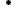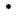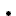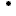
Forecasting of the Traffic Situation in the Hannover Region
The main requirement of road traffic participants is to know the current traffic situation. Such data is typically obtained from routing services where the time of many different individual trips is taken into account.
In the context of Data4UrbanMobility tools were developed that allow to predict the traffic situation based on such time series data. The following figure presents an interface to visualize typical time series patterns as well as outliers present in the data:
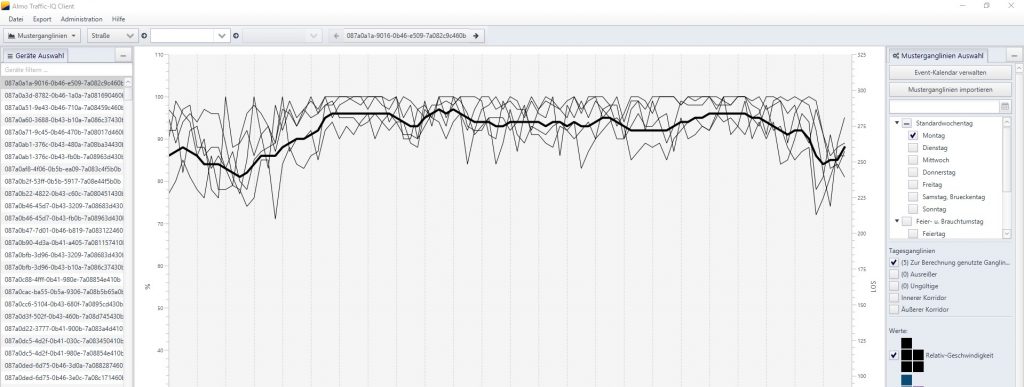
The prediction of the traffic situation is made available in the form of a map based interface for the end user:
Data4UrbanMobility Data Protection Regulation
The work on the Data4UrbanMobility data protection regulation is completed. The document is publicly available and can be found here.
First Version of MiC-App Available
A first version of the novel MiC-App (Move in the City) App is now available for D4UM-associates as well as a protected group of public users. The mobile MiC-App is a tool to gather data.
MiC was developed by the Institute for Sustainable Urbanism at the University of Braunschweig and the Projektionisten GmbH. MiC links the growing awareness of digital citizen rights with the potential of evaluation big datasets. Therefore MiC gives the opportunity to citizen to actively participate in a citizen science project to take part in the development of the mobility of the feature.
