Forecasting of the Traffic Situation in the Hannover Region
The main requirement of road traffic participants is to know the current traffic situation. Such data is typically obtained from routing services where the time of many different individual trips is taken into account.
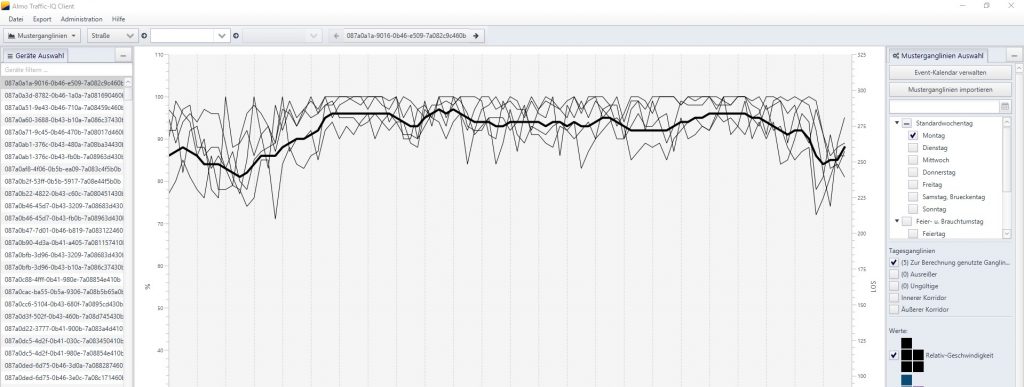
In the context of Data4UrbanMobility tools were developed that allow to predict the traffic situation based on such time series data. The following figure presents an interface to visualize typical time series patterns as well as outliers present in the data:
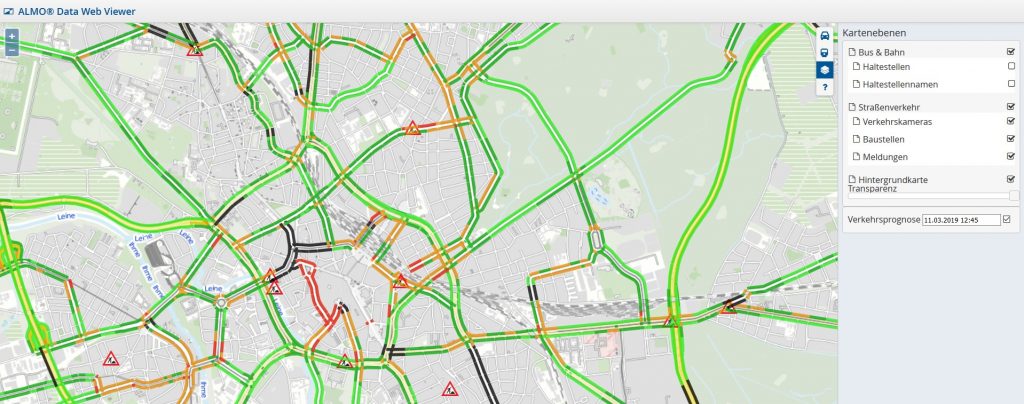
The prediction of the traffic situation is made available in the form of a map based interface for the end user:
Data4UrbanMobility Data Protection Regulation
The work on the Data4UrbanMobility data protection regulation is completed. The document is publicly available and can be found here.
First Version of MiC-App Available
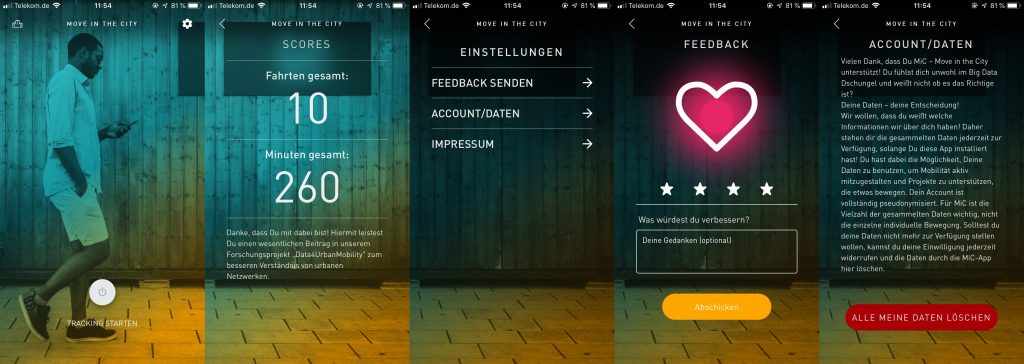
A first version of the novel MiC-App (Move in the City) App is now available for D4UM-associates as well as a protected group of public users. The mobile MiC-App is a tool to gather data.
MiC was developed by the Institute for Sustainable Urbanism at the University of Braunschweig and the Projektionisten GmbH. MiC links the growing awareness of digital citizen rights with the potential of evaluation big datasets. Therefore MiC gives the opportunity to citizen to actively participate in a citizen science project to take part in the development of the mobility of the feature.
MiC gathers data of the users movement, where the user has the about which data should be recorded. All data is pseudonymised such that the privacy of the contributing citizen is ensured.
Current Status:
In the first version of the app, the user can easily start and end the tracking of his/her movement. It is worth to point out, that the user decides when he is tracked and when not. A summary of his/her activity is available for the user as well as the opportunity to issue feedback or even delete all of his contributed data.
Updated System with Dashboard V2
With the new version of our system, the dashboard will provide even more insights into the impact of public events on the traffic situation.
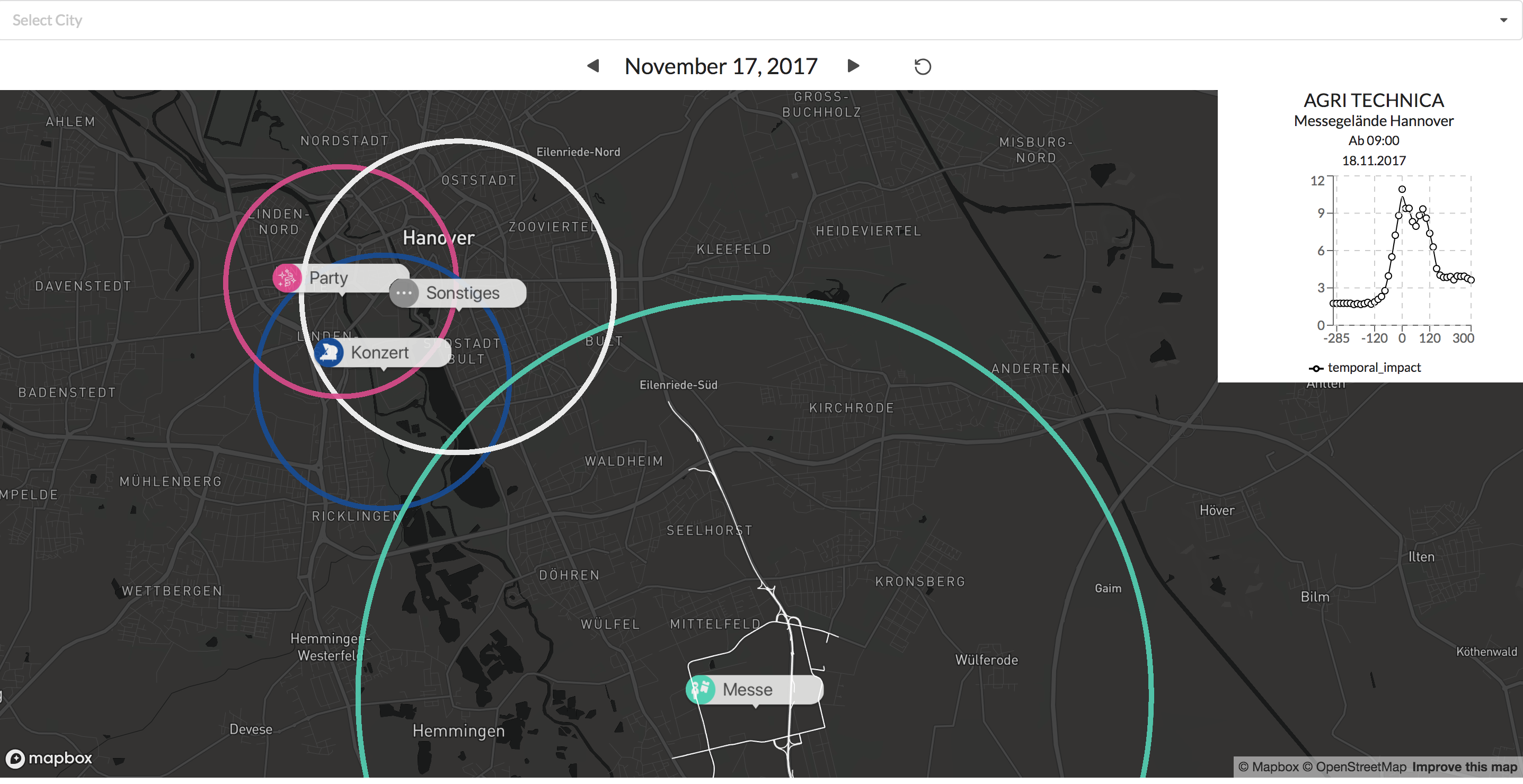
The coloring and labels let us easily distinguish between the different type of events. By clicking on the label we show the typically affected subgraph for that event type. This allows the user to check what specific routes are typically affected by an event at that location.
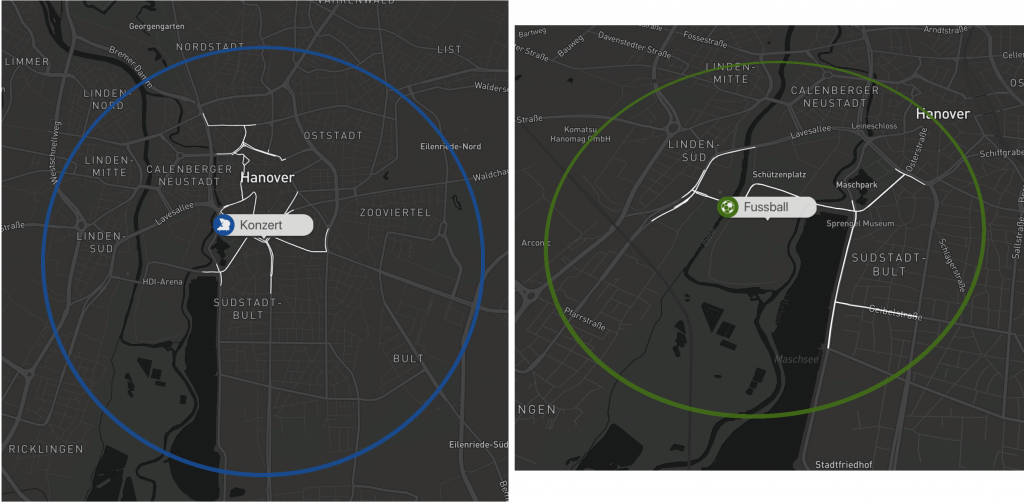
Examples: Visualisation of a concert and a football game.
