die zentrale U-Bahn Station) als Mobilitätsknoten identifiziert.
Analysen der Nachfrage für einzelne Stationen lassen wochentagspezifische Muster erkennen.
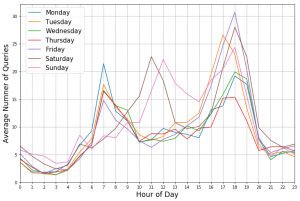
Hier dargestellt sind die durchschnittliche Anzahl der Anfragen mit der Ziel-Haltestelle “Hannover Stadionbrücke”. Zu erkennen sind vor allem Unterschiede zwischen Werktagen und dem Wochenende.
Auch der Einfluss von Veranstaltungen kann mit Hilfe der Anfragen visualisiert werden:
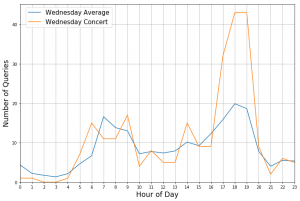
Dargestellt sind die Anzahl der Anfragen mit Ziel “Hannover Stadionbrücke” für Mittwoch, den 26.04.2017 (Orange) sowie die durchschnittlichen Anzahl von Anfragen, die mittwochs mit gleichem Ziel gestellt wird (Blau).
An diesem Tag fand in einer nahe gelegenen Konzerthalle ein Konzert statt, das um 20 Uhr begann. Die signifikante Abweichung zwischen 17 und 19 Uhr wurde sehr wahrscheinlich von den anreisenden Gästen verursacht wurde. Dies illustriert, dass Anfragen an den ÖPNV eine wertvolle Informationsquelle sein können, um Prognosen über die Auswirkung von Veranstaltungen auf Mobilität zu erstellen.
- Dynamical correlations and domain wall relocalization in transverse field Ising chains. Suchsland, Philippe; Douçot, Benoît; Khemani, Vedika; Moessner, Roderich (2025). 112(1) 014311.
- QoS Based Reliable Route in MANET for Military Applications. Shukla, Diksha; Singh, Raghuraj (2025). (Vol. 17) 21–39.
- Attribute-Centric Compositional Text-to-Image Generation. Cong, Yuren; Min, Martin Renqiang; Erran, Li; Rosenhahn, Bodo; Yang, Michael Ying (2025). 133 4555–4570.
- ChemLog: Making MSOL Viable for Ontological Classification and Learning. Flügel, Simon; Glauer, Martin; Mossakowski, Till; Neuhaus, Fabian A. Tamaddoni-Nezhad (ed.) (2025).
- Advancing Natural Language formalization to First Order Logic with Fine-tuned LLMs. Vossel, Felix; Mossakowski, Till; Gehrke, Björn A. Tamaddoni-Nezhad (ed.) (2025).
- Efficient Updates for Worst-Case Optimal Join Triple Stores. Bigerl, Alexander; Heidrich, Liss; Karalis, Nikolaos; Ngonga Ngomo, Axel-Cyrille (2025).
- Development and assessment of an online communication skills course to optimise antibiotic prescribing for children in primary care. Arias-Alonso, Lucía; Barragán-Brun, Nieves; Elizondo-Alzola, Usue; Boldu-Minguell, Andrea; Rocha-Calderón, Claudio Alfonso; Niño-de Guzmán, Ena; Santandreu, Francisca María; Quesada-Carrasco, Fermín; Ricci-Cabello, Ignacio; Gorrotxategi-Gorrotxategi, Pedro Jesús; de la Poza-Abad, Mariam; Mas-Dalmau, Gemma; Gibert-Agulló, Anna; González-Lama, Jesús; Alonso-Coello, Pablo (2025). 26(1) 247–247.
- Random transverse field effects on magnetic noise in spin systems. Pei, Yufei; Castelnovo, Claudio; Moessner, Roderich (2025). 112(1) 014416.