MiC gathers data of the users movement, where the user has the about which data should be recorded. All data is pseudonymised such that the privacy of the contributing citizen is ensured.
Current Status:
In the first version of the app, the user can easily start and end the tracking of his/her movement. It is worth to point out, that the user decides when he is tracked and when not. A summary of his/her activity is available for the user as well as the opportunity to issue feedback or even delete all of his contributed data.
Updated System with Dashboard V2
With the new version of our system, the dashboard will provide even more insights into the impact of public events on the traffic situation.
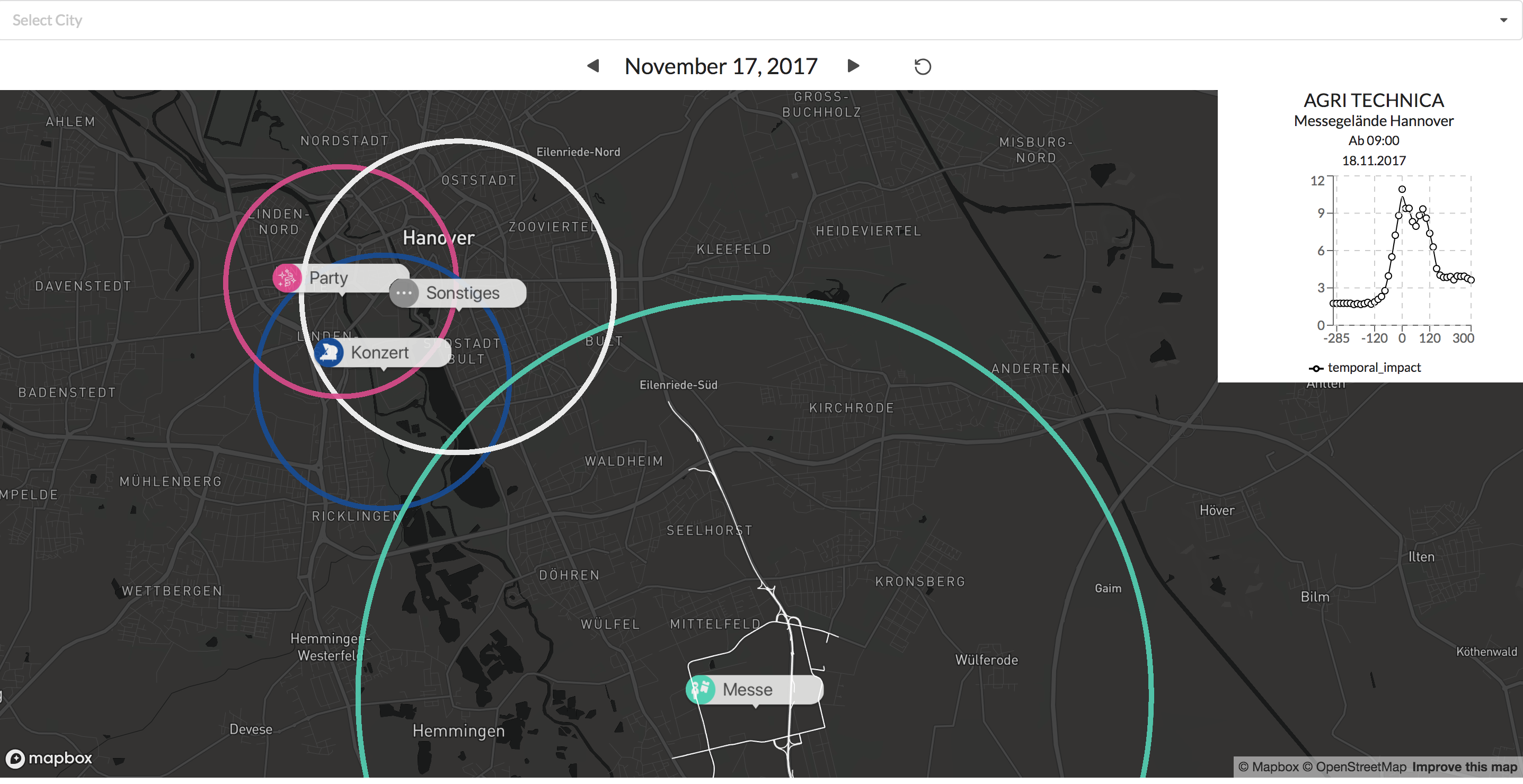
The coloring and labels let us easily distinguish between the different type of events. By clicking on the label we show the typically affected subgraph for that event type. This allows the user to check what specific routes are typically affected by an event at that location.
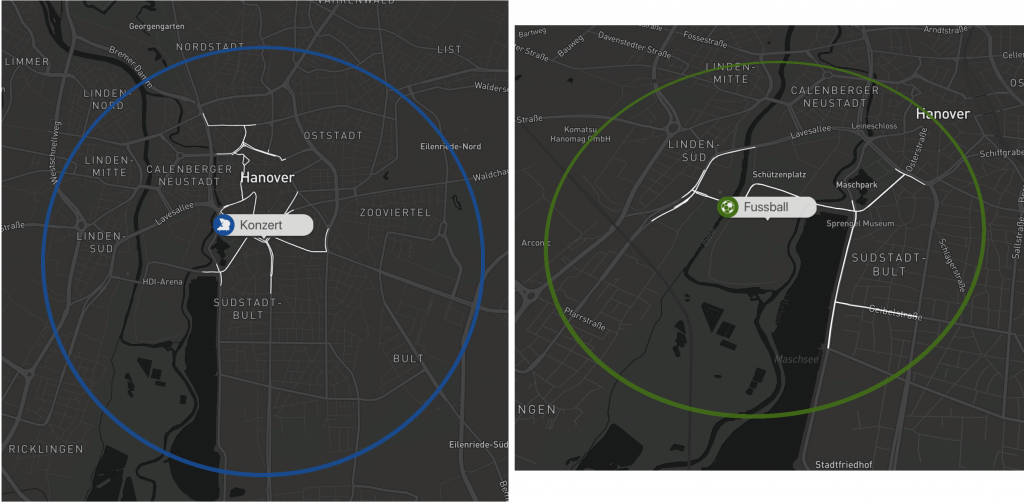
Examples: Visualisation of a concert and a football game.
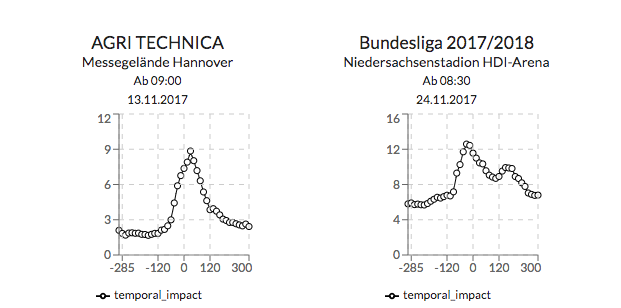
In addition, the graph at the top right gives additional information on how big the impact around the events start time tends to be.
{API}
We enriched the api endpoints with additional information from the data models that were developed as part of the research efforts.
D4UM App Version 1.0
We just released the first Version of the D4UM App. Every project member now has access to the application and can try out its features. Let’s quickly go over some of its main features.
