Prognose der Verkehrslage in der Region Hannover
Die primäre Anforderung der Verkehrsteilnehmer im Bereich des Straßenverkehrs ist die Kenntnis der aktuellen Verkehrslage. Diese basiert in der Regel auf der wirklich benötigten Reisezeit von sehr vielen Verkehrsteilnehmern, deren Daten häufig im Kontext von Routingdiensten abgegriffen werden.
Im Rahmen von Data4UrbanMobility wurden Werkzeuge entwickelt um eine ganglineinbasierte Prognose der Verkehrslage zu ermöglichen. Die folgende Abbildung zeigt eine Oberfläche auf der typische Ganglinienverläufe und Ausreißer visualisiert werden.
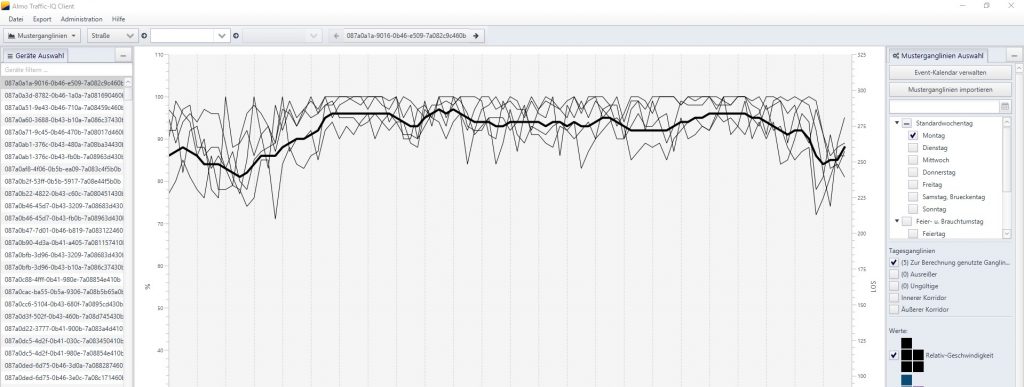
Die Prognose der Verkehrslage kann dann mittels einer Karte für den Endnutzer visualisert werden:
Erste Version der MIC-App bereitgestellt
Eine erste Version der MIC-App (Move in the City) konnte allen Partnerinnen und Partnern des Projekts und einer geschützten Nutzer*innengruppe der Öffentlichkeit zur Verfügung gestellt werden. Die mobile App MiC ist ein Instrument zur Datenerhebung.
Dabei verknüpft MiC – eine Entwicklung des Institute for Sustainable Urbanism ISU der TU Braunschweig und Projektionisten GmbH Hannover – das wachsende Bewusstsein und die Notwendigkeit für digitale Bürger*innenrechte mit den Potentialen mittels der Auswertung großer Datenmengen neue Formen der menschzentrierten Entwicklung von Stadt und Mobilität zu ermöglichen stellt eine Möglichkeit dar, sich aktiv als Bürgerwissenschaftlerin und Bürgerwissenschaftler an der Forschung und Entwicklung der Mobilität für alle in der Stadt der Zukunft zu beteiligen.
MiC erhebt – durch die Nutzerinnen und Nutzer gesteuert – Daten zu Strecken und Art der Fortbewegung. Diese Daten werden pseudonymisiert, so dass ein Rückschluss auf die jeweilige Person nicht mehr möglich ist. Wichtig ist die Vielzahl der Nutzerinnen und Nutzer – nicht die einzelne Bewegung. Die Stadt der Zukunft zeichnet sich aus durch den barrierearmen Zugang zu Mobilität und Erreichbarkeit für alle. Der holistische Ansatz der Forscherinnen und Forscher des Institute for Sustainable Urbanism ISU (TU Braunschweig) sowie der Projektbeteiligten betrachtet Stadt dabei auf verschiedenen Maßstabsebenen und bringt intelligente Planungen – wie z.B. die 5-Minuten Stadt –, Städtebau und innovative Technologien zusammen. Für ein umfassendes Verständnis individueller Mobilität und darauf aufbauende neue Methoden und Werkzeuge für integrierte Verkehrs- und Stadtplanung werden mittels der MiC-App uns umfangreiche und detaillierte Daten darüber geliefert, wie und auf welchem Wege wir uns in der Stadt fortbewegen.
Entwicklungsstand:
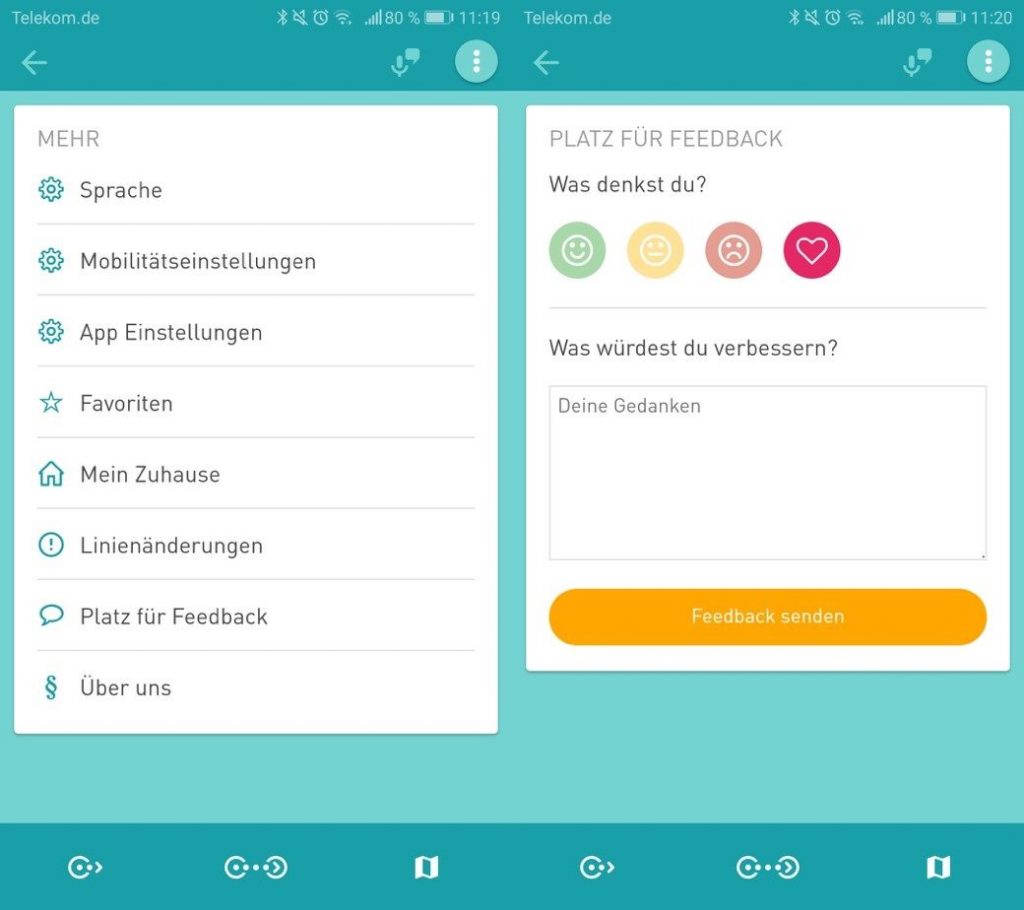
In der ersten Version ermöglicht das Stadtforschungstool MiC den Nutzer*innen durch eine einfach Handhabung das Starten und Beenden der „Tracking-Time“ (Bild 1). Wichtig ist, die Nutzer*innen entscheidet selber über den Zeitraum. Als erstes Ergebnis für die Nutzer*innen steht eine Zusammenfassung ihrer bisher aufgezeichneten Routen (Bild2). In den Einstellung (Bild 3) kann der Nutzer sich aktiv an Feedback beteiligen (Bild 4) sowie seinen Account und somit seiner zur Verfügung gestellten Daten löschen (Bild 5).