- Structural, electronic, and magnetic properties of europium films epitaxially grown on W(110). Härtl, Patrick; Leisegang, Markus; Sankeshwar, Vijayalaxmi; Bode, Matthias (2025). 112(2) 024416.
- Physics of AMOC multistable regime shifts due to freshwater biases in an EMIC. Boot, A. A.; Dijkstra, H. A. (2025). 16(4) 1221–1235.
- Urban Trees for Changing Climates: Insights for Bavarian Cities. Fäth, J.; Friesen, J.; Garcia de León, A. S.; Rieder, J.; Schäfer, C.; Leichtle, T.; Ullmann, T.; Taubenböck, H. (2025). XLVIII-M-7-2025 267–273.
- Superior sulfur-doped carbon anodes for sodium-ion batteries through incorporation of onion-like carbon. Neff, Tobias; Heßdörfer, Johannes; Bilican, Abdurrahman; Kolb, Leonhard; Reinert, Friedrich; Krueger, Anke (2025). 537 146912-.
- Finite-temperature fermion Monte Carlo simulations of frustrated spin-Peierls systems. Inácio, João C.; van den Brink, Jeroen; Assaad, Fakher F.; Sato, Toshihiro (2025). 112(1) 014404.
- Second harmonic generation contrasts of ferroelectric domain structures and composition in lithium niobate–tantalate mixed crystals. Koppitz, Boris; Saxena, Tanya; Bernhardt, Felix; Ganschow, Steffen; Sanna, Simone; Rüsing, Michael; Eng, Lukas M. (2025). 138(3) 034101.
- TlYbSe\($_\mathbf2$\) as a member of the J=\($\mathbf\dfrac12$\) triangular-lattice Yb delafossite family: From spin liquid to field-induced magnetic order. Fujii, T.; Pillaca, M.; Bärtl, F.; Sichelschmidt, J.; Luther, S.; Rosner, H.; Strydom, A. M.; Wosnitza, J.; Kühne, H.; Doert, Th.; Baenitz, M. (2025). 112(2) 024426.
- Crashing hard: why talking about bubbles obscures the real social cost of overinvesting into “Artificial Intelligence”. Blankertz, Aline (2025, August 12).
- Floquet-engineered emergent massive Nambu-Goldstone modes. Hou, Yang; Fu, Zhanpeng; Moessner, Roderich; Bukov, Marin; Zhao, Hongzheng (2025). 112(2) L020305.
- Soil Analysis, Disease Detection and Pesticide Recommendation for Farmers using AI and ML. A, Vijayalakshmi S; D, Varalakshmi B; Rohith R, Sanjay L Y; Shetty, Shashiraj; J, Prasad M E. Wingender (ed.) (2025). 21.
- Photoinduced stepwise charge hopping in pi-stacked perylene bisimide donor--bridge--acceptor arrays. Ernst, Leander; Song, Hongwei; Kim, Dongho; Würthner, Frank (2025). 17(5) 767–776.
- Altermagnetic phase transition in a Lieb metal. Dürrnagel, Matteo; Hohmann, Hendrik; Maity, Atanu; Seufert, Jannis; Klett, Michael; Klebl, Lennart; Thomale, Ronny (2025). 135(3) 036502.
- Chebifier 2: An Ensemble for Chemistry. Flügel, Simon; Glauer, Martin; Hastings, Janna; Mossakowski, Till; Mungall, Christopher J.; Tumescheit, Charlotte; Neuhaus, Fabian S. Tiwari (ed.) (2025).
- Alteration of topology in quantum phase transitions via symmetry enrichment. Rein, Gabriel; Raczkowski, Marcin; Wang, Zhenjiu; Sato, Toshihiro; Assaad, Fakher F. (2025). 112(4) L041112.
- Lifelong Learning for Fault Prognostics in Predictive Maintenance with Bayesian Neural Networks. Xuan, Quy Le; Munderloh, Marco; Ostermann, Jörn (2025).