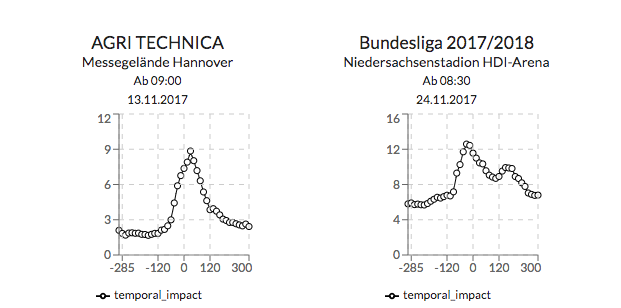
In addition, the graph at the top right gives additional information on how big the impact around the events start time tends to be.
{API}
We enriched the api endpoints with additional information from the data models that were developed as part of the research efforts.
D4UM App Version 1.0
We just released the first Version of the D4UM App. Every project member now has access to the application and can try out its features. Let’s quickly go over some of its main features.
The EFA integration (EFA is a routing engine covering Lower Saxony and Bremen ) allows for quick access to tip information using all available public transport options. Our focus, when designing the application, was on quick and easy navigation to provide a simple and easy to use trip planning tool.
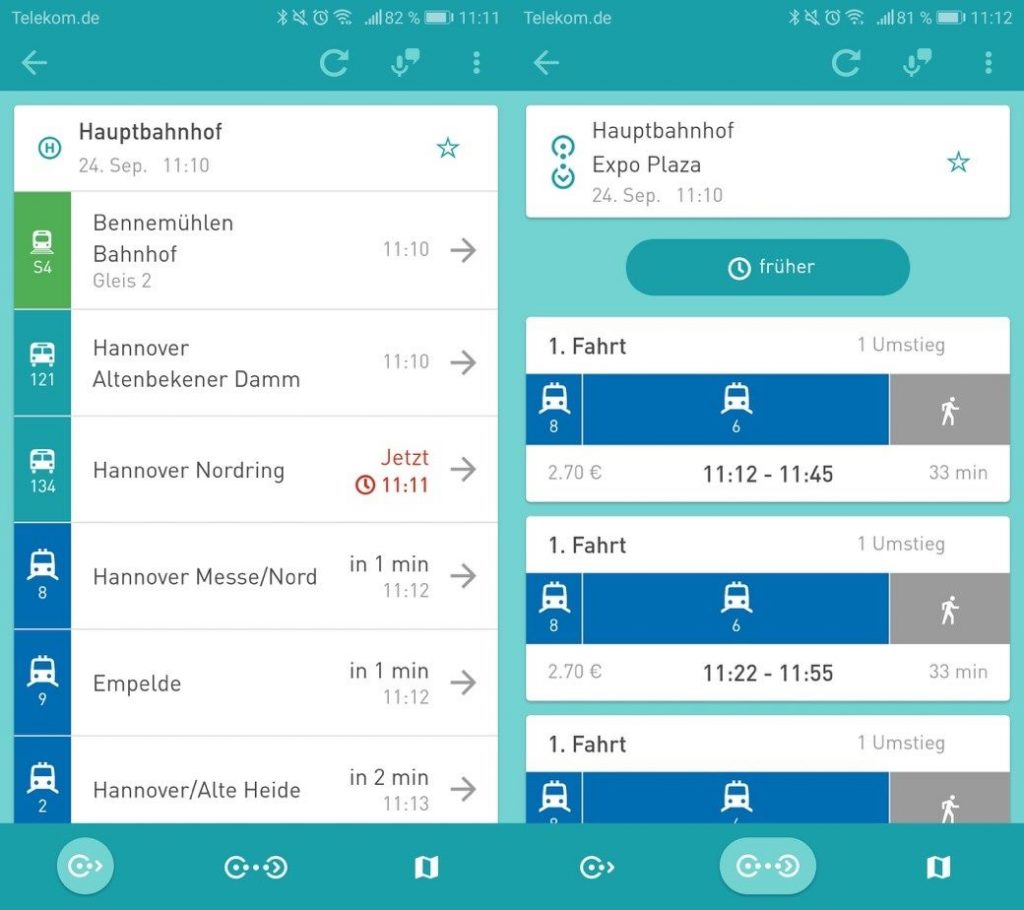
Departures and Connections
On the departure screen we show the user the closes stops for public transportation in his immediate vicinity. On the connection screen the user can fill in his desired starting location( either an address or an existing stop ) and destination and query for what connections are available to him. The provided information contains real time data , meaning we are able to visualized delays for any given connection.
Map
On the map screen you can see and or find all available stops of public transportation. This allows for providing the user with a great way to find out what stops are available in their city. By clicking on any of the shown stops will open the departure screen and provide you with the information mentioned above. To better visualize a selected connection, we show the route you plan to travel on the map.
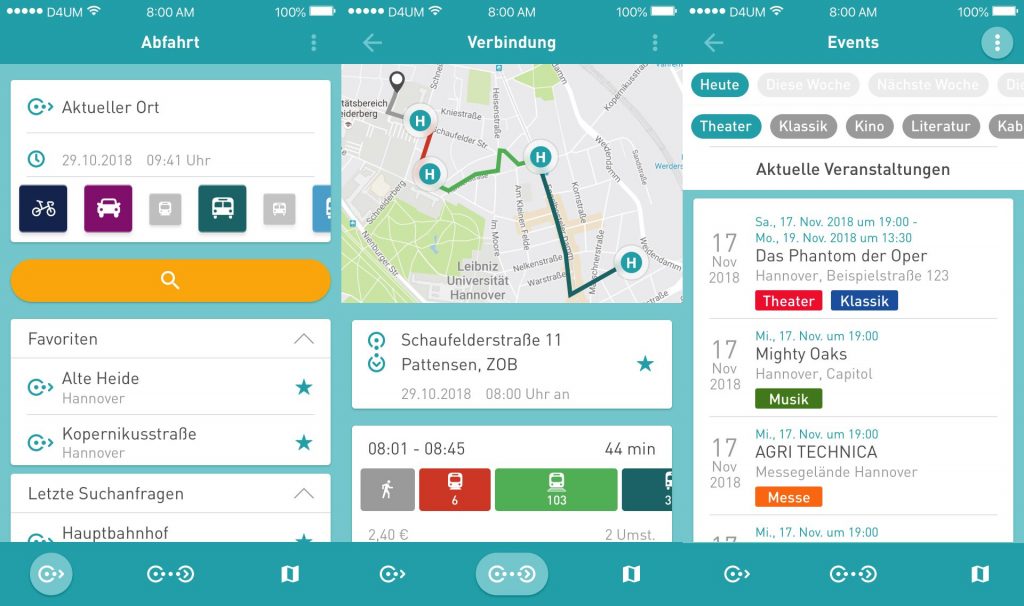
Menu / Settings
Additional features can be found in the settings menu of the application. Here you can find settings that allow you to customize your routing results for both the departures and connection screen. The best way to let us know what you think about the application is to use the feedback module. This can be found here as well. First click on the emoji that best describe how you feel about the app. And then put in any additional information or ideas or thoughts you may have. Now what is left is just to press send and you will send us an email.
We look forward to hearing from you.
Quantification and Prediction of Impact of Public Events
Current Data4UrbanMobility research results allow for measuring and prediction of spatial impact on road traffic of public events. Connected, affected street segments nearby public events are identified to measure the spatial impact. The approach is depicted in the following figure:
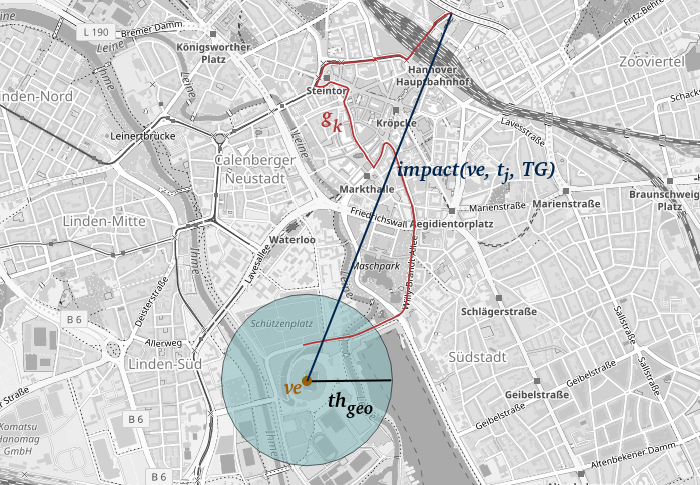
An event is marked as yellow dot, affected streets in red and the measured impact in dark blue. Moreover, an approach making use of machine learning algorithms was developed to predict the impact determined in this way, resulting an error-reduction of up to 40% when compared to existing state-of-the-art approaches.
D4UM – Platform V1 Released
The first version of the Data4UrbanMobiltiy platform has been released. The platform was designed and implemented following a 3-tier-architecture. The platform provides RESTfull Web services for mobility applications like dashboards or mobile apps. As a demonstration, an interactive map application has been developed that visualizes the spatial impact of public events. The following figure shows a screenshot of the application.
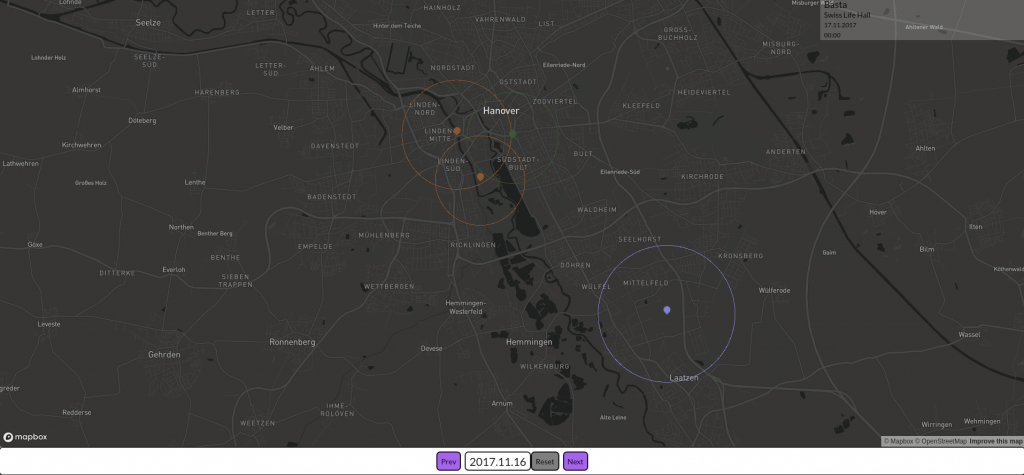
The figure shows 4 public events in the city of Hannover. The colors represent different types of public events (e.g. concerts, fairs, sport events). The circles visualize the spatial impact on road traffic caused by the public events.
Comprehensive Set of Requirements
The Data4UrbanMobility analysis of requirements includes requirements of the application partners Region Hannover (RH) and Wolfsburg AG (WAG) as well as non functional requirements. The requirements were collected by MOMA. The L3S derived research question for data analysis which are based on the requirements of RH and WAG. The research question address especially the information needs of end-users.