The EFA integration (EFA is a routing engine covering Lower Saxony and Bremen ) allows for quick access to tip information using all available public transport options. Our focus, when designing the application, was on quick and easy navigation to provide a simple and easy to use trip planning tool.
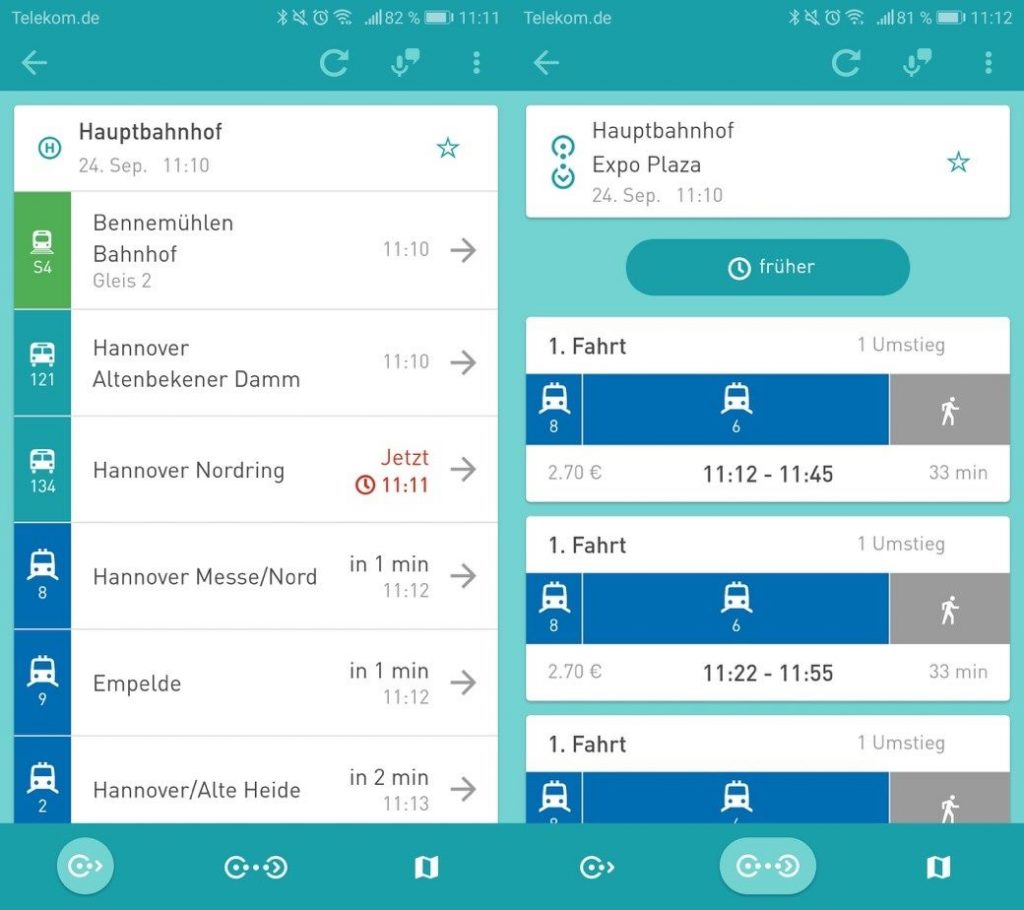
Departures and Connections
On the departure screen we show the user the closes stops for public transportation in his immediate vicinity. On the connection screen the user can fill in his desired starting location( either an address or an existing stop ) and destination and query for what connections are available to him. The provided information contains real time data , meaning we are able to visualized delays for any given connection.
Map
On the map screen you can see and or find all available stops of public transportation. This allows for providing the user with a great way to find out what stops are available in their city. By clicking on any of the shown stops will open the departure screen and provide you with the information mentioned above. To better visualize a selected connection, we show the route you plan to travel on the map.