- Towards an Empirical Study on Transient Phases of Microservice Applications Rohwer, Ivo; Straesser, Martin; Lubas, Yannik; Kounev, Samuel (2024).
- Exposing generative AI: Human-dependent, legally uncertain, environmentally unsustainable Ponce Del Castillo, Aída (2024).
- General Reusability: Ensuring Long-Term Benefits of Deep Active Learning. Hahn, Paul; Huseljic, Denis; Herde, Marek; Sick, Bernhard (2024). 33–46.
- Hashing the Hypertrie: Space- and Time-Efficient Indexing for SPARQL in Tensors. Bigerl, Alexander; Conrads, Lixi; Behning, Charlotte; Saleem, Muhammad; Ngonga Ngomo, Axel-Cyrille U. Sattler, A. Hogan, M. Keet, V. Presutti, J. P. A. Almeida, H. Takeda, P. Monnin, G. Pirrò, C. d’Amato (eds.) (2022). 57–73.
- JOB MATCHING USING ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE. Airccse (2022). 11(3) 12.
- An introduction to univalent foundations for mathematicians. Grayson, Daniel R. (2018).
- Models of IT-Project Management. Doronina, Julia; Doronina, Ekaterina (2018, April).
- San code of research ethics. SASI, South African San Institute (2017).
- Performance Evaluation of SQL and NoSQL Database Management Systems in a Cluster. Niyizamwiyitira, Christine (2017, December).
- Laser pulse trains for controlling excited state dynamics of adenine in water. Petersen, Jens; Wohlgemuth, Matthias; Sellner, Bernhard; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Lischka, Hans; Mitrić, Roland (2012). 14(14) 4687–4694.
- Exploring similarities in reactivity of superatom species: a combined theoretical and experimental investigation. Tyo, Eric C.; Nöβler Melanie; Rabe, Sabine; Harmon, Christopher L.; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Castleman, A. W. (2012). 14(6) 1846–1849.
- Unique optical properties of silver cluster-biochromophore hybrids: Comparison with copper and gold. Kulesza, Alexander; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2011). 501(4–6) 211–214.
- Field-induced surface hopping method for probing transition state nonadiabatic dynamics of Ag3. Mitrić, Roland; Petersen, Jens; Wohlgemuth, Matthias; Werner, Ute; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2011). 13(19) 8690–8696.
- Reactivity of stoichiometric titanium oxide cations. Tyo, Eric C.; Nőβler Melanie; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Castleman Jr., A. W. (2011). 13(10) 4243–4249.
- Simulation of laser-induced coupled electron-nuclear dynamics and time-resolved harmonic spectra in complex systems. Lisinetskaya, Polina G.; Mitrić, Roland (2011). 83(3)
- Tuning Cluster Reactivity by Charge State and Composition: Experimental and Theoretical Investigation of CO Binding Energies to AgnAum+/− (n + m = 3). Popolan, Denisia M.; Nössler, Melanie; Mitrić, Roland; Bernhardt, Thorsten M.; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2011). 115(6) 951–959.
- Time-dependent density functional theory excited state nonadiabatic dynamics combined with quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical approach: Photodynamics of indole in water. Wohlgemuth, Matthias; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Mitrić, Roland (2011). 135(5)
- Electronic Structure Similarities in PbxSby–and SnxBiy–Clusters. Melko, Joshua J.; Werner, Ute; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Castleman, A. W. (2011). 115(37) 10276–10280.
- Investigating Reactive Superoxide Units Bound to Zirconium Oxide Cations. Tyo, Eric C.; Nossler, Melanie; Harmon, Christopher L.; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Castleman, A. W. (2011). 115(44) 21559–21566.
- Structural and Optical Properties of Isolated Noble Metal–Glutathione Complexes: Insight into the Chemistry of Liganded Nanoclusters. Bellina, Bruno; Compagnon, Isabelle; Bertorelle, Franck; Broyer, Michel; Antoine, Rodolphe; Dugourd, Philippe; Gell, Lars; Kulesza, Alexander; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2011). 115(50) 24549–24554.