The current research questions particularly include
- Automated verification of traffic warnings and prediction of their impact
- Identification of events and prediction of their impact
- Investigation of correlation of road traffic data, public transportation query logs, traffic warnings and twitterfeeds
- Determination of optimal traveling timepoints
Growing Data Collection
ISU create a comprehensive data matrix containing potential source of mobility related data. The Data4UrbanMobility data model describes all project relevant data sets and sets them into context. This makes the data available in a unified manor for both analysis and applications. The selected data sources were transformed according to the Data4UrbanMobility data model by L3S. The data quality of selected data sources (i.e. public transportation query logs and road traffic data) was examined.
Tools for extracting the relevant information from the datasets were developed to enable the integration of the datasets.
- Street and graph extraction from OpenStreetMap
- Bulkloader for public transportation queries
- Integration of “Zentrales Haltestellen Verzeichniss” (central registry of public transportation stops)
The current collection (December 12th 2017) contians
EFA-Logs: 17 million public transportation queries
Road traffic data: 174 thousand street sements with a frequency of 15 minutes
GTFS-data: 90 thousand. public transportation stops, 2.6 thousand routes
Weather: Radolan “Regenraster” (rain grid)
Twitter: 2,5 Mio. Tweets starting at June 2017
OSM: 440 thousand streets
Events: 21 thousand public events (August 14th 2016-July 17th 2018)
Traffic warnings: 13 thousand warning (since June 2017)
Visualization of Public Transportation Information
In order to allow intuitive analytics of public transportation information, the PROJEKTIONISTEN (PROJ) developed a dashboard web application. First prototypes visualize queries addressed to the regional timetable information system EFA (www.efa.de). The prototypes serve as foundations for exploration analyses as well as the implementation of future versions of the dashboard. The following figure shows an integrated visualization of the most frequent origins and destinations of the queries.
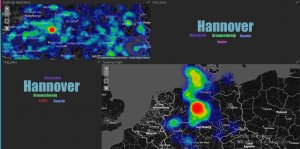
Analysen der EFA-Logs
Analysis of EFA Public Transportation Query Logs
Analyses regarding the impact of public events on public transportation are currently conducted to address early research questions. To this extend, explorative data analyses of the impact of major public events such as football games and medium sized events such as concerts were conducted. Visual analytics were used as a first step towards comprehensive analyses, which show start-like patterns for city center which identify mobility hubs of central importance.
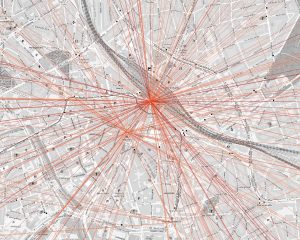
The figure shows the direct connection between origin and destination of public transportation queries. Darker colors correspond to more frequent queried trips. Star-like pattern identify the central train station and the central metro station.
Analyses of single stations reveal weekday dependent patterns.
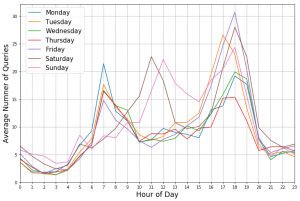
The figure depicts the average number of queries with the destination “Hannover Stadionbrücke”. Differences emerge between Weekends and workdays.
The impact of public events on the queries can be visualized as well.
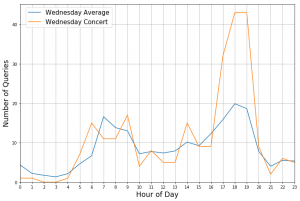
The figure shows the number of queries with the Destination “Hannover Stadionbrücke” for Wednesday, April 26th 2017 (orange) as well as the average number of queries on a Wednesday for the same destination. On this day a concert took place in venue nearby. The concert start at 8 pm. The significant deviations between 5 pm and 7 pm is highly likely to be caused by visitors of the concert. This shows that public transportation queries are a valuable information source to investigate the impact of public events on mobility infrastructure.
Atmospheric and oceanic energy transport during North Atlantic freshening events: influences of moisture transport and hydrologic cycle feedbacks. Baek, Seung H.; Lora, Juan M.; Skinner, Christopher B.; Fu, Minmin; Zhu, Jiang (2025). 63(8) 301.
Analogs of present-day rapid ice melt can be found in episodic discharges of icebergs that occurred during glacial periods called Heinrich events. This introduces excess meltwater into the North Atlantic and weakens the Atlantic thermohaline circulation (AMOC), triggering a hydrologic cycle--AMOC collapse feedback as the atmospheric energy transport compensates for reduced northward heat transport. Here we employ a novel series of 100-year North Atlantic ``hosing'' simulations to investigate atmospheric and oceanic energy transport response from freshwater forcing, focusing in particular on the role of atmospheric rivers (ARs) within atmospheric energy transport. Importantly, we use an ``overwriting'' methodology that allow us to attribute AMOC weakening to added North Atlantic meltwater and subsequent hydrologic cycle responses, respectively. In contrast to far-reaching response of transient eddies, our results show a substantial increase in moisture convergence from ARs that is geographically constrained to the North Atlantic midlatitudes. Such AR changes nevertheless comprise an important component of net precipitation changes over the Euro-Atlantic sector, with the amount being comparable to that from transient eddies over the subpolar Atlantic. Over the course of the century-long simulations, we demonstrate that hydrologic cycle responses to North Atlantic freshening and subsequent feedbacks, including those from ARs, account for approximately half of the simulated AMOC collapse. Our work highlights the dynamics of atmospheric moisture transport response to North Atlantic freshening events and elucidates how intensifying moisture transport may accelerate AMOC collapse in the future.
Neuronal toxicity and recovery from early bortezomib-induced neuropathy: blood-nerve barrier dysfunction without dorsal root ganglion damage. Atalla, Mariam Sobhy; Bettenhausen, Anna-Lena; Verse, Julius M.; Cebulla, Nadine; Krug, Susanne M.; Sauer, Reine-Solange; Srivastava, Mugdha; Bischler, Thorsten; Chen, Jeremy T.C; Kortüm, K. Martin; Kittel, Robert J.; Sommer, Claudia; Rittner, Heike L. (2025).
Background: The use of the first in class proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (BTZ) is highly effective in the treatment of multiple myeloma. However, its long-term use is limited by the fact that most treated patients develop painful polyneuropathy. In some of the treated patients, pain resolves with time; in others, it persists, with the underlying mechanisms poorly understood. One prerequisite for neural toxicity is the ability of a drug to penetrate the blood-nerve barrier. Methods: Here, we analysed the pathways involved in early BTZ-induced polyneuropathy development and its resolution in rats and in myeloma patients using pain behaviour, barrier analysis, transcriptomics, immunohistochemistry, and clinical data. Results: One cycle of BTZ elicited transient tactile and cold allodynia in rats. Transcriptomic signature and network analysis revealed regulation of circadian, extracellular matrix, and immune genes within the nerve and modest changes in the dorsal root ganglia. Recovery processes resealed the small molecule leakiness of the perineurial barrier, reversed axonal swelling, and normalised fibre density in the skin. Expression of the microtubule-associated cytoskeletal protein cortactin matched this process in the perineurium. Netrin-1 as a known barrier sealer was also upregulated in pain resolution in nerve and skin. In patients with painful BTZ-induced polyneuropathy, skin innervation was reduced and netrin-1 was unchanged, compatible with the persistence of pain. Conclusions: In summary, our data demonstrate that early bortezomib toxicity targets mainly peripheral nerves and indicate that pain resolution could be supported by protective growth factors such as netrin-1 for remodelling of the extracellular matrix and neuronal barriers.
Doppler-SLAM: Doppler-Aided Radar-Inertial and LiDAR-Inertial Simultaneous Localization and Mapping. Wang, D.; Haag, H.; Herraez, D. C.; May, S.; Stachniss, C.; Nüchter, A. (2025). 1–8.
Simultaneous localization and mapping is a critical capability for autonomous systems. Traditional SLAM approaches often rely on visual or LiDAR sensors and face significant challenges in adverse conditions such as low light or featureless environments. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel Doppler-aided radar-inertial and LiDAR-inertial SLAM framework that leverages the complementary strengths of 4D radar, FMCW LiDAR, and inertial measurement units. Our system integrates Doppler velocity measurements and spatial data into a tightly-coupled front-end and graph optimization back-end to provide enhanced ego velocity estimation, accurate odometry, and robust mapping. We also introduce a Doppler-based scan-matching technique to improve front-end odometry in dynamic environments. In addition, our framework incorporates an innovative online extrinsic calibration mechanism, utilizing Doppler velocity and loop closure to dynamically maintain sensor alignment. Extensive evaluations on both public and proprietary datasets show that our system significantly outperforms state-of-the-art radar-SLAM and LiDAR-SLAM frameworks in terms of accuracy and robustness. To encourage further research, the code of our Doppler-SLAM and our dataset are available at: https://github.com/Wayne-DWA/Doppler-SLAM.
Pflege zwischen Macht und Ohnmacht – Der Fachkräftemangel in Krankenhäusern. Mohan, Robin (2025). 78(2) 90–98.
Der Fachkräftemangel wird in jüngster Zeit wieder vermehrt diskutiert. In der Regel wird unterstellt, dass er die Machtposition der Beschäftigten gegenüber den Arbeitgebern verbessert. Der Beitrag widmet sich der Frage, warum dieses Machtpotenzial bisher nicht in stärkerem Maße genutzt wird. Es wird dabei davon ausgegangen, dass diese Frage in verschiedenen Arbeitsfeldern unterschiedlich zu beantworten ist, da jeweils spezifische Konstellationen von Angebot und Nachfrage vorherrschen. Das wird anhand der Krankenhauspflege spezifiziert. Dabei werden auch die Deutungen der Arbeitsmarktsituation durch die Akteur*innen selbst fokussiert, denn sie bilden einen Teil der Konstellation von Macht und Ohnmacht, werden jedoch in der bisherigen Forschung zu wenig berücksichtigt. Auf der Grundlage von Interviews mit Führungs- und Pflegekräften, die im Rahmen von qualitativen Betriebsfallstudien in drei Krankenhäusern durchgeführt wurden, wird gezeigt, dass der Fachkräftemangel eine ambivalente Wirkung hat: Er wird zwar zum Teil von den Pflegenden als zu nutzendes Machtpotenzial interpretiert, begründet jedoch auch ein Narrativ der kollektiven Handlungsunfähigkeit.
Conflict Flow Avoided Proactive Rerouting Algorithm using Online Active Learning for Efficient Transmission of Datastream in Software Defined Networks. Subramaniam, Kalaivani; Arumugam, and Sumathi (N. Meghanathan, ed.) (2025). 17(4) 1–19.