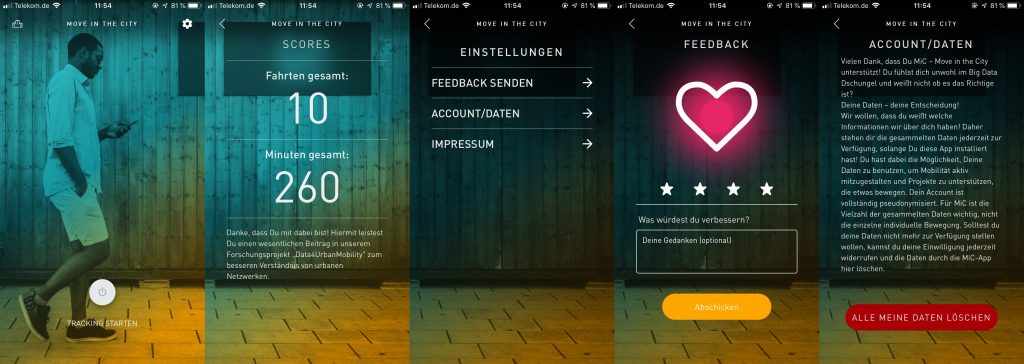
von links nach recht: Bild1-5 MIC App Interface – Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
Die aktuelle Weiterentwicklung sieht eine Visualisierung der Routen für den jeweiligen Nutzer vor.
Um Teil der Testgruppe zu werden ist zur Zeit noch eine Anmeldung unter: www.mic-app.org notwendig. Die Anwendung ist nicht frei im App Store / GooglePlay Store zu erhalten.
Auf der Internetseite www.mic-app.org wird zusätzlich detailliert auf häufige Fragen (FAQ) zur Anwendung sowie über Entwicklungen und Neuheiten informiert
D4UM Plattform und Dashboard V2
Die neue Version der Plattform inklusive des Dashboards gibt noch detailliertere Auskünfte über die Verkehrssituation
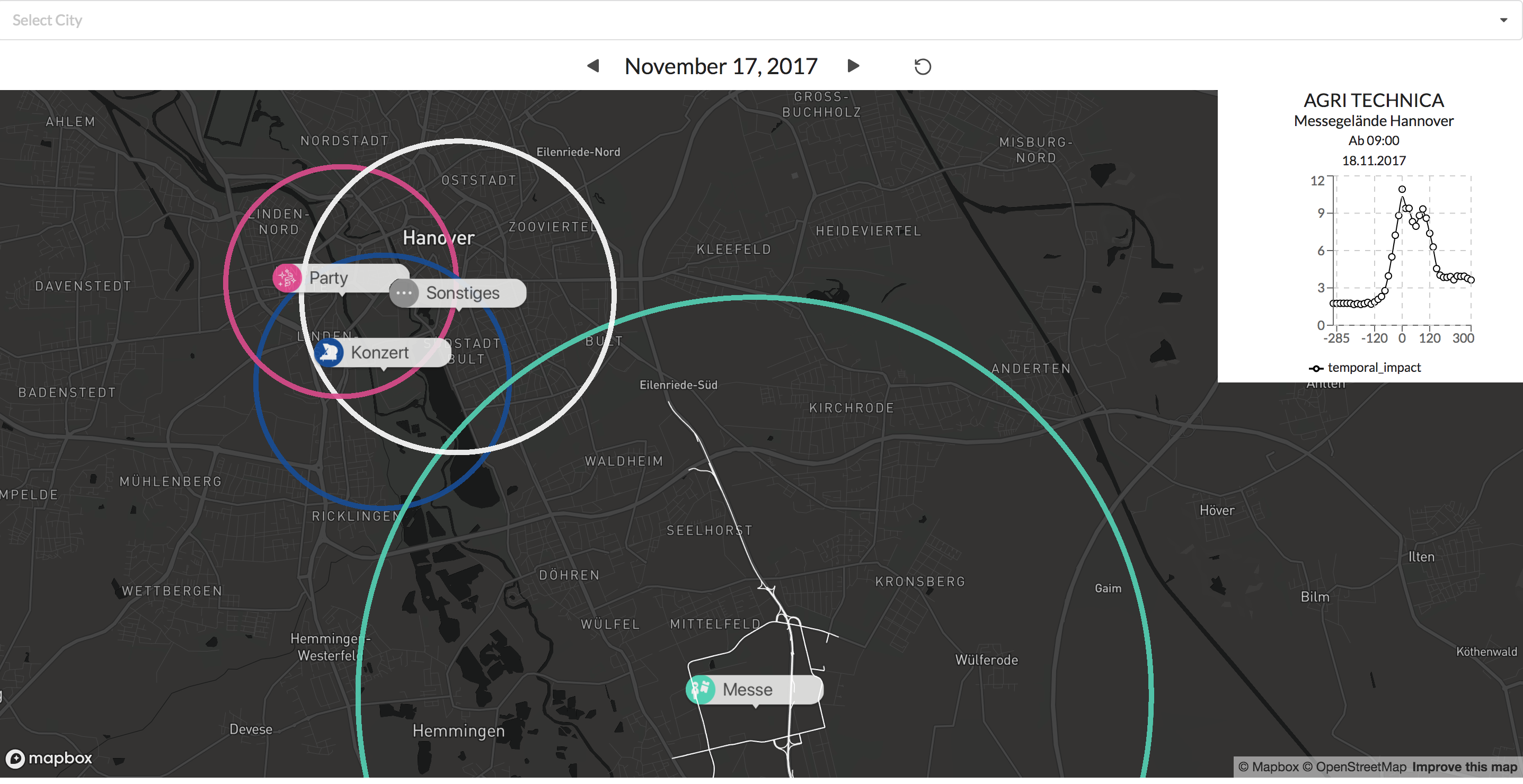
Die farblich unterschiedlichen Label lassen eine schnelle Unterscheidung zwischen den verschiedenen Event typen zu. Durch das klicken auf eines der Events wird der typically affected subgraph angezeigt für diesen Eventtyp.
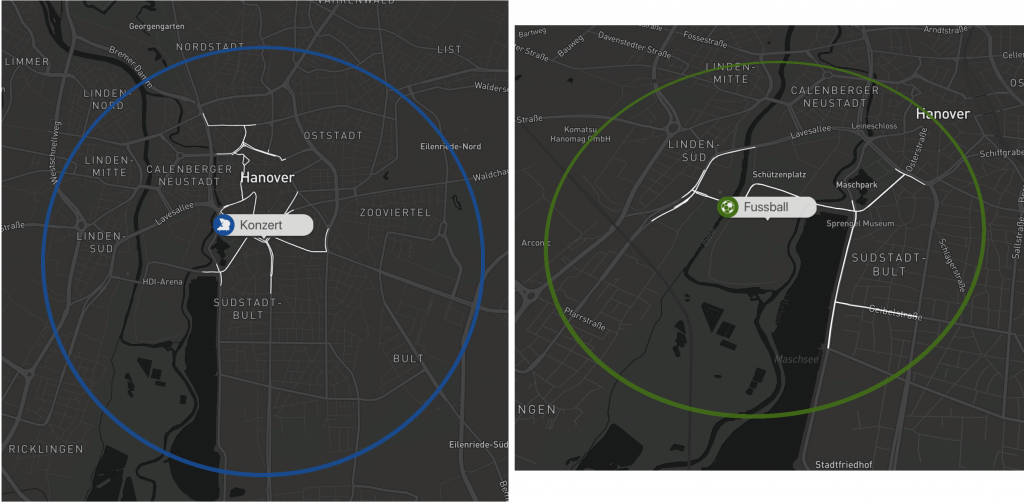
Beispiele: Visualisierungen eines Konzerts und eines Fußballspiels
Zusätzlich gibt der Graph in der oberen rechten Ecke Auskunft über die Verkehrssituation vor und nach dem Eventstart.
{API}
Es wurden die API Endpunkte mit zusätzlichen Information erweitert.
Diese werden mittels der als Teil der Forschung entwickelten Modellen erstellt.
Erste Version der D4UM-App bereitgestellt
Eine erste Version der D4UM-App konnte allen Partnern des Projekts zur Verfügung gestellt werden. Die App stellt eine Möglichkeit dar, sich Fahrtauskünfte mit dem öffentlichen Personennahverkehr in Niedersachsen und Bremen (Datengrundlage: EFA – elektronische Fahrplanauskunft für Niedersachsen und Bremen) ausgeben zu lassen. Im Fokus stand hierbei, dass der Nutzer schnell und einfach an die für ihn wichtigen Informationen gelangen kann, um so seine Reise möglichst simpel planen zu können.