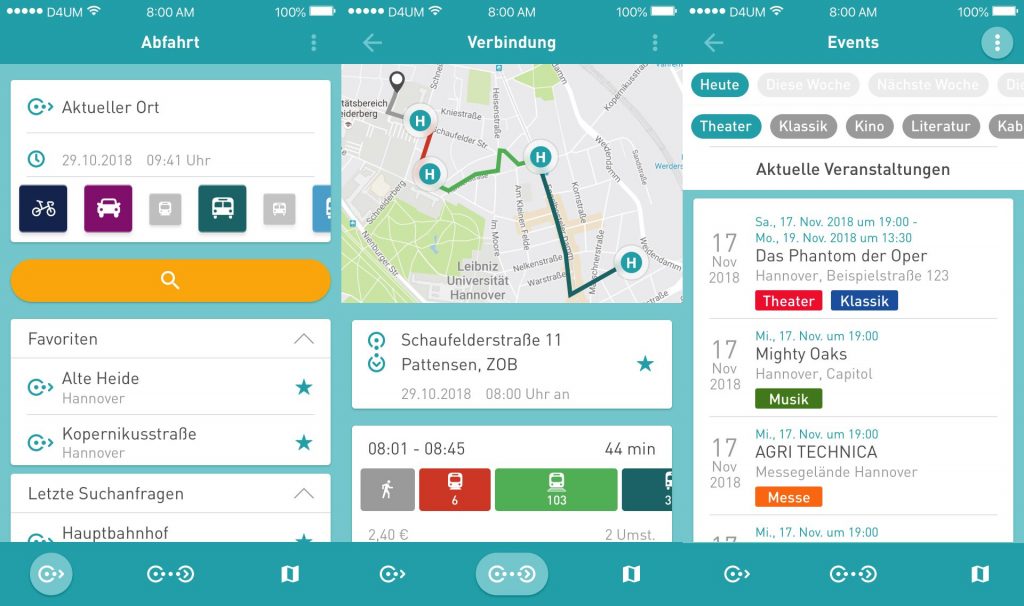
Menu / Settings
Additional features can be found in the settings menu of the application. Here you can find settings that allow you to customize your routing results for both the departures and connection screen. The best way to let us know what you think about the application is to use the feedback module. This can be found here as well. First click on the emoji that best describe how you feel about the app. And then put in any additional information or ideas or thoughts you may have. Now what is left is just to press send and you will send us an email.
We look forward to hearing from you.
Quantification and Prediction of Impact of Public Events
Current Data4UrbanMobility research results allow for measuring and prediction of spatial impact on road traffic of public events. Connected, affected street segments nearby public events are identified to measure the spatial impact. The approach is depicted in the following figure:
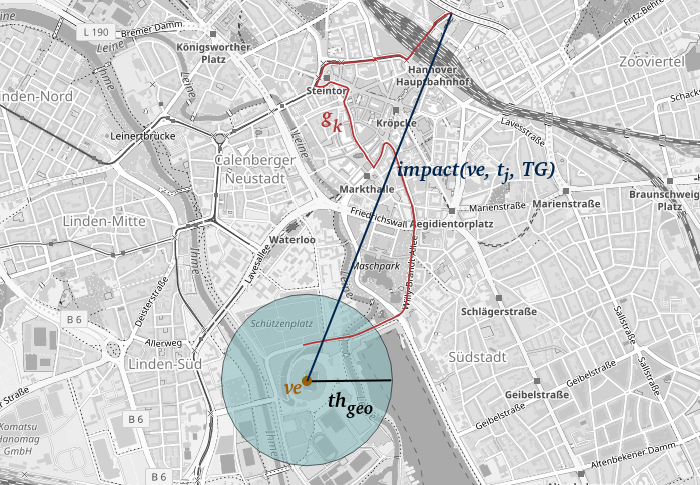
(Karte von https://www.openstreetmap.org)
An event is marked as yellow dot, affected streets in red and the measured impact in dark blue. Moreover, an approach making use of machine learning algorithms was developed to predict the impact determined in this way, resulting an error-reduction of up to 40% when compared to existing state-of-the-art approaches.
D4UM – Platform V1 Released
The first version of the Data4UrbanMobiltiy platform has been released. The platform was designed and implemented following a 3-tier-architecture. The platform provides RESTfull Web services for mobility applications like dashboards or mobile apps. As a demonstration, an interactive map application has been developed that visualizes the spatial impact of public events. The following figure shows a screenshot of the application.
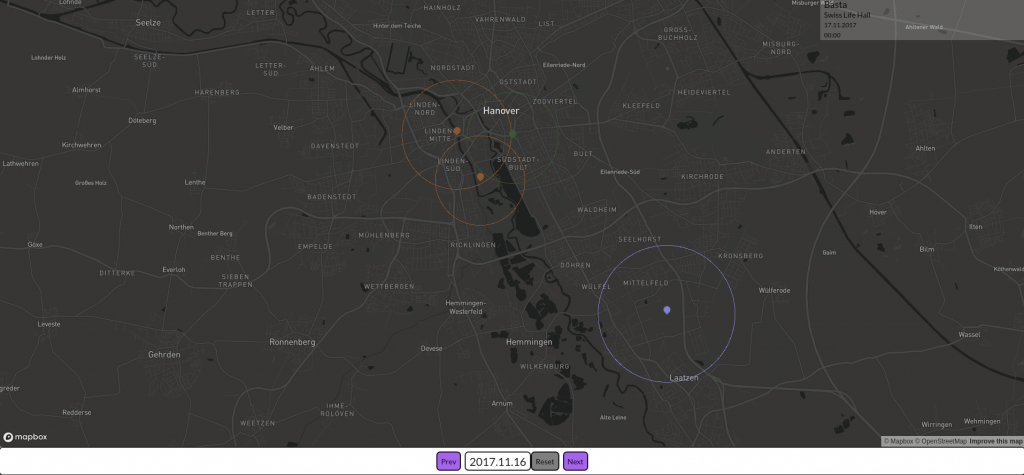
The figure shows 4 public events in the city of Hannover. The colors represent different types of public events (e.g. concerts, fairs, sport events). The circles visualize the spatial impact on road traffic caused by the public events.