Traditional or default Software-Defined Networking (SDN) generally relies on reactive or static routing, where a new flow entry is added for a new arriving packet in a switch. This can create inefficiencies in processing dynamic network conditions. To solve this issue, a Machine Learning-based Proactive Rerouting Scheme (MLPRS) has been developed to dynamically balance load in real-time networks by rerouting flow and enhancing Quality of Service (QoS) compared to the default SDN. However, SDN can face challenges from conflicting flows occurring due to priority and action adjustments that may affect network throughput and bandwidth. Therefore, this article introduces an Online Active ML-based Conflict Flow Avoided Proactive Rerouting Algorithm (OAMLCFAPRA) to discriminate between normal and conflict flows in SDN based on the behavioural changes of flows over time. To achieve this, an online learning algorithm with a customized weighting scheme called Iterative Confidence-Weighted Learning (ICWL) is executed in the controller plane. Initially, it preprocesses the generated flows and trains the ICWL to identify them as normal and conflicting based on their behavioural features. Then, the priorities of each flow are assigned by the ICWL, and the normal flows are directed to OpenFlow. Additionally, the ICWL classifies the conflicting flows into several types based on their features such as priority, IP address, and action. Moreover, the betweenness centrality algorithm determines each link’s significance, and the load on each link is monitored. When the most significant link is overloaded, the flow is rerouted to prevent congestion in real-time. Finally, experimental results show that the ICWL achieves high accuracy in classifying conflict flow types and the OAMLCFAPRA increases network throughput and bandwidth compared to conventional algorithms.
2028-02-14 - HAL - CoreTrustSeal Requirements 2023-2025. HAL (2025).
GF stimulation alters the transcriptome and surface TrkB expression in axons of dorsal root ganglion neurons. Koch, Maximilian; Kshirsagar, Manas; Rawat, Ankita; Zare, Abdolhossein; Schlott, Felicitas; Bischler, Thorsten; Arampatzi, Panagiota; Briese, Michael; Sendtner, Michael (2025). 100194.
Nerve growth factor (NGF) is released after injury from macrophages and other cell types and induces an inflammatory response in neurons, characterized by local subcellular reactions and transcriptomic modulation. NGF-induced axonal transcriptome modulation may be crucial for pain initiation and maintenance. To explore these acute modulations, we cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons in microfluidic chambers and stimulated the axons with NGF. We found that axonal levels of the Il7 transcript encoding interleukin-7 (IL-7) are increased after NGF stimulation, followed by IL-7 release from axons. In growth cones of sensory neurons, we also observed a reorganization of the ribosomal subunits 60S and 40S in response to NGF stimulation. In addition, a dynamic change in the spatio-temporal distribution of the Tropomyosin Kinase B (TrkB) receptor occurs at the plasma membrane of sensory neuron growth cones. TrkB is recruited from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) leading to increased cell surface levels. De-novo synthesis of TrkB seems to be limited to somatic regions of sensory neurons. Thus, cytosolic mechanisms within distal regions of the sensory neurons may autonomously regulate signaling and translation in response to external NGF stimuli.
Überlegungen zu einer wirksamen sozioökologischen Gewerkschaftspolitik. Räthzel, Nora; Stevis, Dimitris (2025). 78(3) 227–230.
Jedes Produkt hat einen Lebenszyklus, der mit der Entnahme von Ressourcen aus der Natur beginnt und mit der Abgabe seiner Reste in die Natur endet. Ob ein Produkt ökologisch sinnvoll und sozial gerecht produziert wurde, kann nur anhand seines Lebenszyklus beurteilt werden. So erfordern z. B. Windturbinen, Solaranlagen, Elektroautos ein Vielfaches an Mineralien, verursachen ein Vielfaches an Naturzerstörung, befördern lokale und globale soziale Ungleichheiten und neue Formen geopolitischer Konkurrenz- und Machtverhältnisse. Das macht grünes Wachstum fragwürdig. Aus diesen Voraussetzungen entwickeln die Autorin und der Autor vier Kriterien für eine effektive sozialökologische Gewerkschaftspolitik.
Wertschöpfungsketten im Wandel. Sorgt die europäische Lieferkettenrichtlinie für soziale Nachhaltigkeit ?. Lorenzen, Stefanie (2025). 78(3) 218–222.
Disruptionen, Geopolitik und Klimawandel beeinflussen globale Wertschöpfungsketten u. a. durch einen Wettbewerb um kritische Rohstoffe. Flankiert wird dies vom politischen Streben nach größerer sozialer und ökologischer Nachhaltigkeit. Die EU-Lieferkettenrichtlinie (CSDDD) soll hierzu beitragen, indem sie großen Unternehmen Sorgfaltspflichten zur Vermeidung von Menschenrechts- und Umweltbeeinträchtigungen in ihren Lieferketten auferlegt. Der Beitrag zeigt, dass die CSDDD Gewerkschaften und NGOs Möglichkeiten einräumt, die Wirksamkeit unternehmerischer Maßnahmen im Sinne der Betroffenen zu beeinflussen. Was das bedeuten kann, wird anhand von drei Beispielen aus der Automobilbranche skizziert.
Der Antichrist, der amerikanische König und Peter Thiel. Schumacher, Jörn (2025).
Tech-Milliardär Peter Thiel zieht im Hintergrund die Strippen in Washington, DC. Er sagt von sich, einen evangelikalen Hintergrund zu haben. Doch an einer entscheidenden Stelle scheint Thiel die christliche Botschaft falsch verstanden zu haben.
What Happened When I Tried to Replace Myself with ChatGPT in My English Classroom. Gelly, Piers (2025, July 28).
LOS MEJORES CARROS EN COLOMBIA EN JULIO de 2025. de 2025, LOS MEJORES CARROS EN COLOMBIA EN JULIO (L. M. C. E. C. E. J. de 2025, ed.) (2025).
LOS MEJORES CARROS EN COLOMBIA EN JULIO de 2025 FIAT Bogotá https://fiat.massymotors.co/fiat-pulse JEEP BOGOTA https://lp-jeep.massymotors.co/lp-jeep-avenger-gads/ RAM https://lp-ram.massymotors.co/lp-ram-1500-gads/ PEUGEOT BOGOTA https://lp-peugeot.massymotors.co/lp-peugeot-2008-gads/ KIA LP CALI https://lp-cali.massymotorskia.com/kia-picanto/ MAZDA CALI https://massymotors.mazkomazda.com/taller/ MERCEDES CALI https://mercedes.massymotorspremium.com/amg_gads/ PEUGEOT LP COSTA https://peugeot-costa.massymotorscosta.com/lp-peugeot-gads/#cotizar FIAT COSTA https://fiat-costa.massymotorscosta.com/lp/fiat-fb/ JEEP COSTA https://jeep-costa.massymotorscosta.com/lp-jeep-gads/ OPEL https://opel-costa.massymotorscosta.com/lps/ RAM COSTA https://ram-costa.massymotorscosta.com/lp-ram-gads/ VOLVO COSTA https://volvo-costa.massymotorscosta.com/ec40-gads/ MAZDA LP MEDELLIN https://mazda.automontana.com/mazda-3-gads/ VOLKSWAGEN MEDELLIN https://volkswagen.germaniamotors.com/razones-elegir-volkswagen-saveiro/ VOLVO XC-90 https://volvo.autolux.com.co/razones-para-elegir-el-volvo-ex30/
Hierarchical Reasoning Model. Wang, Guan; Li, Jin; Sun, Yuhao; Chen, Xing; Liu, Changling; Wu, Yue; Lu, Meng; Song, Sen; Yadkori, Yasin Abbasi (2025).
Promoting students’ motivation in language education with gamified pedagogical conversational agents. Khosrawi-Rad, Bijan; Keller, Paul Felix; Benner, Dennis; Grogorick, Linda; Borchers, Arne; Janson, Andreas; Leimeister, Jan Marco; Robra-Bissantz, Susanne (2025). 238(December, 105374) 1–24.
Pedagogical conversational agents (PCAs) like chatbots are a novel approach to technology-mediated language learning with artificial intelligence. They convey learning content interactively and accompany students in their education. However, many users find conversations with PCAs unmotivating. Gamification is a suitable solution to these motivational hurdles due to its playful nature. Given the difficulty of selecting the appropriate game elements and the scarcity of design recommendations for gamified PCAs, we propose the GNPL framework including a cohesive set of four design principles: goal-setting and reflection, novice-expert relationship, performance-related motivation, and learning story narration. In two design cycles, the article shows the application of the design principles in English learning – a domain commonly associated with motivational challenges – by implementing and evaluating a gamified PCA. The results show that the design principles significantly foster learners' motivation and that learners perceive a solid language learning experience, expressed by higher perceived value and social factors. They highlight the relevance of aligning the PCA's social role, the motivational impact of gamification, and the educational goals of the learning context. The design principles guide educators and developers in gamified PCA design. The paper contributes to the theory stream of PCAs by investigating learners' motivation enhancement when using PCAs. In addition, the paper provides new knowledge on meaningful gamification in an unexplored context and practical insights to solve the design challenges of selecting game elements in this context. Furthermore, it shows how language education can be supported by educational technology.
July 2025 - Top 10 Read Articles in International Journal of Database Management Systems (IJDMS). ijdms (2025).
The International Journal of Database Management Systems (IJDMS) is a bi monthly open access peer-reviewed journal that publishes articles which contribute new results in all areas of the database management systems & its applications. The goal of this journal is to bring together researchers and practitioners from academia and industry to focus on understanding Modern developments in this field, and establishing new collaborations in these areas.
Was von Corona übrig bleibt : Erwerbsarbeit, Sozialstruktur, gesellschaftliche Folgen Kohlrausch, Bettina; Peters, Eileen; Schulze Buschoff, Karin (2025). Campus, Frankfurt am Main.
Die Corona-Pandemie hat das Leben aller Menschen in Deutschland fundamental betroffen. Fünf Jahre nach ihrem Ausbruch im März 2020 ziehen die Beiträge dieses Bandes Bilanz darüber, welche Spuren die Pandemie in der Gesellschaft hinterlassen hat. Von der verstärkten Nutzung des Homeoffice über die Herausforderungen für Selbstständige bis hin zu den Veränderungen in der Mitbestimmung: Die Beiträge zeigen, wie sich Arbeitsformen und soziale Ungleichheiten entwickelt haben und welche Lehren daraus gezogen werden können. Themen wie die Krise in der beruflichen Ausbildung, geschlechtsspezifische Arbeitszeitmuster während der Pandemie sowie soziale Ungleichheit und Armut stehen ebenfalls im Fokus. Ein weiterer Schwerpunkt liegt auf den gesellschaftspolitischen Auswirkungen der Pandemiemaßnahmen: Sorgen und Belastungen führten bei einigen Bürger:innen zu einer politischen Entfremdung und einer nachhaltigen Stärkung antidemokratischer Kräfte. Gestützt auf Daten aus den WSI-Erhebungen und die fundierten Analysen der Autor:innen wird verdeutlicht, was von Corona bleibt – und wie die Gesellschaft in Zukunft besser auf Krisen reagieren kann.
Rapid depletion and super-resolution microscopy reveal dual roles of SRSF5 in coordinating nuclear speckle-paraspeckle crosstalk during cellular stress. Okuda, Ellen Kazumi; Kessler, Laurell Fridolin; Arnold, Benjamin; Riegger, Ricarda J; Hernández Cañás, Maria Clara; Zebrowska, Ewelina; Bakisoglu, Cem; Rudigier, Mara; Krost, Christine; Nagasse, Helder Y; Keiten-Schmitz, Jan; Müller, Stefan; Stanek, David; Dormann, Dorothee; Zarnack, Kathi; Heilemann, Mike; Müller-McNicoll, Michaela (2025). 53(14) gkaf713-.