- Experimental and theoretical study of the absorption properties of thiolated diamondoids. Landt, Lasse; Bostedt, Christoph; Wolter, David; Möller, Thomas; Dahl, Jeremy E. P.; Carlson, Robert M. K.; Tkachenko, Boryslav A.; Fokin, Andrey A.; Schreiner, Peter R.; Kulesza, Alexander; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2010). 132(14)
- Composition dependent adsorption of multiple CO molecules on binary silver–gold clusters AgnAum+ (n + m = 5): theory and experiment. Popolan, Denisia M.; Nößler, Melanie; Mitrić, Roland; Bernhardt, Thorsten M.; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2010). 12(28) 7865–7873.
- Theoretical study of structural and optical properties of small silver and gold clusters at defect centers of MgO. Bürgel, Christian; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić‐Koutecký, Vlasta (2010). 247(5) 1099–1108.
- How Shaped Light Discriminates Nearly Identical Biochromophores. Petersen, Jens; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Wolf, Jean-Pierre; Roslund, Jonathan; Rabitz, Herschel (2010). 105(7)
- Non-adiabatic dynamics of pyrrole: Dependence of deactivation mechanisms on the excitation energy. Barbatti, Mario; Pittner, Jiří; Pederzoli, Marek; Werner, Ute; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Lischka, Hans (2010). 375(1) 26–34.
- Ultrafast photodynamics of furan. Fuji, Takao; Suzuki, Yoshi-Ichi; Horio, Takuya; Suzuki, Toshinori; Mitrić, Roland; Werner, Ute; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2010). 133(23)
- Doubly Charged Silver Clusters Stabilized by Tryptophan: Ag<sub>4</sub><sup>2+</sup> as an Optical Marker for Monitoring Particle Growth. Kulesza, Alexander; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić‐Koutecký, Vlasta; Bellina, Bruno; Compagnon, Isabelle; Broyer, Michel; Antoine, Rodolphe; Dugourd, Philippe (2010). 50(4) 878–881.
- Time-Resolved Femtosecond Photoelectron Spectroscopy by Field-Induced Surface Hopping. Mitrić, Roland; Petersen, Jens; Wohlgemuth, Matthias; Werner, Ute; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Wöste, Ludger; Jortner, Joshua (2010). 115(16) 3755–3765.
- Simulation of time resolved photoelectron spectra with Stieltjes imaging illustrated on ultrafast internal conversion in pyrazine. Werner, Ute; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2010). 132(17)
- Optical and Structural Properties of Copper−Oxytocin Dications in the Gas Phase. Joly, Laure; Antoine, Rodolphe; Albrieux, Florian; Ballivian, Renaud; Broyer, Michel; Chirot, Fabien; Lemoine, Jérôme; Dugourd, Philippe; Greco, Claudio; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2009). 113(32) 11293–11300.
- Generation of Oxygen Radical Centers in Binary Neutral Metal Oxide Clusters for Catalytic Oxidation Reactions. Nößler, Melanie; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić‐Koutecký, Vlasta; Johnson, Grant E.; Tyo, Eric C.; Castleman, A. Welford (2009). 49(2) 407–410.
- Nonadiabatic Dynamics within Time-Dependent Density Functional Tight Binding Method. Mitrić, Roland; Werner, Ute; Wohlgemuth, Matthias; Seifert, Gotthard; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2009). 113(45) 12700–12705.
- Clusters as model systems for investigating nanoscale oxidation catalysis. Johnson, Grant E.; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Castleman, A.W. (2009). 475(1–3) 1–9.
- Laser-field-induced surface-hopping method for the simulation and control of ultrafast photodynamics. Mitrić, Roland; Petersen, Jens; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2009). 79(5)
- Silver Cluster Chromophores for Absorption Enhancement of Peptides. Kulesza, Alexander; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2009). 113(16) 3783–3788.