Comprehensive Set of Requirements
The Data4UrbanMobility analysis of requirements includes requirements of the application partners Region Hannover (RH) and Wolfsburg AG (WAG) as well as non functional requirements. The requirements were collected by MOMA. The L3S derived research question for data analysis which are based on the requirements of RH and WAG. The research question address especially the information needs of end-users.
The current research questions particularly include
- Automated verification of traffic warnings and prediction of their impact
- Identification of events and prediction of their impact
- Investigation of correlation of road traffic data, public transportation query logs, traffic warnings and twitterfeeds
- Determination of optimal traveling timepoints
Growing Data Collection
ISU create a comprehensive data matrix containing potential source of mobility related data. The Data4UrbanMobility data model describes all project relevant data sets and sets them into context. This makes the data available in a unified manor for both analysis and applications. The selected data sources were transformed according to the Data4UrbanMobility data model by L3S. The data quality of selected data sources (i.e. public transportation query logs and road traffic data) was examined.
Tools for extracting the relevant information from the datasets were developed to enable the integration of the datasets.
- Street and graph extraction from OpenStreetMap
- Bulkloader for public transportation queries
- Integration of “Zentrales Haltestellen Verzeichniss” (central registry of public transportation stops)
The current collection (December 12th 2017) contians
EFA-Logs: 17 million public transportation queries
Road traffic data: 174 thousand street sements with a frequency of 15 minutes
GTFS-data: 90 thousand. public transportation stops, 2.6 thousand routes
Weather: Radolan “Regenraster” (rain grid)
Twitter: 2,5 Mio. Tweets starting at June 2017
OSM: 440 thousand streets
Events: 21 thousand public events (August 14th 2016-July 17th 2018)
Traffic warnings: 13 thousand warning (since June 2017)
Visualization of Public Transportation Information
In order to allow intuitive analytics of public transportation information, the PROJEKTIONISTEN (PROJ) developed a dashboard web application. First prototypes visualize queries addressed to the regional timetable information system EFA (www.efa.de). The prototypes serve as foundations for exploration analyses as well as the implementation of future versions of the dashboard. The following figure shows an integrated visualization of the most frequent origins and destinations of the queries.
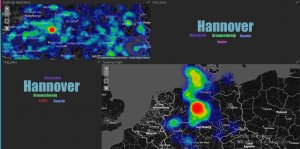
Analysen der EFA-Logs
Analysis of EFA Public Transportation Query Logs
Analyses regarding the impact of public events on public transportation are currently conducted to address early research questions. To this extend, explorative data analyses of the impact of major public events such as football games and medium sized events such as concerts were conducted. Visual analytics were used as a first step towards comprehensive analyses, which show start-like patterns for city center which identify mobility hubs of central importance.
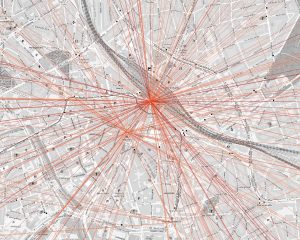
The figure shows the direct connection between origin and destination of public transportation queries. Darker colors correspond to more frequent queried trips. Star-like pattern identify the central train station and the central metro station.
Analyses of single stations reveal weekday dependent patterns.
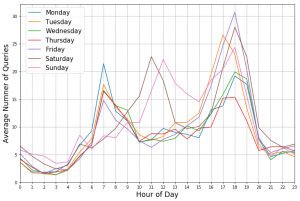
The figure depicts the average number of queries with the destination “Hannover Stadionbrücke”. Differences emerge between Weekends and workdays.
The impact of public events on the queries can be visualized as well.
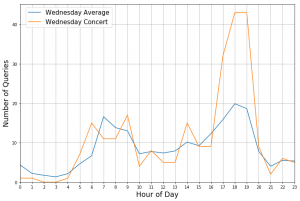
The figure shows the number of queries with the Destination “Hannover Stadionbrücke” for Wednesday, April 26th 2017 (orange) as well as the average number of queries on a Wednesday for the same destination. On this day a concert took place in venue nearby. The concert start at 8 pm. The significant deviations between 5 pm and 7 pm is highly likely to be caused by visitors of the concert. This shows that public transportation queries are a valuable information source to investigate the impact of public events on mobility infrastructure.