Nuclear speckles (NS) and paraspeckles (PS) are adjacent yet distinct nuclear condensates that undergo stress-induced reorganization. Here, we identify a dual role for the splicing factor SRSF5 in coordinating the crosstalk between both condensates. Super-resolution imaging shows that SRSF5, while enriched in NS, also overlaps with the shell of a subset of PS. SRSF5 binds purine-rich sequences at the 5' end of NEAT1_2 promoting its alignment to PS shells and the formation of large PS cluster during stress. We propose that SRSF5 binding occurs transiently during PS maturation and must later be removed from NEAT1_2 by nuclear helicases. Inhibition of this remodeling by rocaglamide A, which locks helicases onto purine-rich RNA leads to the aberrant fusion of PS and NS, which can be partially rescued by acute SRSF5 depletion. Surprisingly, while short-term SRSF5 loss impairs PS formation, prolonged depletion activates a feedback loop involving intron retention and premature polyadenylation of TARDBP, reduction of TDP-43 levels and NEAT1_2 isoform switching, ultimately restoring PS clusters. Our findings reveal that SRSF5 serves both architectural and regulatory roles in PS biogenesis and that helicase-mediated remodeling is essential to maintain PS identity and function under stress. These insights uncover fundamental principles of nuclear body dynamics.
Sentiment Patterns in YouTube Comments: A Comprehensive Analysis. Shetty, Savitha; Shetty, Saritha; B, Priya Kamath; Shetty, Deepthi (2025). 10(3) 157–172.
Archer, W. (2000). Critical inquiry in a text-based environment: Computer conferencing in higher education. The Internet and Higher Education, 2(2–3), 87–105.] community of inquiry (CoI) framework has generated substantial interest among online learning researchers. This literature review examines recent research pertaining to the overall framework as well as to specific studies on social, teaching, and cognitive presence. We then use the findings from this literature to identify potential future directions for research. Some of these research directions include the need for more quantitatively-oriented studies, the need for more cross-disciplinary studies, and the opportunities for identifying factors that moderate and/or extend the relationship between the framework's components and online course outcomes.
Stability of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation inferred by subsidence-corrected sea level change. Boretti, Alberto (2025). 156(8) 434.
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is a crucial component of the global climate system, responsible for regulating heat distribution and carbon sequestration. The stability of the AMOC is a subject of intense scientific debate, with some studies suggesting an impending collapse due to anthropogenic climate change, while others argue for its resilience and stability based on different proxies. This study highlights how sea level differences, corrected for subsidence, provide a robust and simple proxy for AMOC stability. A comparison of tide gauge data from The Battery, New York, and Brest, France, corrected for land subsidence using GPS measurements, reveals a negligible difference in absolute sea level rise between these locations, reinforcing the stability of the AMOC within the period 1960 to 2024. These findings challenge claims of AMOC weakening and emphasize the necessity of accurate corrections for subsidence in sea level analyses. Future research should focus on refining observational methods and integrating multiple proxies to enhance the understanding of AMOC dynamics and its role in climate change.
Non-equilibrium anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy for investigating Higgs modes in superconductors. Glier, Tomke E.; Tian, Sida; Rerrer, Mika; Westphal, Lea; Lüllau, Garret; Feng, Liwen; Dolgner, Jakob; Haenel, Rafael; Zonno, Marta; Eisaki, Hiroshi; Greven, Martin; Damascelli, Andrea; Kaiser, Stefan; Manske, Dirk; Rübhausen, Michael (2025). 16(1) 7027.
Even before its role in electroweak symmetry breaking, the Anderson-Higgs mechanism was introduced to explain the Meissner effect in superconductors. Spontaneous symmetry-breaking yields massless phase modes representing the low-energy excitations of the Mexican-Hat potential. Only in superconductors the phase mode is shifted towards higher energies owing to the gauge field of the charged condensate. This results in a low-energy excitation spectrum governed by the Higgs mode. Consequently, the Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer-like Meissner effect signifies a macroscopic quantum condensate in which a photon acquires mass, representing a one-to-one analogy to high-energy physics. We report on an innovative spectroscopic technique to study symmetries and energies of the Higgs modes in the high-temperature superconductor Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8 after a soft quench of the Mexican-Hat potential. Population inversion induced by an initial laser pulse leads to an additional anti-Stokes Raman-scattering signal, which is consistent with polarization-dependent Higgs modes. Within Ginzburg-Landau theory, the Higgs-mode energy is connected to the Cooper-pair coherence length. Within a Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer weak-coupling model we develop a quantitative and coherent description of single-particle and two-particle channels. This opens the avenue for Higgs Spectroscopy in quantum condensates and provides a unique pathway to control and explore Higgs physics.
Einwanderungsgewerkschaften? Arbeitsmigration als strategische Herausforderung für Gewerkschaften. Diekmann, Marie; Pichl, Maximilian (2025). 78(3) 234–236.
Der Beitrag untersucht die strategische Bedeutung der Arbeitsmigration für Gewerkschaften im Kontext des Arbeitskräftemangels und eines radikalisierten Migrationsdiskurses. Obwohl die Gewerkschaften in ihrer Beziehung zu Migrant*innen in der Vergangenheit zwischen Solidarität und Distanzierung geschwankt haben, sind sie zu wichtigen Räumen für die Organisation der Interessen von Arbeitsmigrant*innen und zu Schlüsselakteuren bei der Verteidigung ihrer Rechte geworden. Die Organisierung von Arbeitsmigrant*innen im hochgradig prekären Niedriglohnsektor ist nach wie vor eine besondere Herausforderung. Zu den Strategien der Gewerkschaften gehören nicht nur spezialisierte Beratungs- und Unterstützungsstrukturen, sondern auch politische Lobbyarbeit für gleiche Arbeitsstandards.
Abschieben und anwerben. Gewerkschaftliche Handlungsmöglichkeiten in der aktuellen migrationspolitischen Debatte. Löw, Neva (2025). 78(3) 231–233.
Wie können sich Gewerkschaften in der aufgeheizten Debatte um Migration solidarisch positionieren? Die aktuelle migrationspolitische Debatte ist durch zwei Momente gekennzeichnet, die sich gegenseitig bedingen, aber auf den ersten Blick widersprüchlich erscheinen: das Abschieben und Anwerben ausländischer Arbeitskräfte. In dieser aufgeladenen politischen Situation ist es wichtiger denn je, dass es den Gewerkschaften gelingt, durch den Ausbau solidarischer Strategien das Kräfteverhältnis zu ihren Gunsten zu verschieben. Die Erfahrungen aus den Willkommensbewegungen 2015 können Hinweise darauf liefern, wie dies zu bewerkstelligen ist.
Der Wandel betrieblicher Mitbestimmungspraxis in Ostdeutschland. Fischer, Andreas (2025). 78(4) 245–252.
Fire Impacts, vegetation Recovery, and environmental drivers in West African savannas (2014–2023): A High-Resolution remote sensing assessment. Ouattara, Boris; Thiel, Michael; Forkuor, Gerald; Mouillot, Florent; Laris, Paul; Tondoh, Ebagnerin Jérôme; Sponholz, Barbara (2025). 143(104783) 22.
Savanna fires are a dominant ecological force in West Africa, shaping land systems, carbon dynamics, and biodiversity. Yet, their impacts on ecosystem productivity and recovery remain poorly quantified at meaningful spatial and temporal scales. This study presents a decadal assessment (2014–2023) of fire activity and post-fire vegetation response across a ~ 229,000 km2 transboundary region of Burkina Faso, Ghana, and Cˆote d’Ivoire. Using Harmonized Landsat–Sentinel (HLS) imagery and VIIRS active fire detections, we mapped burned areas (BA) at 30 m resolution—capturing extensive small fires often missed by global datasets. Fire-induced Net Primary Productivity (NPP) losses were estimated using downscaled MODIS productivity data, and post-fire recovery times were tracked at monthly and annual scales. Fires were highly seasonal, with > 80 % of BA occurring between November and January, peaking in December. Despite a dip around 2017, interannual BA remained relatively stable (0.29 % / yr increase, p > 0.05). Immediate NPP losses averaged ~ 11 × 10–2 Mg C ha per year, with higher per-hectare losses in forested and high-biomass zones. Roughly 65 % of BA recovered to pre-fire NPP levels within a year, primarily in grasslands and croplands. However, recovery in woody and mesic areas was slower and more variable. We emphasize that recovery was assessed in terms of NPP (carbon uptake), not structural biomass or species composition—functional recovery does not necessarily imply full ecological recovery. Using machine learning, we identified soil moisture (dry-season NDMI) and temperature as dominant predictors of recovery time, with soil fertility (nitrogen content) and water retention capacity emerging as key drivers. Interestingly, fire frequency and land cover type had limited predictive power once climate and soil factors were accounted for, suggesting that environmental factors, more than fire regime characteristics, shape recovery. These findings support the idea that well-timed, low-intensity fires—particularly early-season burns—can promote carbon resilience in fire-adapted landscapes. This underscores the value of high-resolution remote sensing and soil data in guiding fire-smart management and balancing ecological and livelihood goals under climate change.
Deutscher Alterssurvey (DEAS): Documentation of instruments and variables 1996-2023. Stuth, Stefan; Hameister, Nicole; Schwichtenberg, Beate; Erdmann-Linge, Anke; Engstler, Heribert; Lozano, Alberto; Luitjens, Maren; Klaus, Daniela; Kortmann, Lisa (2025).
Reducing Income Variability in Natural Resource Portfolios via Integer Programming. Greenstreet, Laura; Shi, Qinru; Grimson, Marc; Simon, Franz W.; Sethi, Suresh Andrew; Gomes, Carla P.; Lodi, Andrea; Shmoys, David B. in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, G. Tack (ed.) (2025). (Vol. 15763) 18–34.
RevTogether: Supporting Science Story Revision with Multiple AI Agents. Zhang, Yu; Fu, Kexue; Lu, Zhicong N. Yamashita, V. Evers, K. Yatani, S. X. Ding (eds.) (2025). 462:1–462:7.
Linear Multistep Solver Distillation for Fast Sampling of Diffusion Models. Liang, Yuchen; Fang, Xiangzhong; Chen, Hanting; Wang, Yunhe (2025).
CAIDAS at SemEval-2025 Task 7: Enriching Sparse Datasets with LLM-Generated Content for Improved Information Retrieval. Benchert, Dominik; Meßlinger, Severin; Goller, Sven; Kaiser, Jonas; Pfister, Jan; Hotho, Andreas S. Rosenthal, A. Rosá, D. Ghosh, M. Zampieri (eds.) (2025). 1623–1638.
The focus of SemEval-2024 Task 7 is the retrieval of relevant fact-checks for social media posts across multiple languages. We approach this task with an enhanced bi-encoder retrieval setup, which is designed to match social media posts with relevant fact-checks using synthetic data from LLMs. We explored and analyzed two main approaches for generating synthetic posts. Either based on existing fact-checks or on existing posts. Our approach achieved an S@10 score of 89.53% for the monolingual task and 74.48% for the crosslingual task, ranking 16th out of 28 and 13th out of 29, respectively. Without data augmentation, scores would have been 88.69 (17th) and 72.93 (15th).