Folgende Funktionen dienen dabei in der ersten Version der schnellen Auskunft:
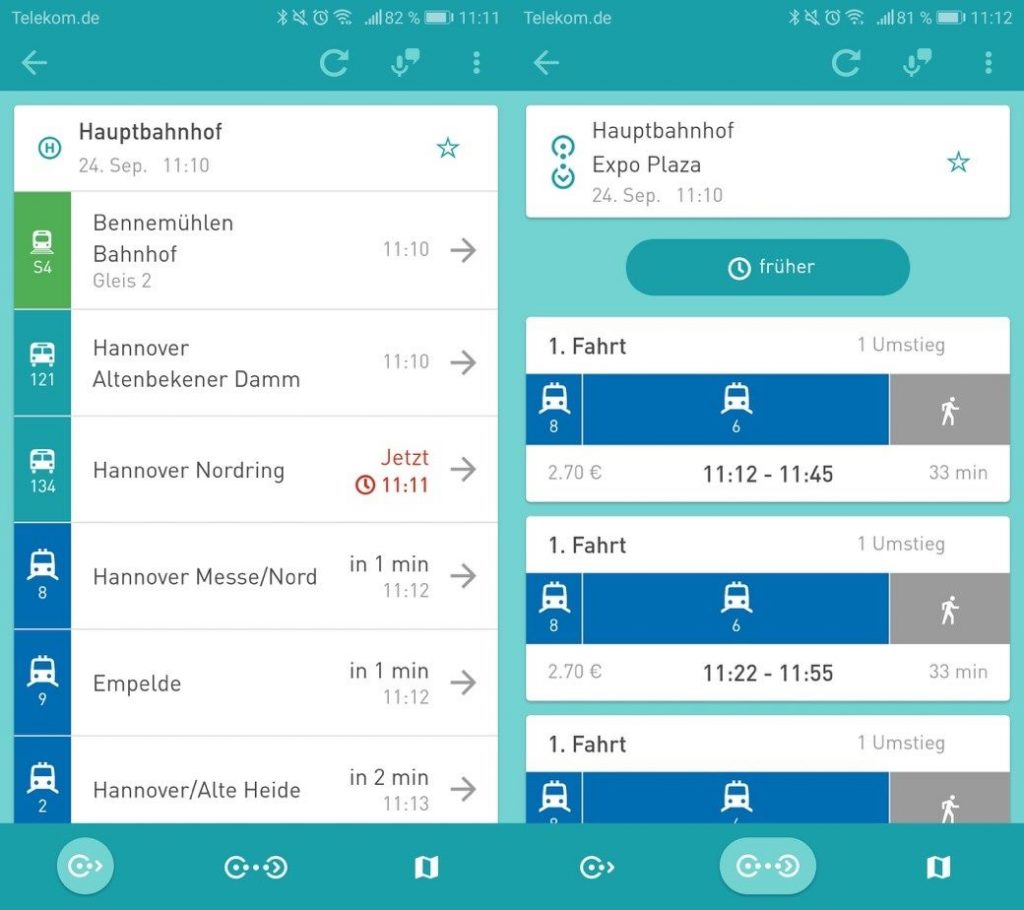
Abfahrten und Verbindungen
Über die Funktion Abfahrten lassen sich Abfahrtszeiten an einer bestimmten oder an nahegelegenen Haltestellen ermitteln. Unter Verbindungen können hingegen Fahrtvorschläge von einem Startpunkt (Adresse oder Haltestelle) zu einem Zielpunkt gesucht werden. Zeiten stehen dabei auch in Echtzeit zur Verfügung, sodass auch Verspätungen direkt von dem Nutzer erkannt werden können.
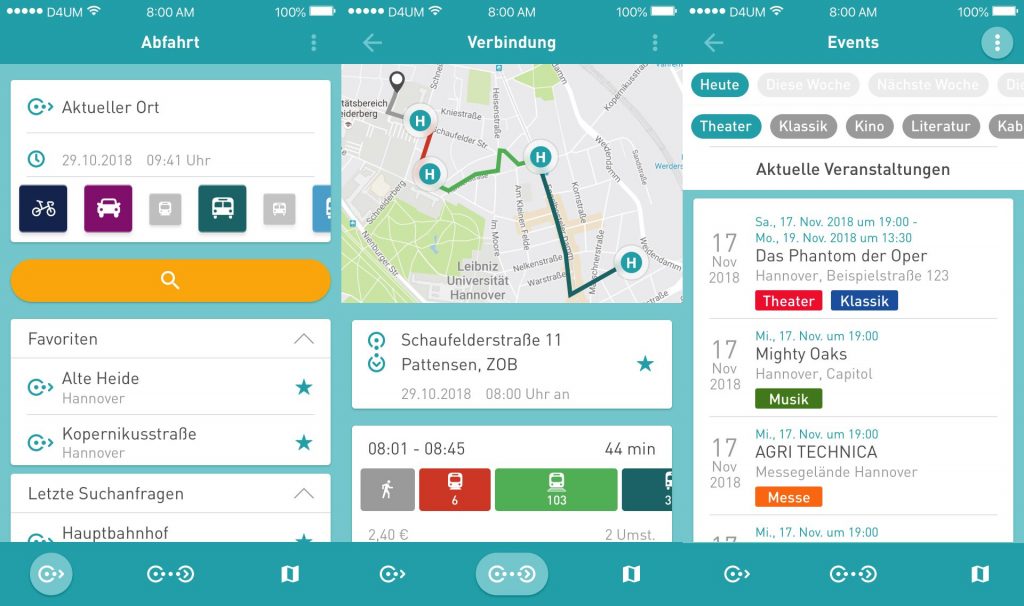
Karte
Über die Karte sind alle Haltestellen zu finden, sodass sich der Nutzer einen Überblick über die nähere Umgebung oder auch den Weg zur Haltestelle oder einem Ziel verschaffen kann.
Wird auf der Karte auf ein Haltestellensymbol oder den zugehörigen Haltestellennamen geklickt, öffnet sich der Abfahrtsmonitor zu dieser Haltestelle. Die nächsten Abfahrten können somit auch über diesen Weg aufgerufen werden.
Darüber hinaus kann sich der Nutzer auch den Verlauf seiner Fahrt anzeigen lassen.
Menü/Einstellungen
Weitere Funktionen und Einstellungen finden sich ergänzend im Menü der App.
Der Nutzer bekommt hier zum einen die Möglichkeit, dass erweiterte Einstellungen zu den Suchanfragen bei Verbindungen oder Abfahrten vorgenommen werden können, und zum anderen, dass er weitere Features verwenden kann. Darunter befindet sich zum Beispiel das Feedbackformular. Hierüber kann unkompliziert Kontakt mit den Entwicklern der D4UM-App per Mail aufgenommen werden. Icons ermöglichen es, dass ein Eindruck zu der App übermittelt werden kann. Ein weiteres Feld für Freitext bietet zudem Platz für individuelle Kritik und einer Meinung zu der App. So kann in Zukunft kundennah an der App weiterentwickelt und einfach auf Wünsche und Meinungen reagiert werden.