- Discovery and Preliminary Characterization of a Third Interstellar Object: 3I/ATLAS. Seligman, Darryl Z.; Micheli, Marco; Farnocchia, Davide; Denneau, Larry; Noonan, John W.; Hsieh, Henry H.; Santana-Ros, Toni; Tonry, John; Auchettl, Katie; Conversi, Luca; Devogèle, Maxime; Faggioli, Laura; Feinstein, Adina D.; Fenucci, Marco; Ferrais, Marin; Frincke, Tessa; Hainaut, Olivier R.; Hart, Kyle; Hoffman, Andrew; Holt, Carrie E.; Hoogendam, Willem B.; Huber, Mark E.; Jehin, Emmanuel; Kareta, Theodore; Keane, Jacqueline V.; Kelley, Michael S. P.; Lister, Tim; Mandt, Kathleen; Marčeta, Dušan; Meech, Karen J.; Miftah, Mohamed Amine; Morgan, Marvin; Ocaña, Francisco; Peña-Asensio, Eloy; Shappee, Benjamin J.; Siverd, Robert J.; Taylor, Aster G.; Tucker, Michael A.; Wainscoat, Richard; Weryk, Robert; Wray, James J.; Yaginuma, Atsuhiro; Yang, Bin; Ye, Quanzhi; Zhang, Qicheng (2025).
- Low-Constraint Ray Optimization for Photogrammetric Shallow Water Bathymetry. Liebender, C.; Meyer, P.; Bleier, M.; Nüchter, A. in The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, XLVIII-2/W10-2025 (2025). 163–168.
- Introduction to Posthuman Convergences. Klumbytė, Goda; Jones, Emily; Braidotti, Rosi G. Klumbytė, E. Jones, R. Braidotti (eds.) (2025). 1–25.
- Posthuman Convergences: Transdisciplinary Methods and Practices. Klumbytė, Goda; Jones, Emily; Braidotti, Rosi (2025, August). 408.
- Posthuman Convergences: Transdisciplinary Methods and Practices. Klumbytė, Goda; Jones, Emily; Braidotti, Rosi (2025, August). 408.
- New Materialist Informatics: New Materialism/Computer Science/Technology Design. Klumbytė, Goda; Draude, Claude G. Klumbytė, E. Jones, R. Braidotti (eds.) (2025). 184–216.
- New Materialist Informatics: New Materialism/Computer Science/Technology Design. Klumbytė, Goda; Draude, Claude G. Klumbytė, E. Jones, R. Braidotti (eds.) (2025). 184–216.
- New Materialist Informatics: New Materialism/Computer Science/Technology Design. Klumbytė, Goda; Draude, Claude G. Klumbytė, E. Jones, R. Braidotti (eds.) (2025). 184–216.
- Posthuman Convergences: Transdisciplinary Methods and Practices. Klumbytė, Goda; Jones, Emily; Braidotti, Rosi (2025, August). 408.
- Posthuman Convergences. Transdisciplinary Methods and Practices. Klumbytė, Goda; Jones, Emily; Braidotti, Rosi (2025, August). 408.
- Posthuman Convergences. Transdisciplinary Methods and Practices. Klumbytė, Goda; Jones, Emily; Braidotti, Rosi (2025, August). 408.
- Twist-tuned quantum criticality in moiré bilayer graphene. Biedermann, Jan; Janssen, Lukas (2025). 112(4) L041109.
- Robustness of Question Answering Systems in the Biomedical Domain: a study of the BioASQ dataset. Reeves, Andrew; Dong, Hang (2025). 247–252.
- Introduction to Posthuman Convergences. Klumbytė, Goda; Jones, Emily; Braidotti, Rosi G. Klumbytė, E. Jones, R. Braidotti (eds.) (2025). 1–25.
- Applying Cfahp to Explore the Key Models of Semiconductor Pre-Sales. Kao, Fei-Hon; Hsieh, Chia-Hsiang; Pei, Wen in Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications, R. Mizoguchi, P. Dillenbourg, Z. Zhu (eds.) (2025). (Vol. 151) 149–156.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Based Plant Monitoring. Rampure, Shrutika C; P, Bhavyashree S; T, Rakshitha B (2025).
- A Tutorial on Data-Driven Quality of Experience Modeling with Explainable Artificial Intelligence. Wehner, Nikolas; Seufert, Anika; Hoßfeld, Tobias; Seufert, Michael (2025).
- Jahresbericht 2024. van Ackeren, Janine (2025). 90–92.
- Security and Privacy of Current and Emerging IoT Devices and Systems (Dagstuhl Seminar 2431). Crispo, Bruno; Dmitrienko, Alexandra; Tsudik, Gene; Xu, Wenyuan; Sendner, Christoph (2025).
- Sibai: A Few-Shot Meta-Classifier for Poisoning Detection in Federated Learning. Götz, Melanie; Krauß, Torsten; Dmitrienko, Alexandra (2025).