CAIDAS at SemEval-2025 Task 7: Enriching Sparse Datasets with LLM-Generated Content for Improved Information Retrieval. Benchert, Dominik; Meßlinger, Severin; Goller, Sven; Kaiser, Jonas; Pfister, Jan; Hotho, Andreas S. Rosenthal, A. Rosá, D. Ghosh, M. Zampieri (eds.) (2025). 1623–1638.
The focus of SemEval-2024 Task 7 is the retrieval of relevant fact-checks for social media posts across multiple languages. We approach this task with an enhanced bi-encoder retrieval setup, which is designed to match social media posts with relevant fact-checks using synthetic data from LLMs. We explored and analyzed two main approaches for generating synthetic posts. Either based on existing fact-checks or on existing posts. Our approach achieved an S@10 score of 89.53% for the monolingual task and 74.48% for the crosslingual task, ranking 16th out of 28 and 13th out of 29, respectively. Without data augmentation, scores would have been 88.69 (17th) and 72.93 (15th).
SALT at SemEval-2025 Task 2: A SQL-based Approach for LLM-Free Entity-Aware-Translation. Völker, Tom; Pfister, Jan; Hotho, Andreas S. Rosenthal, A. Rosá, D. Ghosh, M. Zampieri (eds.) (2025). 852–864.
Entity-aware machine translation faces significant challenges when translating culturally-adapted named entities that require knowledge beyond the source text.We present SALT (SQL-based Approach for LLM-Free Entity-Aware-Translation), a parameter-efficient system for the SemEval-2025 Task 2.Our approach combines SQL-based entity retrieval with constrained neural translation via logit biasing and explicit entity annotations.Despite its simplicity, it achieves state-of-the-art performance (First Place) among approaches not using gold-standard data, while requiring far less computation than LLM-based methods.Our ablation studies show simple SQL-based retrieval rivals complex neural models, and strategic model refinement outperforms increased model complexity.SALT offers an alternative to resource-intensive LLM-based approaches, achieving comparable results with only a fraction of the parameters.
SALT at SemEval-2025 Task 2: A SQL-based Approach for LLM-Free Entity-Aware-Translation. Völker, Tom; Pfister, Jan; Hotho, Andreas S. Rosenthal, A. Rosá, D. Ghosh, M. Zampieri (eds.) (2025). 852–864.
Entity-aware machine translation faces significant challenges when translating culturally-adapted named entities that require knowledge beyond the source text.We present SALT (SQL-based Approach for LLM-Free Entity-Aware-Translation), a parameter-efficient system for the SemEval-2025 Task 2.Our approach combines SQL-based entity retrieval with constrained neural translation via logit biasing and explicit entity annotations.Despite its simplicity, it achieves state-of-the-art performance (First Place) among approaches not using gold-standard data, while requiring far less computation than LLM-based methods.Our ablation studies show simple SQL-based retrieval rivals complex neural models, and strategic model refinement outperforms increased model complexity.SALT offers an alternative to resource-intensive LLM-based approaches, achieving comparable results with only a fraction of the parameters.
The Impact of AI-Based Real-Time Gesture Generation and Immersion on the Perception of Others and Interaction Quality in Social XR. Merz, Christian; Krome, Niklas; Wienrich, Carolin; Kopp, Stefan; Latoschik, Marc Erich (2025).
This study explores how people interact in dyadic social eXtended Reality (XR), focusing on two main factors: the animation type of a conversation partner’s avatar and how immersed the user feels in the virtual environment. Specifically, we investigate how 1) idle behavior, 2) AI-generated gestures, and 3) motion-captured movements from a confederate (a controlled partner in the study) influence the quality of conversation and how that partner is perceived. We examined these effects in both symmetric interactions (where both participants use VR headsets and controllers) and asymmetric interactions (where one participant uses a desktop setup). We developed a social XR platform that supports asymmetric device configurations to provide varying levels of immersion. The platform also supports a modular avatar animation system providing idle behavior, real-time AI-generated co-speech gestures, and full-body motion capture. Using a 2×3 mixed design with 39 participants, we measured users’ sense of spatial presence, their perception of the confederate, and the overall conversation quality. Our results show that users who were more immersed felt a stronger sense of presence and viewed their partner as more human-like and believable. Surprisingly, however, the type of avatar animation did not significantly affect conversation quality or how the partner was perceived. Participants often reported focusing more on what was said rather than how the avatar moved.
Collision-Aware MPCC Integrated with Neural Augmentation for Quadrotor Trajectory Tracking. Hu, Chuanqi; Wang, Jin; Chen, Yikai; Chen, Yonghang; Zheng, Zhi; Meng, Jun; Lu, Guodong (2025). 1–6.
Durchsetzung von Arbeitsrecht - das Arbeitsschutzkontrollgesetz als Modell? Verfassungs- und europarechtliche Fragen mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Direktanstellungsgebots Kärcher, Anneliese; Walser, Manfred in HSI-Schriftenreihe (2025). Bund-Verlag, Frankfurt am Main.
Durch das Arbeitsschutzkontrollgesetz wurde im Jahr 2021 der Einsatz von Fremdpersonal in der Fleischindustrie verboten. Damit wurde die organisierte Verantwortungslosigkeit beendet, die zuvor durch den extensiven Einsatz von Subunternehmen bestand. Ziel des Gesetzes war es, die zahlreichen Verstöße gegen den Arbeitnehmerschutz und andere arbeitsrechtliche Schutzvorschriften zu beenden. Die häufig migrantischen Beschäftigten erhielten dadurch erstmals die faktische Möglichkeit, Betriebsräte zu wählen und sich gewerkschaftlich zu betätigen. Prof. Dr. Manfred Walser und Dipl.-Jur. Anneliese Kärcher untersuchen die Vereinbarkeit dieses Gesetzes mit dem Verfassungs- und Unionsrecht. Eine Fragestellung, der hohe Praxisrelevanz zukommt, weil Unternehmen der Fleischwirtschaft gegen das Gesetz Verfassungsbeschwerden erhoben haben, von denen zumindest eine derzeit noch beim Bundesverfassungsgericht anhängig ist. Ausgehend von den Erfahrungen mit diesem Gesetz hinterfragen sie zudem, inwiefern seine Regelungen auf andere Branchen mit prekären Arbeitsbedingungen, konkret die Paketzustellung und die Landwirtschaft, übertragen werden könnten. Auch in diesen Branchen werden, von der Öffentlichkeit breit wahrgenommen, immer wieder gesetzliche Mindeststandards erheblich verletzt. Untersucht wird daher, ob auch hier Direktanstellungsgebote verfassungs- und europarechtlich zulässig wären und ob diese Verbesserungen versprechen würden.
Drowsiness and Fatigue Recognition Systems for Connected Vehicles, 6G and the EU AI Act. Ferreira, Ana; Özparlak, Basak Ozan; Aden, Hartmut; Symeonidis, Iraklis; ÇetIn, Müge; Kanaki, Eirini; Chatzimisios, Periklis (2025). 428–433.
"Becoming My Own Audience": How Dancers React to Avatars Unlike Themselves in Motion Capture-Supported Live Improvisational Performance. Zhang, Fan; Li, Molin; Chang, Xiaoyu; Fu, Kexue; Allen, Richard William; LC, Ray N. Yamashita, V. Evers, K. Yatani, S. X. Ding, B. Lee, M. Chetty, P. O. T. Dugas (eds.) (2025). 1057:1–1057:24.
Empower Real-World BCIs with NIRS-X: An Adaptive Learning Framework that Harnesses Unlabeled Brain Signals. Wang, Liang; Zhang, Jiayan; Liu, Jinyang; McKeon, Devon; Brizan, David Guy; Blaney, Giles; Jacob, Robert J. K. L. Yao, M. Goel, A. Ion, P. Lopes (eds.) (2024). 50:1–50:16.
Gewerkschaftsrechte heute: Sammelband zur Tagung des Hugo Sinzheimer Instituts für Arbeits- und Sozialrecht am 23./24. Juni 2022 Sozialrecht, Hugo-Sinzheimer-Institut für Arbeits- und in HSI-Schriftenreihe (2024). Bund Verlag, Frankfurt am Main.
Mit der Tagung „Gewerkschaftsrechte heute“ wurde das zehnjährige Jubiläum des Hugo-Sinzheimer-Instituts – nach pandemiebedingten Verschiebungen – am 23. und 24. Juni 2022 nachgefeiert. Gemeinsam mit Gästen aus den Gewerkschaften, der Arbeits- und Sozialgerichtsbarkeit, der Wissenschaft, den Ministerien sowie der betrieblichen und anwaltlichen Praxis wurde über Gegenwart und Zukunft der Gewerkschaftsrechte auf nationaler, europäischer und internationaler Ebene diskutiert. Dieser Band stellt einige der Reden, wissenschaftlichen Vorträge und Praxisberichte der Tagung zusammen und gibt so vielgestaltige Einblicke in Wissenschaft und Praxis der Gewerkschaftsrechte - von der Stärkung der Tarifautonomie über tarifrechtliche Fragestellungen und das Arbeitskampfrecht bis hin zu Gewerkschaftsrechten in der unternehmerischen und der betrieblichen Mitbestimmung.
Pilot Contamination Resilient Dual-Space Channel Estimation for Massive MIMO-HBF Systems. Qin, Ruqiao; Zhu, Xu; Zhang, Yanfeng; Liu, Yujie; Jiang, Yufei (2024). 4052–4057.
Artificial intelligence in applied linguistics a content analysis and future prospects. Obied Alaqlobi, Ahmed Alduais (2024).
In Palantir we trust? Regulation of data analysis platforms in public security. Ulbricht, Lena; Egbert, Simon (2024). 11(3)
Organizations increasingly rely on digital technologies to perform tasks. To do so, they have to integrate data banks to make the data usable. We argue that there is a growing, academically underexplored market consisting of data integration and analysis platforms. We explain that, especially in the public sector, the regulatory implications of data integration and analysis must be studied because they affect vulnerable citizens and because it is not just a matter of state agencies overseeing technology companies but also of the state overseeing itself. We propose a platform-theory-based conceptual approach that directs our attention towards the specific characteristics of platforms—such as datafication, modularity, and multilaterality and the associated regulatory challenges. Due to a scarcity of empirical analyses about how public sector platforms are regulated, we undertake an in-depth case study of a data integration and analysis platform operated by Palantir Technologies in the German federal state of Hesse. Our analysis of the regulatory activities and conflicts uncovers many obstacles to effective platform regulation. Drawing on recent initiatives to improve intermediary liability, we ultimately point to additional paths for regulating public sector platforms. Our findings also highlight the importance of political factors in platform regulation-as-a-practice. We conclude that platform regulation in the public sector is not only about technology-specific regulation but also about general mechanisms of democratic control, such as the separation of power, public transparency, and civil rights.
"Sit on me please": Investigating Perception of Furniture Robotic Movements Using Video Prototyping. LC, Ray; Zamfirescu-Pereira, J. D.; Friedman, Natalie; Fu, Kexue; Li, Yanheng; Ju, Wendy F. ’Floyd’ Mueller, P. Kyburz, J. R. Williamson, C. Sas (eds.) (2024). 9:1–9:6.