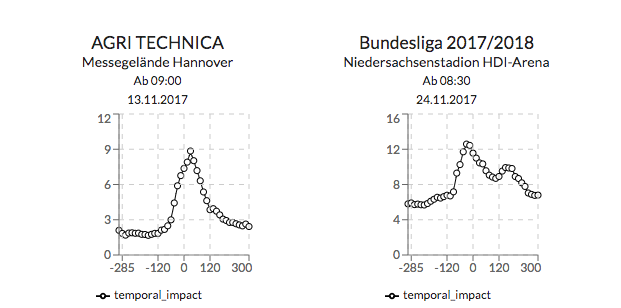
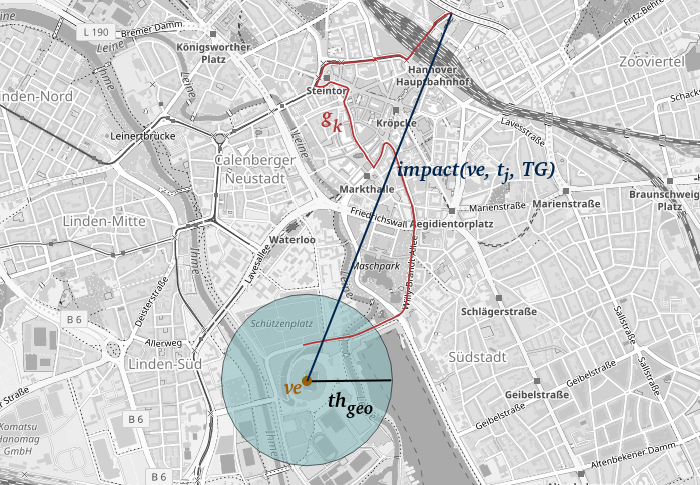
Quantifizierungen und Vorhersage von Auswirkungen von Veranstaltungen
Neue Data4UrbanMobility-Forschungsergebnisse ermöglichen es, die räumlichen Auswirkungen von Veranstaltungen zu quantifizieren und vorherzusagen. Dazu werden zusammenhängende, betroffene Straßenabschnitte in der Nähe von Veranstaltungen identifiziert. Auf dieser Grundlage kann dann die räumliche Auswirkung quantifiziert werden. Das Verfahren ist in der folgenden Grafik dargestellt.
(Karte von https://www.openstreetmap.org)
Hier in Gelb markiert ist eine Veranstaltung, in Rot betroffene Straßenabschnitte und in Dunkelblau die gemessene Auswirkung. Weiterhin wurden Verfahren des Maschinellen Lernens angewandt, um diese Auswirkungen zu prognostizieren. Dabei konnte der Fehler gegenüber bestehenden state-of-the-art Ansätzen um bis zu 40% verringert werden.
D4UM – Plattform V1 fertiggestellt
Die erste Version der Data4UrbanMobility Plattform wurde fertiggestellt. Dazu wurde zunächst eine 3-Schichten Architektur der Plattform konzipiert und implementiert. Die Plattform bietet RESTfull Webservices für Mobilitätsapplikationen wie Dashboard-Anwendungen oder Apps an. Als erste Beispielanwendung wurde dazu eine interaktive Karte entwickelt, die die Auswirkungen von Veranstaltungen visualisiert. Ein Ausschnitt aus der Anwendung ist im folgenden Screenshot zu sehen.
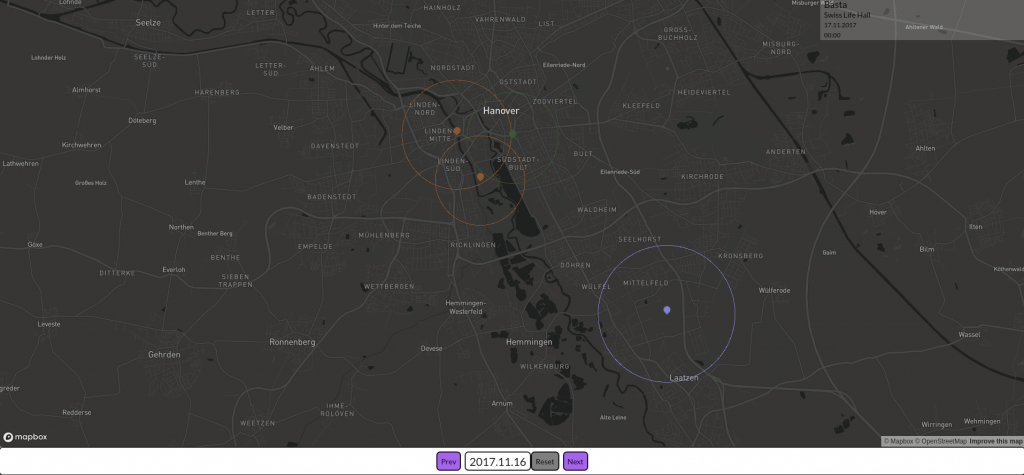
Zu sehen sind 4 Veranstaltungen in Hannover. Die Farben entsprechen dabei unterschiedlichen Veranstaltungsarten (etwa Konzerte, Messen, Fußballspiele). Die Kreise visualisieren die räumlichen Auswirkungen, die diese Veranstaltungen auf den Verkehr hatten.
Umfangreicher Anforderungskatalog
Die Data4UrbanMobility Anforderungsanalyse umfasst die Erfassung der Anforderungen der Anwendungspartner Region Hannover (RH) und Wolfsburg AG (WAG), sowie der nicht-funktionalen Anforderungen. Aus den Anforderungen der AnwendungspartnerInnen (RH und WAG), die von MOMA erhoben wurden, sind von L3S Forschungsfragen für die Datenanalyse abgeleitet worden, die sich speziell auf die Informationsbedürfnisse der AnwenderInnen beziehen und im weiteren Projektverlauf adressiert werden.
Die aktuelle Forschungsfragen adressieren insbesondere:
- Automatische Verifikation von Verkehrswarnmeldungen und Prognose von deren Auswirkungen.
- Identifikation von Veranstaltungen und Prognose verkehrsrelevanter Auswirkungen.
- Korrelation von IV-Reiseflussdaten, EFA-Querylogs, Warnmeldungen und Twitterfeeds.
- Bestimmung von optimalen Reisezeitpunkte.
Wachsende Datensammlung
Das ISU hat einen umfassende Datenmatrix mit potentiellen Quellen für mobilitätsrelevante Daten erstellt. Das von L3S entwickelte Data4UrbanMobility Datenmodell beschreibt alle projektrelevanten Daten und setzt diese in Verbindung um die Daten sowohl für die Analyse als auch für die Anwendungen und Apps einheitlich zur Verfügung zu stellen. Die ausgewählten Datenquellen sind von L3S in das Data4UrbanMobility Datenmodell überführt. Einige der Datenquellen wie EFA-logs, und IV-Daten sind dabei auf deren Qualität geprüft worden.
Um die Datenintegration zu ermöglichen sind Werkzeuge zur Extraktion der relevanten Daten aus Mobilitätsrelevanten Datenquellen entwickelt worden:
- Straßen- und Graphextraktion aus OpenStreetMap
- EFA-Anfragen Bulkloader für die Extraktion der ÖPNV Anfragen aus EFA Logs
- Integration von Daten aus dem Zentralen Haltestellen Verzeichnis (ZHV) inklusive Verknüpfung der Daten mit den EFA-Anfragen
Die aktuelle Datensammlung (Stand: 12 Dezember 2017) umfasst:
EFA-Logs: 17 Mio. Suchanfragen
IV-Daten: 174 Tsd. Straßen, alle 15 Minuten
GTFS-Daten: 90 Tsd. Haltestellen, 2,6 Tsd. Routen
Wetter: Radolan Regenraster
Twitter: 2,5 Mio. Tweets ab Juni 2017
OSM: 440 Tsd. Straßen
Events: 21 Tsd. Veranstaltungen (14.08.2016-17.07.2018)
Warnmeldungen: 13 Tsd. Warnmeldungen (ab 06.2017)
Visualisierungen der ÖPNV Informationen
Zur intuitiven Analyse von mobilitätsrelevanten Informationen, insbesondere von ÖPNV Informationen, wurde von den PROJEKTIONISTEN (PROJ) eine Dashboard-Webapplikation konzipiert. Erste Prototypen visualisieren Anfragen an das regionale Fahrplanauskunftsystem EFA (www.efa.de) und dienen als Ausgangsbasis für explorative Analysen und die Implementierung der produktiven Version des Dashboards. Im Folgenden ist eine im Dashboard integrierte Visualisierung der häufigsten Start- und Ziel-punkte zu sehen.
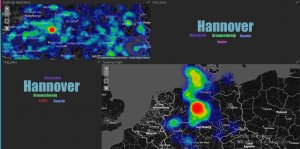
Analysen der EFA-Logs
Als erste Forschungsfrage wird aktuell die Analyse der Auswirkungen der Veranstaltungen auf dem ÖPNV mit Methoden des Maschinellen Lernens analysiert. Hierzu wurden in explorativen Datenanalysen der Einfluss von großen Veranstaltungen wie z.B. Fussballspielen und mittelgroßen Veranstaltungen, etwa Konzerte, auf Anfragen an den ÖPNV betrachtet. Als Grundlage für umfassende Analysen wurden mit Hilfe visueller Methoden exemplarisch Korrelation zwischen ÖPNV-Nachfrage und Veranstaltungszeiträumen detektiert.