- Influence of Charge State on Catalytic Oxidation Reactions at Metal Oxide Clusters Containing Radical Oxygen Centers. Johnson, Grant E.; Mitrić, Roland; Nössler, Melanie; Tyo, Eric C.; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Castleman, A. W. (2009). 131(15) 5460–5470.
- Gas‐Phase Synthesis and Intense Visible Absorption of Tryptophan–Gold Cations. Antoine, Rodolphe; Bertorelle, Franck; Broyer, Michel; Compagnon, Isabelle; Dugourd, Philippe; Kulesza, Alexander; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić‐Koutecký, Vlasta (2009). 48(42) 7829–7832.
- Stoichiometric Zirconium Oxide Cations as Potential Building Blocks for Cluster Assembled Catalysts. Johnson, Grant E.; Mitrić, Roland; Tyo, Eric C.; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Castleman, A. W. (2008). 130(42) 13912–13920.
- Nonadiabatic dynamics within the time dependent density functional theory: Ultrafast photodynamics in pyrazine. Werner, Ute; Mitrić, Roland; Suzuki, Toshinori; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2008). 349(1–3) 319–324.
- Nonadiabatic dynamics and simulation of time resolved photoelectron spectra within time-dependent density functional theory: Ultrafast photoswitching in benzylideneaniline. Mitrić, Roland; Werner, Ute; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2008). 129(16)
- Absorption Enhancement and Conformational Control of Peptides by Small Silver Clusters. Tabarin, Thibault; Kulesza, Alexander; Antoine, Rodolphe; Mitrić, Roland; Broyer, Michel; Dugourd, Philippe; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2008). 101(21)
- Ultrafast dynamics in noble metal clusters: The role of internal vibrational redistribution. Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Mitrić, Roland; Bürgel, Christian; Nößler, Melanie (2008). 350(1–3) 111–117.
- A DFT study of EPR parameters in Cu(ii) complexes of the octarepeat region of the prion protein. Bruschi, Maurizio; De Gioia, Luca; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Fantucci, Piercarlo (2008). 10(31) 4573–4583.
- Influence of Charge State on the Mechanism of CO Oxidation on Gold Clusters. Bürgel, Christian; Reilly, Nelly M.; Johnson, Grant E.; Mitrić, Roland; Kimble, Michele L.; Castleman, A. W.; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2008). 130(5) 1694–1698.
- Absorption properties of cationic silver cluster–tryptophan complexes: A model for photoabsorption and photoemission enhancement in nanoparticle–biomolecule systems. Mitrić, Roland; Petersen, Jens; Kulesza, Alexander; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Tabarin, Thibault; Compagnon, Isabelle; Antoine, Rodolphe; Broyer, Michel; Dugourd, Philippe (2008). 343(2–3) 372–380.
- Size-dependent dynamics in excited states of gold clusters: From oscillatory motion to photoinduced melting. Stanzel, Jörg; Burmeister, Florian; Neeb, Matthias; Eberhardt, Wolfgang; Mitrić, Roland; Bürgel, Christian; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2007). 127(16)
- Photoabsorption and photofragmentation of isolated cationic silver cluster–tryptophan hybrid systems. Mitrić, Roland; Petersen, Jens; Kulesza, Alexander; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Tabarin, Thibault; Compagnon, Isabelle; Antoine, Rodolphe; Broyer, Michel; Dugourd, Philippe (2007). 127(13)
- Optimal control of mode-selective femtochemistry in multidimensional systems. Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2007). 76(3)
- Reactivity-promoting criterion based on internal vibrational energy redistribution. Mitrić, Roland; Bürgel, Christian; Bonǎić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2007). 104(25) 10314–10317.
- Ultrafast dynamics in atomic clusters: Analysis and control. Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Mitrić, Roland; Werner, Ute; Wöste, Ludger; Berry, R. Stephen (2006). 103(28) 10594–10599.