Exploiting Causal Graph Priors with Posterior Sampling for Reinforcement Learning. Mutti, Mirco; Santi, Riccardo De; Restelli, Marcello; Marx, Alexander; Ramponi, Giorgia (2024).
„Carmen de triumpho Christi” Macaria Muzia (‘Carmen de Triumpho Christi’ by Macario Muzio). Górka, Elżbieta (2024). 34(1) 77–109.
A model of a DDoS attack scenario on elements of specialized information technology and methods of combating cybercriminals. Stetsyuk, Mykola; Cheshun, Viktor; Stetsyuk, Yuriy; Kozelskiy, Oleksandr; Salem, Abdel-Badeeh M. in CEUR Workshop Proceedings, T. Hovorushchenko, O. Savenko, P. T. Popov, S. Lysenko (eds.) (2024). (Vol. 3675) 260–269.
Ecosystem function associated with soil organic carbon declines with tropical dry forest degradation. De Sosa, Laura L.; Carmona, Inmaculada; Panettieri, Marco; Griffith, Daniel M.; Espinosa, Carlos I.; Jara‐Guerrero, Andrea; Plaza, César; Madejón, Engracia (2024). 35(6) 2109–2121.
Forest degradation is increasingly recognized as a major threat to global biodiversity and the multiple ecosystem services forests provide. This study examined the impacts of forest degradation on soil quality and function in a seasonally dry tropical forest (SDTF) of Ecuador. Previous studies of SDTFs have focused on the impacts of land-use conversion on soils, while this study assessed the less visible but pervasive effects of degradation. We compared soil physical–chemical properties, enzymatic activity, particulate organic carbon (POC) and mineral-associated organic carbon (MAOC) along a gradient of SDTF degradation in both the dry and rainy season. Our findings showed a consistent and steady reduction in soil quality (total C and N) and function (dehydrogenase and β-glucosidase activity) that paralleled the loss of vegetative structure and diversity along the degradation gradient. Soil physical–chemical properties were less variable and enzymatic activity was generally higher in the dry season compared to the rainy season. We also showed for the first time a significant and uniform decrease in POC and MAOC with degradation in SDTF. The relative proportion of these two components was constant along the gradient except in the most degraded state (arid land), where POC was higher in proportion to MAOC, suggesting that extreme forest degradation may cause this ecosystem to cross a functional tipping point. These findings address an important knowledge gap for SDTFs by showing a consistent loss of soil quality and functionality with degradation, and suggest that extreme degradation can result in an alternate state with compromised resilience.
Distributed Continuous-Time Resource Allocation Algorithm for Networked Double-Integrator Systems with Time-Varying Non-Identical Hessians and Resources. Ding, Yong; Ren, Wei; Meng, Ziyang (2023). 1159–1164.
"I Am a Mirror Dweller": Probing the Unique Strategies Users Take to Communicate in the Context of Mirrors in Social Virtual Reality. Fu, Kexue; Chen, Yixin; Cao, Jiaxun; Tong, Xin; LC, Ray A. Schmidt, K. Väänänen, T. Goyal, P. O. Kristensson, A. Peters, S. Mueller, J. R. Williamson, M. L. Wilson (eds.) (2023). 385:1–385:19.
Deep Joint Source-Channel Coding for Wireless Image Transmission with Entropy-Aware Adaptive Rate Control. Chen, Weixuan; Chen, Yuhao; Yang, Qianqian; Huang, Chongwen; Wang, Qian; Zhang, Zhaoyang (2023). 2239–2244.
The Virtual Maze: a Tool for Measuring Trust towards Virtual Humans. Lin, Jinghuai; Cronjé, Johrine; Käthner, Ivo; Pauli, Paul; Latoschik, Marc Erich in IVA ’23 (2023). 1–3.
Homeoffice und Betriebsrat: Neue Herausforderungen für einen „alten Hasen“. Wirth, Carsten (2023). 76(4) 305–311.
In der Studie „Homeoffice und Betriebsrat“ wird untersucht, ob sich Sichtweisen auf Homeoffice-Arbeit verändern, welche Herausforderungen diese Arbeitsform für Betriebsräte generiert, wie Betriebsräte mit diesen umgehen und welche ökonomischen Effekte entstehen. Es wird gezeigt, dass sich im Management die Sichtweisen im Zuge der Pandemie ändern. Betriebsräte behalten ihre Promotorenrolle bei. Die Ergebnisse zeigen ferner, dass Homeoffice-Arbeit wahrscheinlich Teil eines neuen Normal wird. Die Betriebsräte stehen dann vielfältigen Herausforderungen gegenüber. Die Kommunikation mit der Belegschaft und deren Aktivierung erweisen sich dabei als zentrale Probleme. Diesen Schwierigkeiten begegnen sie vor allem mit einer Virtualisierung der Betriebsratsarbeit, der Nutzung ihrer Mitbestimmungsrechte und einer „Politik des offenen Ohrs“. Aus der Perspektive der Betriebsräte steigert Homeoffice-Arbeit i. d. R. die Wirtschaftlichkeit. Sie trägt durch Entgrenzung, geringere Koordinations‑ und Mietkosten sowie eine höhere Produktivität zur Ökonomisierung bei.
The Virtual Maze: a Tool for Measuring Trust towards Virtual Humans. Lin, Jinghuai; Cronjé, Johrine; Käthner, Ivo; Pauli, Paul; Latoschik, Marc Erich in IVA ’23 (2023). 1–3.
Anaximander : and the nature of science Rovelli, Carlo (2023). Allen Lane, an imprint of Penguin Books, [London].
Identifiability Results for Multimodal Contrastive Learning. Daunhawer, Imant; Bizeul, Alice; Palumbo, Emanuele; Marx, Alexander; Vogt, Julia E. (2023).
Der Fragmentierung begegnen. Zur Organisierung migrantischer Reinigungskräfte in der Plattformökonomie. Niebler, Valentin; Altenried, Moritz; Animento, Stefania (2023). 76(4) 252–260.
Der Beitrag beschäftigt sich mit der Frage nach den Arbeitsbedingungen, kollektiven Ressourcen und der Organisierung von vor allem migrantischen Arbeitskräften auf der Reinigungsplattform Helpling. Auf Basis qualitativer Forschung in Berlin gehen die Autor*innen der Frage nach, weshalb sich Arbeit und Organisierung auf Reinigungsplattformen in anderen Dynamiken vollzieht als in anderen Bereichen der Plattformarbeit. Sie argumentieren, dass die räumliche Verteilung auf Privathaushalte, die Abwesenheit einer Betriebssozialisation und die rechtlichen Rahmenbedingungen eine Organisierung von Arbeitskräften auf Reinigungsplattformen erschweren. Gleichzeitig zeigen sie, dass dies nicht zu einer Abwesenheit von Organisierung und sozialen Kämpfen führt, sondern vielmehr deren Formen verändert. Arbeiter*innen auf Helpling in Berlin organisieren sich vorwiegend in informellen Gruppen zur gegenseitigen Hilfe, durch eine Beratungsstelle sowie in migrantischen politischen Gruppen. Aus diesen Umständen ergeben sich sowohl Potenziale wie Hürden für die Entwicklung kollektiver Gegenmacht, die auch für die Analyse anderer Formen der Plattformarbeit relevant sind.
Learning Features via Transformer Networks for Cardiomyocyte Profiling. Plier, Jan; Zisler, Matthias; Furkel, Jennifer; Knoll, Maximilian; Marx, Alexander; Fischer, Alena; Polsterer, Kai; Konstandin, Mathias H.; Petra, Stefania in Informatik Aktuell, K. H. Maier-Hein, T. M. Deserno, H. Handels, A. Maier, C. Palm, T. Tolxdorff (eds.) (2022). 167–172.
Groom Styles Interpolation with Features Preservation for Digital Creatures Effects. Romeo, Marco; Mañas, Carlos Monteagudo; Arabadzhiyski, Hristo; Rovira, Isabela; Vasudevan, Srijith; Traynar, Matt L. Fouqué, C. A. Wilson, C. C. Sanii, V. Bernard (eds.) (2022). 4:1–4:8.
DATA WAREHOUSING AS KNOWLEDGE POOL : A VITAL COMPONENT OF BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE. Aljuwaiber, Abobakr (A. Aljuwaiber, ed.) (2022). 12(2/3/4)
Increasing amounts of information and diverse formats have forced organizations to create large data repositories in response to the information explosion in the 21st century. As a result, the model of a data warehouse has been introduced to define a large data repository. The purpose of this article is to describe the principles of data warehousing in business and how it can enhance the generation of new knowledge throughout the organization. Definitions of data warehousing are considered and include methods of its use, namely query and data simulation. The steps required prior to transforming the raw data into a data warehouse and project goals for data warehouses and metadata are also discussed. The objective of this document is to provide a clear and simple description of data warehousing terms and concepts, especially for busy managers and laymen. They may only need basic and direct information about data warehouses to gain a complete understanding of the principles of the data warehouse.
Questions as beliefs: investigating teachers’ beliefs in reading through inquiry questions. Mante-Estacio, Ma Joahna; Tupas, Ruanni (2022). 10(3) 157–172.
Archer, W. (2000). Critical inquiry in a text-based environment: Computer conferencing in higher education. The Internet and Higher Education, 2(2–3), 87–105.] community of inquiry (CoI) framework has generated substantial interest among online learning researchers. This literature review examines recent research pertaining to the overall framework as well as to specific studies on social, teaching, and cognitive presence. We then use the findings from this literature to identify potential future directions for research. Some of these research directions include the need for more quantitatively-oriented studies, the need for more cross-disciplinary studies, and the opportunities for identifying factors that moderate and/or extend the relationship between the framework's components and online course outcomes.
Karamelo: an open source parallel C++ package for the material point method. de Vaucorbeil, Alban; Nguyen, Vinh Phu; Nguyen-Thanh, Chi (2021). 8(4) 767–789.
A simple and robust C++ code for the material point method (MPM) called Karamelo is presented here. It was designed to provide an open source, fast, light and easy-to-modify framework for both conducting research on the MPM and research using the MPM, instead of a finite element package. This paper presents the overall philosophy, the main design choices and some of the original algorithms implemented in Karamelo. Simulations of solids and fluids involving extreme deformation are provided to illustrate the capabilities of the code.
A Search Method for Large Polarization Kernels. Trofimiuk, Grigorii (2021). 2084–2089.
HMM-Based Traffic State Prediction and Adaptive Routing Method in VANETs. Gao, Kaihan; Ding, Xu; Xu, Juan; Yang, Fan; Zhao, Chong in Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, H. Gao, X. Wang, M. Iqbal, Y. Yin, J. Yin, N. Gu (eds.) (2020). (Vol. 350) 236–252.
A DNN Inference Acceleration Algorithm in Heterogeneous Edge Computing: Joint Task Allocation and Model Partition. Shi, Lei; Xu, Zhigang; Shi, Yi; Fan, Yuqi; Ding, Xu; Sun, Yabo in Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, H. Gao, X. Wang, M. Iqbal, Y. Yin, J. Yin, N. Gu (eds.) (2020). (Vol. 349) 237–254.