Dabei zeichnen sich z.B. für Hannovers Innenstadt klare, sternförmige Muster ab, die zentrale Mobilitätsknoten identifizieren.
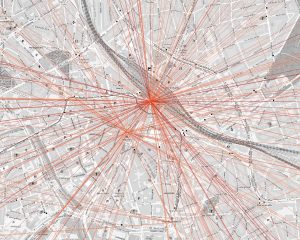
Das Bild stellt die Luftlinie zwischen Start- und Ziel-Ort der Anfragen dar. Dabei entsprechen dunklere Farben häufigeren Strecken. Hier werden deutlich Hannover Hauptbahnhof und Hannover Kröpcke (die zentrale U-Bahn Station) als Mobilitätsknoten identifiziert.
Analysen der Nachfrage für einzelne Stationen lassen wochentagspezifische Muster erkennen.
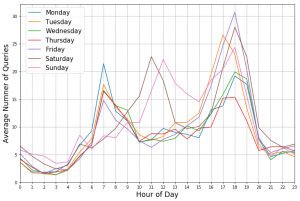
Hier dargestellt sind die durchschnittliche Anzahl der Anfragen mit der Ziel-Haltestelle “Hannover Stadionbrücke”. Zu erkennen sind vor allem Unterschiede zwischen Werktagen und dem Wochenende.
Auch der Einfluss von Veranstaltungen kann mit Hilfe der Anfragen visualisiert werden:
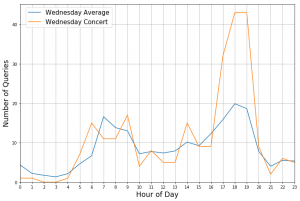
Dargestellt sind die Anzahl der Anfragen mit Ziel “Hannover Stadionbrücke” für Mittwoch, den 26.04.2017 (Orange) sowie die durchschnittlichen Anzahl von Anfragen, die mittwochs mit gleichem Ziel gestellt wird (Blau).
An diesem Tag fand in einer nahe gelegenen Konzerthalle ein Konzert statt, das um 20 Uhr begann. Die signifikante Abweichung zwischen 17 und 19 Uhr wurde sehr wahrscheinlich von den anreisenden Gästen verursacht wurde. Dies illustriert, dass Anfragen an den ÖPNV eine wertvolle Informationsquelle sein können, um Prognosen über die Auswirkung von Veranstaltungen auf Mobilität zu erstellen.
- A novel graph kernel algorithm for improving the effect of text classification. Yang, Fan; Zhu, Tan; Huang, Jing; Huang, Zhilin; Xie, Guoqi (2026). 95 101818.
- Universal constituency treebanking and parsing: A pilot study. Li, Jianling; Zhang, Meishan; Wang, Jianrong; Zhang, Min; Zhang, Yue (2026). 95 101826.
- ASVspoof 5: Design, collection and validation of resources for spoofing, deepfake, and adversarial attack detection using crowdsourced speech. Wang, Xin; Delgado, Héctor; Tak, Hemlata; weon Jung, Jee; jin Shim, Hye; Todisco, Massimiliano; Kukanov, Ivan; Liu, Xuechen; Sahidullah, Md.; Kinnunen, Tomi; Evans, Nicholas W. D.; Lee, Kong Aik; Yamagishi, Junichi; Jeong, Myeonghun; Zhu, Ge; Zang, Yongyi; Zhang, You; Maiti, Soumi; Lux, Florian; Müller, Nicolas; Zhang, Wangyou; Sun, Chengzhe; Hou, Shuwei; Lyu, Siwei; Maguer, Sébastien Le; Gong, Cheng; Guo, Hanjie; Chen, Liping; Singh, Vishwanath Pratap (2026). 95 101825.
- Learning Theory from First Principles Bach, Francis (2025). The MIT Press.
- TDDet: A novel lightweight and efficient tea disease detector. Sun, Yange; Li, Zhihao; Guo, Huaping; Feng, Yan; Tang, Yongqiang; Zhang, Wensheng; Gu, Jingqiu (2025). 237 110481.
- Prompt Inversion Attack Against Collaborative Inference of Large Language Models. Qu, Wenjie; Zhou, Yuguang; Wu, Yongji; Xiao, Tingsong; Yuan, Binhang; Li, Yiming; Zhang, Jiaheng (2025). 1695–1712.
- Alternating Guided Training for Robust Adversarial Defense. Liu, Xinlei; Ma, Chunlai; Chen, Bo; Hu, Tao; Ma, Hailong; Yi, Peng; Jiang, Yiming; Hu, Yuxiang Z. (Mark) Zhang, E. Ricci, Y. Yan, L. Nie, V. Oria, L. Ballan (eds.) (2025). 2008–2012.
- Unveiling the multifunctional use of ochre in the Middle Stone Age: Specialized ochre retouchers from Blombos Cave. Velliky, Elizabeth C.; d’Errico, Francesco; van Niekerk, Karen L.; Henshilwood, Christopher S. (2025). 11(26) eads2797.
- Introduction to Cryptographic Definitions - A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners Guo, Fuchun; Susilo, Willy; Nguyen, Khou; Chen, Xiaofeng; Zhao, Zhen in Undergraduate Topics in Computer Science (2025). 1–221. Springer.
- Intelligent and Efficient Video Moment Localization Liu, Meng; Hu, Yupeng; Guan, Weili; Nie, Liqiang (2025). 1–154. Springer.
- Adaptive Trust Architecture for Secure IoT Communication in 6G. Ahmad, Ijaz; Gimhana, Shakthi; Ahmad, Ijaz; Harjula, Erkki (2025). 7(2) 113–116.
- Distributionally robust optimization methods and applications. Li, Xiang; Liu, Yankui (2025). 182 107121.
- Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problem using graph neural networks and reinforcement learning. Liu, Xi; Chen, Xin; Chau, Vincent; Musial, Jedrzej; Blazewicz, Jacek (2025). 182 107139.
- Efficient configuration of high-dimensional hyperparameters in deep convolutional neural networks for classification assisted by surrogate models. Zhang, Rui; Zhang, Yuanyuan; Sun, Chaoli; Zhang, Yanjun; Dong, Zehua; Wang, Xiaobing (2025). 95 101940.
- Towards real-time weed detection and segmentation with lightweight CNN models on edge devices. Islam, Md Didarul; Liu, Wenxin; Izere, Pascal; Singh, Puranjit; Yu, Chong; Riggan, Benjamin; Zhang, Kuan; Jhala, Amit J.; Knezevic, Stevan; Ge, Yufeng; Pitla, Santosh K.; Luck, Joe D.; Shi, Yeyin (2025). 237 110600.
- Inference Scaling for Long-Context Retrieval Augmented Generation. Yue, Zhenrui; Zhuang, Honglei; Bai, Aijun; Hui, Kai; Jagerman, Rolf; Zeng, Hansi; Qin, Zhen; Wang, Dong; Wang, Xuanhui; Bendersky, Michael (2025).
- Bi-classifier with neighborhood aggregation for unsupervised domain adaptation. Lü, Shuai; Zhang, Xinyu; Li, Zongze; Li, Jingyao; Kang, Meng (2025). 718 122399.