- Ab initiononadiabatic dynamics study of ultrafast radiationless decay over conical intersections illustrated on the Na3F cluster. Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Pittner, Jiří; Lischka, Hans (2006). 125(2)
- Spectroscopy of isolated, mass-selected tryptophan-Ag3 complexes: A model for photoabsorption enhancement in nanoparticle-biomolecule hybrid systems. Compagnon, Isabelle; Tabarin, Thibault; Antoine, Rodolphe; Broyer, Michel; Dugourd, Philippe; Mitrić, Roland; Petersen, Jens; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2006). 125(16)
- The Gas‐Phase Chemistry of cis‐Diammineplatinum(II) Complexes: A Joint Experimental and Theoretical Study. Springer, Andreas; Bürgel, Christian; Böhrsch, Verena; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić‐Koutecký, Vlasta; Linscheid, Michael W. (2006). 7(8) 1779–1785.
- Joint experimental and theoretical investigations of the reactivity of Au2On− and Au3On− (n=1–5) with carbon monoxide. Kimble, Michele L.; Moore, Nelly A.; Johnson, Grant E.; Castleman, A. W.; Bürgel, Christian; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2006). 125(20)
- Analysis and Control of Ultrafast Dynamics in Clusters: Theory and Experiment. Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Mitrić, Roland; Bernhardt, Thorsten M.; Wöste, Ludger; Jortner, Joshua (2005). 179–246.
- Tailoring the chemical reactivity and optical properties of clustersby size, structures and lasers. Bonačić-Koutecký, V.; Mitrić, R.; Bürgel, C.; Noack, H.; Hartmann, M.; Pittner, J. (2005). 34(1) 113–118.
- Femtosecond Time‐Resolved Geometry Relaxation and Ultrafast Intramolecular Energy Redistribution in Ag2Au. Bernhardt, Thorsten M.; Hagen, Jan; Socaciu, Liana D.; Mitrić, Roland; Heidenreich, Andreas; Le Roux, Jérôme; Popolan, Denisia; Vaida, Mihai; Wöste, Ludger; Bonačić‐Koutecký, Vlasta; Jortner, Joshua (2005). 6(2) 243–253.
- Reactivity of Atomic Gold Anions toward Oxygen and the Oxidation of CO: Experiment and Theory. Kimble, Michele L.; Castleman, A. Welford; Mitrić, Roland; Bürgel, Christian; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2004). 126(8) 2526–2535.
- Cooperative Effects in the Activation of Molecular Oxygen by Anionic Silver Clusters. Hagen, Jan; Socaciu, Liana D.; Le Roux, Jérôme; Popolan, Denisia; Bernhardt, Thorsten M.; Wöste, Ludger; Mitrić, Roland; Noack, Holger; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2004). 126(11) 3442–3443.
- Optimal Control of Ionization Processes in NaK: Comparison between Theory and Experiment. Schäfer-Bung, Boris; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Bartelt, Andreas; Lupulescu, Cosmin; Lindinger, Albrecht; Vajda, Štefan; Weber, Stefan M.; Wöste, Ludger (2004). 108(19) 4175–4179.
- Isomer-specific spectroscopy of metal clusters trapped in a matrix: \($\mathrmAg_9$\). Sieber, Christoph; Buttet, Jean; Harbich, Wolfgang; Félix, Christian; Mitriifmmode acutecelse ’cfi, Roland; Bonaifmmode checkcelse vcfiiifmmode acutecelse ’cfi Kouteck’y, Vlasta (2004). 70(4) 041201.
- Different approaches for the calculation of electronic excited states of nonstoichiometric alkali halide clusters: The example of Na3F. Durand, G.; Heitz, M.-C.; Spiegelman, F.; Meier, C.; Mitrić, R.; Bonačić-Koutecký, V.; Pittner, J. (2004). 121(20) 9898–9905.