- TwinBreak: Jailbreaking LLM Security Alignments based on Twin Prompts. Krauß, Torsten; Dashtbani, Hamid; Dmitrienko, Alexandra (2025).
- Jahresbericht 2024. van Ackeren, Janine (2025). 90–92.
- A Comprehensive Survey on Vector Database: Storage and Retrieval Technique, Challenge. Ma, Le; Zhang, Ran; Han, Yikun; Yu, Shirui; Wang, Zaitian; Ning, Zhiyuan; Zhang, Jinghan; Xu, Ping; Li, Pengjiang; Ju, Wei; Chen, Chong; Wang, Dongjie; Liu, Kunpeng; Wang, Pengyang; Wang, Pengfei; Fu, Yanjie; Liu, Chunjiang; Zhou, Yuanchun; Lu, Chang-Tien (2025).
- Monadic ULLER: A Unified Categorical Semantics of the Neurosymbolic ULLER Framework. Schellhorn, Daniel; Mossakowski, Till G. Eleonora, P. Hitzler, E. van Krieken (eds.) (2025).
- A Cluster-Based Trusted Secure Multipath Routing Protocol for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. Bartwal, Himanshu; Sivaraman, Himani; Kumar, Jogendra N. Meghanathan (ed.) (2025). (Vol. 17) 89–109.
- Introduction to Posthuman Convergences. Klumbytė, Goda; Jones, Emily; Braidotti, Rosi G. Klumbytė, E. Jones, R. Braidotti (eds.) (2025). 1–25.
- Conclusion: (Infra)Structures for the Convergences. Klumbytė, Goda; Jones, Emily; Braidotti, Rosi G. Klumbytė, E. Jones, R. Braidotti (eds.) (2025). 365–278.
- The evolution of bone-eating worm diversity in the Upper Cretaceous Chalk Group of the United Kingdom. Jamison-Todd, Sarah; Witts, James D.; Jones, Marc E. H.; Tangunan, Deborah; Chandler, Kim; Bown, Paul; Twitchett, Richard J. (2025). 20(4) 1–20.
- Conclusion: (Infra)Structures for the Convergences. Klumbytė, Goda; Jones, Emily; Braidotti, Rosi G. Klumbytė, E. Jones, R. Braidotti (eds.) (2025). 365–278.
- Frequently Used References For Atomic Data In X-ray Spectroscopy. Hell, N.; Brown, G. V.; Eckart, M. E.; Fairchild, A. J.; Kilbourne, C. A.; Leutenegger, M. A.; Porter, F. S.; Witthoeft, M. C. (2025).
- Leveraging Large Language Models for Automated Definition Extraction with TaxoMatic A Case Study on Media Bias. Spinde, Timo; Lin, Luyang; Hinterreiter, Smi; Echizen, Isao (2025). (Vol. 19)
- NewsUnfold: Creating a News-Reading Application That Indicates Linguistic Media Bias and Collects Feedback. Hinterreiter, Smi; Wessel, Martin Paul; Schliski, Fabian; Echizen, Isao; Latoschik, Marc Erich; Spinde, Timo J. An, Y.-R. Lin, Y. Mejova, E. Mustafaraj, J. Kulshrestha, I. Weber (eds.) (2025). 804–822.
- CRS Arena: Crowdsourced Benchmarking of Conversational Recommender Systems. Bernard, Nolwenn; Joko, Hideaki; Hasibi, Faegheh; Balog, Krisztian in WSDM ’25 (2025). 1028–1031.
- Heat Storage Pattern Linked to the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation Slowdown. Ren, Qiuping; Li, Yuanlong; Hu, Shineng; Xie, Shang-Ping; Lyu, Yilong; Wang, Fan (2025). 52(13) e2025GL116801.
- SimLab: A Platform for Simulation-based Evaluation of Conversational Information Access Systems. Bernard, Nolwenn; Suresh, Sharath Chandra Etagi; Balog, Krisztian; Zhai, ChengXiang (2025).
- VIA-VR: A Platform to Streamline the Development of Virtual Reality Serious Games for Healthcare. Truman, Samuel; Von Mammen, Sebastian (2025). 463–468.
- VIA-VR: A Platform to Streamline the Development of Virtual Reality Serious Games for Healthcare. Truman, Samuel; Von Mammen, Sebastian (2025). 463–468.
- Aggregation-Free Uncertainty Estimation for CTC-Based Automatic Speech Recognition. Rumberg, Lars; Gebauer, Christopher; Ostermann, Jörn (2025).
- A Survey of Non-Learning-Based Abstractions for Sequential Decision-Making. Schmöcker, Robin; Dockhorn, Alexander (2025). 13 100808–100830.
- Cascade - A sequential ensemble method for continuous control tasks. Schmöcker, Robin; Dockhorn, Alexander (2025).
- Time-critical and confidence-based abstraction dropping methods. Schmöcker, Lennart Kampmann Robin (2025).