- MOOSE-Chem2: Exploring LLM Limits in Fine-Grained Scientific Hypothesis Discovery via Hierarchical Search. Yang, Zonglin; Liu, Wanhao; Gao, Ben; Liu, Yujie; Li, Wei; Xie, Tong; Bing, Lidong; Ouyang, Wanli; Cambria, Erik; Zhou, Dongzhan (2025). abs/2505.19209
- MEGADance: Mixture-of-Experts Architecture for Genre-Aware 3D Dance Generation. Yang, Kaixing; Tang, Xulong; Peng, Ziqiao; Hu, Yuxuan; He, Jun; Liu, Hongyan (2025). abs/2505.17543
- SRDiffusion: Accelerate Video Diffusion Inference via Sketching-Rendering Cooperation. Cheng, Shenggan; Wei, Yuanxin; Diao, Lansong; Liu, Yong; Chen, Bujiao; Huang, Lianghua; Liu, Yu; Yu, Wenyuan; Du, Jiangsu; Lin, Wei; You, Yang (2025). abs/2505.19151
- MIDB: Multilingual Instruction Data Booster for Enhancing Multilingual Instruction Synthesis. Liu, Yilun; Zhao, Chunguang; Yang, Xinhua; Zeng, Hongyong; Tao, Shimin; Meng, Weibin; He, Minggui; Su, Chang; Yu, Yan; Ma, Hongxia; Zhang, Li; Wei, Daimeng; Yang, Hao (2025). abs/2505.17671
- R1-Compress: Long Chain-of-Thought Compression via Chunk Compression and Search. Wang, Yibo; Shen, Li; Yao, Huanjin; Huang, Tiansheng; Liu, Rui; Tan, Naiqiang; Huang, Jiaxing; Zhang, Kai; Tao, Dacheng (2025). abs/2505.16838
- Does Representation Intervention Really Identify Desired Concepts and Elicit Alignment?. Yang, Hongzheng; Chen, Yongqiang; Qin, Zeyu; Liu, Tongliang; Xiao, Chaowei; Zhang, Kun; Han, Bo (2025). abs/2505.18672
- FlowCut: Rethinking Redundancy via Information Flow for Efficient Vision-Language Models. Tong, Jintao; Jin, Wenwei; Qin, Pengda; Li, Anqi; Zou, Yixiong; Li, Yuhong; Li, Yuhua; Li, Ruixuan (2025). abs/2505.19536
- Wolf Hidden in Sheep’s Conversations: Toward Harmless Data-Based Backdoor Attacks for Jailbreaking Large Language Models. Kong, Jiawei; Fang, Hao; Yang, Xiaochen; Gao, Kuofeng; Chen, Bin; Xia, Shu-Tao; Wang, Yaowei; Zhang, Min (2025). abs/2505.17601
- B-score: Detecting biases in large language models using response history. Vo, An; Taesiri, Mohammad Reza; Kim, Daeyoung; Nguyen, Anh Totti (2025). abs/2505.18545
- SimpleDeepSearcher: Deep Information Seeking via Web-Powered Reasoning Trajectory Synthesis. Sun, Shuang; Song, Huatong; Wang, Yuhao; Ren, Ruiyang; Jiang, Jinhao; Zhang, Junjie; Bai, Fei; Deng, Jia; Zhao, Wayne Xin; Liu, Zheng; Fang, Lei; Wang, Zhongyuan; Wen, Ji-Rong (2025). abs/2505.16834
- MPO: Multilingual Safety Alignment via Reward Gap Optimization. Zhao, Weixiang; Hu, Yulin; Deng, Yang; Wu, Tongtong; Zhang, Wenxuan; Guo, Jiahe; Zhang, An; Zhao, Yanyan; Qin, Bing; Chua, Tat-Seng; Liu, Ting (2025). abs/2505.16869
- MTSA: Multi-turn Safety Alignment for LLMs through Multi-round Red-teaming. Guo, Weiyang; Li, Jing; Wang, Wenya; Li, Yu; He, Daojing; Yu, Jun; Zhang, Min (2025). abs/2505.17147
- HyperPianist: Pianist with Linear-Time Prover and Logarithmic Communication Cost. Li, Chongrong; Zhu, Pengfei; Li, Yun; Hong, Cheng; Qu, Wenjie; Zhang, Jiaheng (2025). 3383–3401.
- LLM Meeting Decision Trees on Tabular Data. Ye, Hangting; Li, Jinmeng; Zhao, He; Guo, Dandan; Chang, Yi (2025). abs/2505.17918
- Key components of effective non-pharmacological interventions for childhood obesity: a review considering social determinants of health. Zamanillo-Campos, R; Colom-Rossello, M; Rodríguez-Calero, M A; Martín, M I; Planas, T; Núñez-Jiménez, C; Ramos, M (2025). 184(7) 449–449.
- On the O(frac√d. Li, Huan; Dong, Yiming; Lin, Zhouchen (2025).
- Extreme synchronization transitions. Lee, Seungjae; Kuklinski, Lennart J.; Timme, Marc (2025). 16(1)
- Sustainable visions: unsupervised machine learning insights on global development goals. García-Rodríguez, Alberto; Núñez, Matias; Pérez, Miguel Robles; Govezensky, Tzipe; Barrio, Rafael A; Gershenson, Carlos; Kaski, Kimmo K; Tagüeña, Julia (2025). 20(3)
- Eye-to-Eye or Face-to-Face? Face and Head Substitution for Co-Located AR. Kullmann, Peter; Schell, Theresa; Botsch, Mario; Latoschik, Marc Erich (J. Saint-Aubert, ed.) (2025). 6
- ANTS: Abstractive Entity Summarization in Knowledge Graphs. Firmansyah, Asep Fajar; Zahera, Hamada M.; Sherif, Mohamed Ahmed; and Moussallem, Diego; Ngonga Ngomo, Axel-Cyrille (2025).
- On the role of AMOC weakening in shaping wintertime Euro-Atlantic atmospheric circulation. Vacca, Andrea Vito; Bellomo, Katinka; Fabiano, Federico; von Hardenberg, Jost (2025). 63(6) 273.
- AI Narrative Breakdown. A Critical Assessment of Power and Promise. Rehak, Rainer in FAccT ’25 (2025). 1250–1260.
- Security and Privacy of Current and Emerging IoT Devices and Systems (Dagstuhl Seminar 2431). Crispo, Bruno; Dmitrienko, Alexandra; Tsudik, Gene; Xu, Wenyuan; Sendner, Christoph (2025).
- A 5.76GS/s 180MHz-BW 74.1dB-DR 2x TI Extrapolated CT DSM with Broadband Hybrid-Inputs Current-Mode Adder in 28nm CMOS. Liu, Yuekai; Guo, Meng; Jin, Yichen; Liu, Yan; Guo, Mingqiang; Sin, Sai-Weng; Tan, Zhichao; Qi, Liang (2024). 1–3.
- A 2.8-to-7.2GT/s DDR5 Registering Clock Driver IC with Parallel-Data Timing and Pin-to-Pin Skew Calibration for a Dual In-Line Memory Module. Kim, Joomyoung; Jung, Jaehong; Lim, Kwangmin; Sung, Barosaim; Kim, Jaekwon; Lim, Baekmin; Noh, Tae-Gun; Lee, Jaehoon; Seok, Hyun-Gi; Cho, Youngsea; Kim, Gyusik; Nomiyama, Takahiro; Kang, Sunhye; Jeong, Yeongcheol; Cho, Sanguk; Kim, Gyumin; Oh, Do-Hyun; Kim, Jaenam; Lim, Yong; Kim, Seungjin; Oh, Seunghyun; Lee, Jongwoo (2024). 1–3.
- A 33.6nW Capacitively Coupled Chopper Amplifier with Stacked Input-Boosted Gate-and-Bulk-Driven Inverter Achieving 0.59 NEF and 0.42 PEF in 180nm CMOS. Hu, Ke; Wu, Jiangchao; Wang, Bo; Law, Man Kay (2024). 1–3.
- A Real-Time Optical-Flow-based SLAM FPGA Accelerator with Inter-Frame Similarity Exploitation and Correlation-Guided Mixed-Precision Flow Update. Li, Mengjie; Zhu, Haozhe; Zhang, Yiming; He, Siqi; Liu, Qi; Zeng, Xiaoyang; Chen, Chixiao (2024). 1–3.
- A 28nm 128-kb Exponent- and Mantissa-Computation-InMemory Dual-macro for Floating-point and INT CNNs. Guo, An; Dong, Xueshan; Dong, Fangyuan; Li, Dongqi; Zhang, Yiran; Zhang, Jingmin; Tang, Yuchen; Shi, Yuhui; Tan, Xiao; Liu, Bo; Shan, Weiwei; Cai, Hao; Yang, Jun; Si, Xin (2024). 1–3.
- A 130-to-170 GHz Reconfigurable Heterodyne/Homodyne Transceiver Achieving 20.5-dBm Psat for Emerging Integrated Wireless Access and Backhaul Networks. Wu, Qixiu; Deng, Wei; Guo, Ziyuan; Jia, Haikun; Ma, Taikun; Peng, Qiuyu; Liu, Chang; Chi, Baoyong (2024). 1–3.