Point Cloud Overlapping Region Co-Segmentation Network. Fu, Kexue; Luo, Xiaoyuan; Wang, Manning in Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, L. Bertinetto, J. F. Henriques, S. Albanie, M. Paganini, G. Varol (eds.) (2020). (Vol. 148) 1–13.
Comprehensive Grassland Degradation Monitoring by Remote Sensing in Xilinhot, Inner Mongolia, China. Lyu, Xin; Li, Xiaobing; Gong, Jirui; Wang, Hong; Dang, Dongliang; Dou, Huashun; Li, Shengkun; Liu, Siyu (2020). 12(9) 3682.
Grassland degradation is a complex process and cannot be thoroughly measured by a single indicator, such as fractional vegetation cover (FVC), aboveground biomass (AGB), or net primary production (NPP), or by a simple combination of these indicators. In this research, we combined measured data with vegetation and soil characteristics to establish a set of standards applicable to the monitoring of regional grassland degradation by remote sensing. We selected indicators and set their thresholds with full consideration given to vegetation structure and function. We optimized the indicator simulation, based on which grassland degradation in the study area during 2014–2018 was comprehensively evaluated. We used the feeding intensity of herbivores to represent the grazing intensity. We analyzed the effects of climate and grazing activities on grassland degradation using the constraint line method. The results showed degradation in approximately 69% of the grassland in the study area and an overall continued recovery of the degraded grassland from 2014 to 2018. We did not identify any significant correlation between temperature and grassland degradation. The increase in precipitation promoted the recovery of degraded grassland, whereas increased grazing may have aggravated degradation. Our findings can not only improve the scientific quality and accuracy of grassland degradation monitoring by remote sensing but also provide clear spatial information and decision-making help in sustainable management of grassland regions.
Relational Galois connections between transitive digraphs: Characterization and construction. Cabrera, Inma P.; Cordero, Pablo; Muñoz-Velasco, Emilio; Ojeda-Aciego, Manuel; De Baets, Bernard (2020). 519 439–450.
Reduced complexity window processing of binary polarization kernels. Trofimiuk, Grigorii; Trifonov, Peter (2019). 1412–1416.
PyGran: An object-oriented library for DEM simulation and analysis. Abi-Mansour, Andrew (2019). 9 168–174.
PyGran is a simulation and analysis toolkit designed for particle systems with emphasis on discrete element method (DEM) simulation. PyGran enables DEM programmers to develop computational tools and perform interactive analysis of granular systems in Python. The toolkit provides an interface for running DEM simulations in parallel using the open-source LIGGGHTS-PUBLIC software, routines for performing structural and temporal analysis, and an intuitive way for building and manipulating granular systems. The object-oriented design of PyGran enables post-processing of coupled CFD–DEM simulation, and constructing coarse-grained representations of DEM systems. PyGran is released under the GNU General Public License (GPL v2.0), and its source code is available from github.
Ergo + 50: Ergonomic Assessment Methodology Aimed at Older Workers. Ferreras-Remesal, Alberto; Moreno, Carlos Chirivella; Cuesta, Alicia Piedrabuena; Poveda-Puente, Rakel; Arnau, Sonia Serna; Latorre-Sánchez, Consuelo; Almenara, Mercedes Sanchís in Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, R. H. M. Goossens, A. Murata (eds.) (2019). (Vol. 970) 27–36.
TensorFlow for Dummies Scarpino, Matthew (2018). Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey.
Open Source Technology : An Emerging and Vital Paradigm in Institutions of Learning in Kenya. Muthamia, Cosmas Kabii; Wanyembi, Gregory; Matoke, Nahason (2018).
Failures related to inadequate spacers and spacer dampers have forced utilities to review all aspects of bundled transmission line design. Most utilities are now using spacer dampers instead of rigid spacers. Many are looking at new bundle designs, including diamond and six bundle. Utilities are also requiring much stricter quality test.
A randomized construction of polar subcodes. Trifonov, Peter; Trofimiuk, Grigorii (2017). 1863–1867.
IoT Infrastructure and Potential Application to Smart Grid Communications. Rana, Md. Masud; Xiang, Wei; Wang, Eric; Jia, Min (2017). 1–6.
Enlargement of the Hand-Dorsa Vein Database Based on PCA Reconstruction. Li, Kefeng; Zhang, Guangyuan; Wang, Yiding; Wang, Peng; Ni, Cui in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Z. You, J. Zhou, Y. Wang, Z. Sun, S. Shan, W.-S. Zheng, J. Feng, Q. Zhao (eds.) (2016). (Vol. 9967) 288–295.
The Termolator: Terminology Recognition based on Chunking, Statistical and Search-based Scores. Meyers, Adam; He, Yifan; Glass, Zachary; Babko-Malaya, Olga in CEUR Workshop Proceedings, I. Atanassova, M. Bertin, P. Mayr (eds.) (2015). (Vol. 1384) 34–43.
Conditional Colored Petri Net for Modelling an Automated GDM System. Medina-Marín, Joselito; López-Morales, Virgilio; Karelin, Oleksandr in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, O. Pichardo-Lagunas, O. Herrera-Alcántara, G. Arroyo-Figueroa (eds.) (2015). (Vol. 9414) 602–616.
Hand-dorsa Vein Recognition Based on Improved Partition Local Binary Patterns. Li, Kefeng; Zhang, Guangyuan; Wang, Yiding; Wang, Peng; Ni, Cui in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, J. Yang, J. Yang, Z. Sun, S. Shan, W.-S. Zheng, J. Feng (eds.) (2015). (Vol. 9428) 312–320.
Block sequential decoding of polar codes. Trofimiuk, Grigorii; Trifonov, Peter (2015). 326–330.
Kurzskala zur Messung computer- und internetbezogener Motivationen bei jungen Erwachsenen. Senkbeil, Martin; Ihme, Jan Marten (2014). 61(3)
Startkohorte 3: Klasse 5 (SC3). Welle 1. Erhebungsinstrumente (Feldversion). NEPS (2013).
Relationship between Petri Nets and Cellular Automata for the Analysis of Flexible Manufacturing Systems. Barragán, Irving; Mora, Juan Carlos Seck Tuoh; Medina-Marín, Joselito in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, I. Z. Batyrshin, M. González-Mendoza (eds.) (2012). (Vol. 7630) 338–349.
Distributed finite-time cooperative tracking of networked Lagrange systems via local interactions. Meng, Ziyang; Lin, Zongli (2012). 4951–4956.
On global consensus of linear multi-agent systems subject to input saturation. Meng, Ziyang; Zhao, Zhiyun; Lin, Zongli (2012). 4516–4521.
Beiträge zur Gesundheitsberichterstattung des Bundes. Daten und Fakten: Ergebnisse der Studie »Gesundheit in Deutschland aktuell 2009«. Institut, Robert Koch (2011).
Some stability and boundedness conditions for second-order leaderless and leader-following consensus with communication and input delays. Meng, Ziyang; Ren, Wei; Cao, Yongcan; You, Zheng (2010). 574–579.
Distributed finite-time containment control for multiple Lagrangian systems. Meng, Ziyang; Ren, Wei; You, Zheng (2010). 2885–2890.
Decentralized finite-time sliding mode estimators with applications to formation tracking. Cao, Yongcan; Ren, Wei; Meng, Ziyang (2010). 4610–4615.
Distributed containment control for double-integrator dynamics: Algorithms and experiments. Cao, Yongcan; Stuart, Daniel; Ren, Wei; Meng, Ziyang (2010). 3830–3835.
A Bayesian decision fusion approach for microRNA target prediction. Yue, Dong; Liu, Hui; Lu, Mingzhu; Chen, Philip; Chen, Yidong; Huang, Yufei A. Zhang, M. Borodovsky, G. Özsoyoglu, A. R. Mikler (eds.) (2010). 214–221.
Practice in a Second Language: Perspectives from Applied Linguistics and Cognitive Psychology. DeKeyser, Robert M. (2007).
Kurz und gut: Eine deutsche Kurzskala zur Erfassung des Bedürfnisses nach kognitiver Geschlossenheit. Schlink, Susanne; Walther, Eva (2007). 38(3) 153–161.
Tomislav, prvi hrvatski kralj Macan, Darko (2007). 27 str.-. Astoria, Rijeka.
An Active Rule Base Simulator based on Petri Nets. Medina-Marín, Joselito; Li, Xiaoou U. Ultes-Nitsche, J. C. Augusto, J. Barjis (eds.) (2005). 96–101.
Kognitive Geschlossenheit und Persönliches Strukturbedürfnis. Collani, G. (2003).
High capacity motors on-line diagnosis based on ultra wide band partial discharge detection. Carvajal, A.; Garcia-Colon, V.R. (2003). 168–170.
A noninvasive ultra-wide band (UWB) partial discharge technique was employed in high capacity motors diagnosis. Those motors are installed and operating in an oil pumping plant. The technique presented here was applied to 13 motors rated at 13.8 kV and 2500 HP of capacity. The technique allowed motors insulation system status classification, according to UWB partial discharges activity measured and recorded on the cable feeders' ground connection. The PD defection technique used, employs near field sensors (HF CT) working within the 80 MHz range and whose information is digitized and fed to a conventional PD digital detector, where a traditional N-Q-/spl Phi/ PD pattern is obtained to facilitate motor insulation system problems identification. Those results of on-line evaluation of these motors, during normal operation, using UWB techniques are presented and discussed in the paper.
Measuring Epistemic Curiosity and Its Diversive and Specific Components. Litman, Jordan A.; Spielberger, Charles D. (2003). 80(1) 75–86.
Open Research Questions for Linguistics in Information Access. Karlgren, Jussi in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, S. Renals, G. Grefenstette (eds.) (2000). (Vol. 2705) 182–191.
Motivated resistance and openness to persuasion in the presence or absence of prior information. Kruglanski, Arie W.; Webster, Donna M.; Klem, Adena (1993). 65(5) 861–876.
Handbook of the Normal Distribution Patel, Jagdish K.; Read, Campbell B. in Statistics: Textbooks and Monographs (1982). (First , Vol. 40) Marcel Dekker, Basel.
This book contains a collection of results relating to the normal distribution. It is a compendium of properties, and problems of analysis and proof are not covered. The aim of the authors has been to list results which will be useful to theoretical and applied researchers in statistics as well as to students. Distributional properties are emphasized, both for the normal law itself and for statistics based on samples from normal populations. The book covers the early historical development of the normal law (Chapter 1); basic distributional properties, including references to tables and to algorithms suitable for computers (Chapters 2 and 3); properties of sampling distributions, including order statistics (Chapters 5 and 8), Wiener and Gaussian processes (Chapter 9); and the bivariate normal distribution (Chapter 10). Chapters 4 and 6 cover characterizations of the normal law and central limit theorems, respectively; these chapters may be more useful to theoretical statisticians. A collection of results showing how other distributions may be approximated by the normal law completes the coverage of the book (Chapter 7). Several important subjects are not covered. There are no tables of distributions in this book, because excellent tables are available elsewhere; these are listed, however, with the accuracy and coverage in the sources. The multivariate normal distribution other than the bivariate case is not discussed; the general linear v vi Preface model and regression models based on normality have been amply documented elsewhere; and the applications of normality in the methodology of statistical inference and decision theory would provide material for another volume on their own.