- Ultrafast excited state dynamics of the Na3F cluster: Quantum wave packet and classical trajectory calculations compared to experimental results. Heitz, M.-C.; Durand, G.; Spiegelman, F.; Meier, C.; Mitrić, R.; Bonac̆ić-Koutecký V. (2004). 121(20) 9906–9916.
- Theoretical approach for simulation of femtosecond spectra: New strategies for optimal control of complex systems. Bonac̆ić‐Koutecký V.; Mitrić, R.; Hartmann, M.; Pittner, J. (2003). 99(4) 408–420.
- Oxygen Adsorption on Hydrated Gold Cluster Anions: Experiment and Theory. Wallace, William T.; Wyrwas, Richard B.; Whetten, Robert L.; Mitrić, Roland; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2003). 125(27) 8408–8414.
- The Structures of Vanadium Oxide Cluster−Ethene Complexes. A Combined IR Multiple Photon Dissociation Spectroscopy and DFT Calculation Study. Fielicke, André; Mitrić, Roland; Meijer, Gerard; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; von Helden, Gert (2003). 125(51) 15716–15717.
- Theoretical and Experimental Consideration of the Reactions between VxOy+ and Ethylene. Justes, Dina R.; Mitrić, Roland; Moore, Nelly A.; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Castleman, A. Welford (2003). 125(20) 6289–6299.
- Structural properties and reactivityof bimetallic silver-gold clusters. Mitrić, R.; Bürgel, C.; Burda, J.; Bonačić-Koutecký, V.; Fantucci, P. (2003). 24(1) 41–44.
- Kinetics and equilibrium of smallmetallic clusters: Ab initio confinement molecular dynamicsstudy of 4. Chekmarev, S. F.; Mitrić, R.; Bonacić-Koutecký, V. (2003). 24(1) 45–48.
- New strategy for optimal control offemtosecond pump-dump processes applicable to systems of moderate complexity. Mitrić, R.; Hartmann, M.; Pittner, J.; Bonačić-Koutecký, V. (2003). 24(1) 177–180.
- V<sub>2</sub>O<sub>5</sub><sup>+</sup> reaction with C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>4</sub>: Theoretical considerations of experimental findings. Justes, D. R.; Castleman, A. W.; Mitrić, R.; Bonačić-Koutecký, V. (2003). 24(1) 331–334.
- Vibrational spectra and DFT calculations of PPV-oligomers. Hrenar, T; Mitrić, R; Meić, Z; Meier, H; Stalmach, U (2003). 661–662 33–40.
- Density functional study of structural and electronic properties of bimetallic silver–gold clusters: Comparison with pure gold and silver clusters. Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta; Burda, Jaroslav; Mitrić, Roland; Ge, Maofa; Zampella, Giuseppe; Fantucci, Piercarlo (2002). 117(7) 3120–3131.
- New Strategy for Optimal Control of Femtosecond Pump−Dump Processes. Mitrić, Roland; Hartmann, Michael; Pittner, Jiří; Bonačić-Koutecký, Vlasta (2002). 106(44) 10477–10481.
- Theoretical investigation of the ultrafast NeNePo spectroscopy of Au4 and Ag4 Clusters. Hartmann, M.; Mitrić, R.; Stanca, B.; Bonačić-Koutecký, V. (2001). 16(1) 151–155.
- Ab Initio Adiabatic Dynamics Combined with Wigner Distribution Approach to Femtosecond Pump−Probe Negative Ion to Neutral to Positive Ion (NeNePo) Spectroscopy of Ag2Au, Ag4, and Au4 Clusters. Mitrić, R.; Hartmann, M.; Stanca, B.; Bonačić-Koutecký, V.; Fantucci, P. (2001). 105(39) 8892–8905.
- Ab initio study of the absorption spectra of Agn (n=5–8) clusters. Bonačić-Koutecky, Vlasta; Veyret, Vincent; Mitrić, Roland (2001). 115(22) 10450–10460.