- Temporal Dynamics and Success Patterns of Online Petitions: A Time-Series Clustering Approach. Kovács, Máté; Buryakov, Daniil; Gohourou, Didier; Serdült, Uwe (2024). 103–109.
- A 28nm 76.25TOPS/W RRAM/SRAM-Collaborative CIM Fine-Tuning Accelerator with RRAM-Endurance/Latency-Aware Weight Allocation for CNN and Transformer. Mu, Chen; Huang, Zhirui; Jiang, Hao; Liao, Jie; Jiao, Bo; Zhou, Yuliang; Zhu, Haozhe; Yang, Jianguo; Liu, Qi; Chen, Chixiao (2024). 1–3.
- Time Series Diffusion in the Frequency Domain. Crabbé, Jonathan; Huynh, Nicolas; Stanczuk, Jan Pawel; Van Der Schaar, Mihaela in Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, R. Salakhutdinov, Z. Kolter, K. Heller, A. Weller, N. Oliver, J. Scarlett, F. Berkenkamp (eds.) (2024). (Vol. 235) 9407–9438.
- Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model for Realistic Financial Correlation Matrices. Kubiak, Szymon; Weyde, Tillman; Galkin, Oleksandr; Philps, Daniel; Gopal, Ram (2024). 1–9.
- HyperPianist: Pianist with Linear-Time Prover via Fully Distributed HyperPlonk. Li, Chongrong; Li, Yun; Zhu, Pengfei; Qu, Wenjie; Zhang, Jiaheng (2024). 2024 1273.
- A TFT-Based Flexible PPG Acquisition Circuit in a 3-μm LTPS Process for Packaging-Free Smart Ring Applications. Zhang, Hanbo; Lou, Yuqing; Bo, Yang; Ma, Zhouchen; Wu, Hao; Qi, Liang; Li, Yongfu; Guo, Xiaojun; Wang, Guoxing; Zhao, Jian (2024). 1–3.
- Robust LS-VCE for the Nonlinear Gauss-Helmert Model: Case Studies for Point Cloud Fitting and Geodetic Symmetric Transformation. Wang, Bin; Zhao, Zhisheng; Wang, Shuai; Yu, Jie; Chen, Yu (2024). 62 1–13.
- SANet: A Self-Attention Network for Agricultural Hyperspectral Image Classification. Zhang, Bo; Chen, Yaxiong; Li, Zhiheng; Xiong, Shengwu; Lu, Xiaoqiang (2024). 62 1–15.
- Ant-Search Algorithm for Distributed Knowledge Graphs. Chepizhko, Oleksandr; Forgács, Péter; Schranz, Melanie (2024).
- The Two-Bridge Ant Experiment as an Interactive Netlogo Library Model. Umlauft, Martina; Schranz, Melanie (2024).
- Efficient self-organization of informal public transport networks. Mittal, Kush Mohan; Timme, Marc; Schröder, Malte (2024). 15(1)
- A 28nm 166.9 TOPS/W x Mb/mm2 DRAM-Free QLC Compute-in-ROM Macro Supporting High Task-Level Inference Energy Efficiency for Tiny AI Edge Devices. Cheong, Ling-An; Wang, Chen; Zhou, Mufeng; Liao, Tianyu; Lee, Mingyen; Ke, Yue; Tang, Wenjun; Chen, Yiming; Du, Xirui; Liu, Yongpan; Yang, Huazhong; Li, Xueqing (2024). 1–3.
- A 0.9V CMOS Voltage Reference with 0.41% Untrimmed Accuracy and 44.7 ppm/°C TC from -35°C to 130°C. Chen, Xuanlin; Wu, Jiangchao; Wang, Bo; Law, Man Kay (2024). 1–3.
- A 48MHz Temperature Compensated Crystal Oscillator Utilizing Time-Domain Accuracy Boosting Techniques Achieving ±1.4ppm Frequency Stability from -55°C to 115°C. Yin, Junyang; Deng, Wei; Jia, Haikun; Wang, Minshuo; Chi, Baoyong (2024). 1–3.
- A 32×32 SPAD LiDAR Sensor with In-pixel Spatial-temporal Coincidence and Per-SPAD Pulse Delay for Resolution-lossless Imaging. Chen, Bu; Huang, Zhangcheng; Wang, Jingyi; Shang, Hongyang; Lv, Hankun; Liu, Qi; Liu, Ming (2024). 1–3.
- SDNet: Noise-Robust Bandwidth Extension under Flexible Sampling Rates. Yang, Junkang; Liu, Hongqing; Gan, Lu; Zhou, Yi; Li, Xing; Jia, Jie; Yao, Jinzhuo (2024). 1–6.
- A 64-channel SPAD-based LiDAR sensor with Compact Coincidence Detection Circuit and Inter-frame Correlation-based Nonlinear Partial Histogram Builder. Hu, Jin; Li, Dong; Wang, Xiayu; Ma, Rui; Liu, Yang; Zhu, Zhangming (2024). 1–3.
- A reduced complexity MLSD-based adaptive Duo-PAM4 detector in 28-nm CMOS for 56-Gb/s wireline receiver. Xu, Chaolong; Lv, Fangxu; Lai, Mingche; Luo, Zhang; Qi, Xingyun; Xu, Jiaqing; Wang, Qiang; Xiao, Liquan; Liu, Cewen; Xu, Hua (2024). 1–3.
- HPL-ESS: Hybrid Pseudo-Labeling for Unsupervised Event-based Semantic Segmentation. Jing, Linglin; Ding, Yiming; Gao, Yunpeng; Wang, Zhigang; Yan, Xu; Wang, Dong; Schaefer, Gerald; Fang, Hui; Zhao, Bin; Li, Xuelong (2024). 23128–23137.
- Knowledge Generation for Zero-shot Knowledge-based VQA. Cao, Rui; Jiang, Jing Y. Graham, M. Purver (eds.) (2024). 533–549.
- A 13.75-14.75-GHz 32.1-fsRMS Jitter -100.6-dBc Reference Spur -261.4-dB FoM Sub-Sampling PLL Using a KPD-Doubled Isolated Sub-Sampling Phase Detector for Reliable Spur-Jitter-Joint Optimization. Xu, Yiqing; Li, Yixi; Zhang, Zhao; Qi, Nan; Liu, Jian; Wu, Nanjian; Liu, Liyuan (2024). 1–3.
- ANVMP: A 28nm 52.6 μW 1.25pJ/SOP Asynchronous Non- Volatile-Memory-based Computing-In-Memory Neuromorphic Processor for Edge-Al Applications. Zhang, Jilin; Wei, Qiumeng; Huo, Dexuan; Li, Tao; Gao, Bin; Qian, He; Wu, Huaqiang; Tang, Kea-Tiong; Chen, Hong (2024). 1–3.
- A 75.6Gb/S 22-Bit Floating-Point Reconfigurable DSP Accelerator Embedding 2048×256-Point Complex FFT and 26K-Point 1-D Signal Processing. Xu, Xuanzhe; Liu, Xianjun; Wei, Siyuan; Yu, Shuangming; Dou, Runjiang; Yang, Xu; Wang, Zhe; Liu, Jian; Wu, Nanjian; Liu, Liyuan (2024). 1–3.
- A Wireless Battery-Free Cerebral-Oxygen-Monitoring Micro-System Featuring 0.028% Sensing Resolution. Wang, Weixiao; Zhu, Boyu; Xuan, Yangfan; Shen, Yili; Xiao, Qijing; Wang, Zhiyu; Luo, Yuxuan; Pan, Gang; Su, Bin; Zhao, Bo (2024). 1–3.
- RMMIC: A 40 μW Reconfigurable Multi-modal Multi-channel Interface Circuit System for Bio-signals Monitoring. Zhou, Ting; Huang, Jiajie; Wang, Chao; Hao, Yuzhi; Ji, Yuxin; Gu, Zhiwen; Gao, Zhuo; Yang, Feng; Zhang, Yuhang; Zhao, Yang; Zhao, Jian; Liu, Yan; Chen, Mingyi; Wang, Guoxing; Lian, Yong; Li, Yongfu (2024). 1–3.
- A 28-nm 323 TOPS/mm2/b and 2007 TOPS/W/b Ternary Latch Based Sparsity-Aware CIM Macro With Double-Sampling Ternary ADC. Kim, Myoung; Jeong, Hoichang; Kim, Woo-Seok; Jeong, Yesong; Choi, Young-Eun; Park, Junyoung; Ryu, Min Woo; Lee, Yong Kyu; Lee, Kyuho Jason; Kim, Kyung Rok (2024). 1–3.
- A 28nm 118.26TOPS/W Multi-Dimensional Fault-Tolerant Al Processor Enabling Voltage-Frequency Scaling Below Point-of-First-Failure. Wang, Yang; Yang, Xiaolong; Qin, Yubin; Zhao, Zhiren; Guo, Ruiqi; Yue, Zhiheng; Wei, Shaojun; Hu, Yang; Yin, Shouyi (2024). 1–3.
- A 0.04 μJ/ Classification High-Accuracy Energy-Efficient ECG Processor with SNN On-Chip Backpropagation and Adaptive Threshold Encoding. Fan, Haodong; Zhou, Junlu; Guo, Zilong; Chang, Zhiyuan; Yang, Xi; Hu, Zhicheng; Zeng, Jiahao; Lin, Shuisheng; Zhou, Liang; Zhou, Jun; Zhang, Li; Huang, Jinxi; Su, Jianlei; Gao, Wei; Wu, Qiang; Chang, Liang (2024). 1–3.
- A 0.0006-mm2 0.13-pJ/bit 9-21-Gb/s Sampling CDR with Inverter-Based Frequency Multiplier and Embedded 1: 3 DEMUX in 65-nm CMOS. Dong, Zhicheng; Zhao, Xiaoteng; Yang, Zekai; Su, Xianting; Han, Haolin; Bu, Feng; Zhou, Rong; Sun, Depeng; Chen, Yong; Liu, Shubin; Ding, Ruixue; Zhu, Zhangming (2024). 1–3.
- RePreM: Representation Pre-training with Masked Model for Reinforcement Learning. Cai, Yuanying; Zhang, Chuheng; Shen, Wei; Zhang, Xuyun; Ruan, Wenjie; Huang, Longbo B. Williams, Y. Chen, J. Neville (eds.) (2023). 6879–6887.
- Hierarchical Relational Learning for Few-Shot Knowledge Graph Completion. Wu, Han; Yin, Jie; Rajaratnam, Bala; Guo, Jianyuan (2023).
- MATNet: A Combining Multi-Attention and Transformer Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Zhang, Bo; Chen, Yaxiong; Rong, Yi; Xiong, Shengwu; Lu, Xiaoqiang (2023). 61 1–15.
- Imitation Learning to Outperform Demonstrators by Directly Extrapolating Demonstrations. Cai, Yuanying; Zhang, Chuheng; Shen, Wei; He, Xiaonan; Zhang, Xuyun; Huang, Longbo M. A. Hasan, L. Xiong (eds.) (2022). 128–137.
- A Transformer-Based User Satisfaction Prediction for Proactive Interaction Mechanism in DuerOS. Shen, Wei; He, Xiaonan; Zhang, Chuheng; Zhang, Xuyun; Xie, Jian M. A. Hasan, L. Xiong (eds.) (2022). 1777–1786.
- Dynamics of ranking. I~niguez, Gerardo; Pineda, Carlos; Gershenson, Carlos; Barabási, Albert-László (2022). 13(1)
- Efficient and Robust Solution to Universal Symmetric Transformation for 3-D Point Sets. Wang, Bin; Yu, Jie; Chen, Yu; Zhao, Zhisheng; Liu, Chao (2022). 60 1–15.
- Experimental Characterization Techniques for Solid-Liquid Slurry Flows in Pipelines: A Review. Silva, Rui C. (2022). 10(3)
- TD3 with Reverse KL Regularizer for Offline Reinforcement Learning from Mixed Datasets. Cai, Yuanying; Zhang, Chuheng; Zhao, Li; Shen, Wei; Zhang, Xuyun; Song, Lei; Bian, Jiang; Qin, Tao; Liu, Tieyan X. Zhu, S. Ranka, M. T. Thai, T. Washio, X. Wu (eds.) (2022). 21–30.
- Variational multimodal machine translation with underlying semantic alignment. Liu, Xiao; Zhao, Jing; Sun, Shiliang; Liu, Huawen; Yang, Hao (2021). 69 73–80.
- COVID-19 in South Africa: outbreak despite interventions. Schröder, Malte; Bossert, Andreas; Kersting, Moritz; Aeffner, Sebastian; Coetzee, Justin; Timme, Marc; Schlüter, Jan (2021). 11(1)
- cCorrGAN: Conditional Correlation GAN for Learning Empirical Conditional Distributions in the Elliptope. Marti, Gautier; Goubet, Victor; Nielsen, Frank in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, F. Nielsen, F. Barbaresco (eds.) (2021). (Vol. 12829) 613–620.
- Incentive-driven transition to high ride-sharing adoption. Storch, David-Maximilian; Timme, Marc; Schröder, Malte (2021). 12(1)
- Feldmessgeräte: 1. AgriSens FELDTAG „Einsatz von Fernerkundungstechnologien in der Landwirtschaft“. Truckenbrodt, Sina; Ahmadian, Nima; Borg, Erik; Gerighausen, Heike; Böttcher, Falk; Conrad, Christopher; Dahms, Thorsten; Harfenmeister, Katharina; Hüttich, Christian; Dhillon, Maninder Singh; Spengler, Daniel; Thürkow, Detlef; Thiel, Michael (2021).
- CORRGAN: Sampling Realistic Financial Correlation Matrices Using Generative Adversarial Networks. Marti, Gautier (2020). 8459–8463.
- Comparing the performance of crop growth models using synthetic remote sensing data at DEMMIN, Germany. Dhillon, Maninder Singh; Dahms, Thorsten; Kuebert-Flock, Carina; Conrad, Christopher (2019).
- Light Use Efficiency Model to Estimate Biomass and YIELD with and Without Vapour Pressure Deficit Dhillon, Maninder Singh; Dahms, Thorsten; Nill, Leon (2018). University of Würzburg.
- Experience in the implementation of projects in professional environment in a 1st cycle of studies of Civil Engineering. Ribeiro, Diogo; Neto, Teresa; Santos, Ricardo; de Fátima Portela, Maria F. J. García-Peñalvo (ed.) (2018). 93–99.
- Joint Modeling of Users’ Interests and Mobility Patterns for Point-of-Interest Recommendation. Yin, Hongzhi; Cui, Bin; Huang, Zi; Wang, Weiqing; Wu, Xian; Zhou, Xiaofang X. Zhou, A. F. Smeaton, Q. Tian, D. C. A. Bulterman, H. T. Shen, K. Mayer-Patel, S. Yan (eds.) (2015). 819–822.
- Unifying Local and Global Agreement and Disagreement Classification in Online Debates. Yin, Jie; Narang, Nalin; Thomas, Paul; Paris, Cécile A. Balahur, A. Montoyo, P. Martínez-Barco, E. Boldrini (eds.) (2012). 61–69.
- Addressing the out-of-vocabulary problem for large-scale Chinese spoken term detection. Meng, Sha; Shao, Jian; Yu, Roger Peng; Liu, Jia; Seide, Frank (2008). 2146–2149.
- Abrasive Flow Polishing of Micro Bores. Yin, Ling; Ramesh, Kuppuswamy; Wan, Stephen; Liu, Xiang Dong; Huang, Han; Liu, Yu Chan (2004). 19(2) 187–207.
- Slurry systems handbook Abulnaga, Baha E. in McGraw-Hill Handbooks (2002). McGraw-Hill, New York.
- Development of high speed slurry flow finishing of the inner wall of stainless steel capillary: Polishing and gas flow characteristics of various size of capillaries. Kurobe, T.; Yamada, Y.; Yamamoto, K. (2001). 25(2) 100–106.
- An inverse of the evaluation functional for typed Lambda-calculus. Berger, Ulrich; Schwichtenberg, Helmut R. Vermuri (ed.) (1991). 203–211.