- Cell Tracking according to Biological Needs - Strong Mitosis-aware Multi-Hypothesis Tracker with Aleatoric Uncertainty. Kaiser, Timo; Schier, Maximilian; Rosenhahn, Bodo (2025).
- Pruning by Block Benefit: Exploring the Properties of Vision Transformer Blocks during Domain Adaptation. Glandorf, Patrick; Bodo, Rosenhahn (2025).
- VaMEx3-MarsSymphony: Technology Demonstration for Martian exploration swarm robotics. Riegler, Clemens; Kayal, Hakan; Maurer, Andreas; Mutter, Julian; Neuhaus, Lennart; Stadler, Joshua (2025).
- The Resound Sphere: Co-Exploring Alternatives for Community Remote Practice of Faith. Wolf, Sara; Chatting, David; Morris, Ben; Claisse, Caro; Durrant, Abigail C. (2025).
- High-pass noise suppression in the mosquito auditory system. Lapshin, Dmitry N.; Vorontsov, Dmitry D. (2025).
- The Resound Sphere: Co-Exploring Alternatives for Community Remote Practice of Faith. Wolf, Sara; Chatting, David; Morris, Ben; Claisse, Caro; Durrant, Abigail C. (2025).
- Assessment of Abrupt Shifts in CMIP6 Models Using Edge Detection. Terpstra, Sjoerd; Falkena, Swinda K. J.; Bastiaansen, Robbin; Bathiany, Sebastian; Dijkstra, Henk A.; von der Heydt, Anna S. (2025). 6(3) e2025AV001698.
- Levels of Automation Revisited: Standardizing Human-Machine Interaction with Process Patterns. Janiesch, Christian; Ciftci, Seyyid A. (2025).
- Sustainable, Situation-Aware Multi Objective Spatial Load Scheduling for Data Centers. Schiller, Jonas; Pruckner, Marco in E-Energy ’25 (2025). 874–881.
- Conclusion: (Infra)Structures for the Convergences. Klumbytė, Goda; Jones, Emily; Braidotti, Rosi G. Klumbytė, E. Jones, R. Braidotti (eds.) (2025). 365–278.
- News Ninja: Gamified Annotation of Linguistic Bias in Online News. Hinterreiter, Smi; Spinde, Timo; Oberdörfer, Sebastian; Echizen, Isao; Latoschik, Marc Erich (2024). 8(CHI PLAY, Article 327)
- Alice in Wonderland: Simple Tasks Showing Complete Reasoning Breakdown in State-Of-the-Art Large Language Models. Nezhurina, Marianna; Cipolina-Kun, Lucia; Cherti, Mehdi; Jitsev, Jenia (2024, June).
- The Optically Thick Rotating Magnetic Wind from a Massive White Dwarf Merger Product. II. Axisymmetric Magnetohydrodynamic Simulations. Zhong, Yici; Kashiyama, Kazumi; Takasao, Shinsuke; Shigeyama, Toshikazu; Fujisawa, Kotaro (2024). 963(1) 26.
- Can Large Language Models Understand Symbolic Graphics Programs?. Qiu, Zeju; Liu, Weiyang; Feng, Haiwen; Liu, Zhen; Xiao, Tim Z.; Collins, Katherine M.; Tenenbaum, Joshua B.; Weller, Adrian; Black, Michael J.; Schölkopf, Bernhard (2024).
- Towards a Formal Characterization of User Simulation Objectives in Conversational Information Access. Bernard, Nolwenn; Balog, Krisztian in ICTIR ’24 (2024). 185–193.
- PKG API: A Tool for Personal Knowledge Graph Management. Bernard, Nolwenn; Kostric, Ivica; Łajewska, Weronika; Balog, Krisztian; Galuščáková, Petra; Setty, Vinay; Skjæveland, Martin G. in WWW ’24 (2024). 1051–1054.
- An Ecosystem for Personal Knowledge Graphs: A Survey and Research Roadmap. Skjæveland, Martin G.; Balog, Krisztian; Bernard, Nolwenn; Lajewska, Weronika; Linjordet, Trond (2024). 55–69.
- Identifying Breakdowns in Conversational Recommender Systems using User Simulation. Bernard, Nolwenn; Balog, Krisztian in CUI ’24 (2024). 1–10.
- IAI MovieBot 2.0: An Enhanced Research Platform with Trainable Neural Components and Transparent User Modeling. Bernard, Nolwenn; Kostric, Ivica; Balog, Krisztian in WSDM ’24 (2024). 1042–1045.
- Leveraging User Simulation to Develop and Evaluate Conversational Information Access Agents. Bernard, Nolwenn in WSDM ’24 (2024). 1136–1138.
- Digital labour platforms and social dialogue at EU level: How new players redefine actors and their roles and what this means for collective bargaining. Piasna, Agnieszka (2024). 58(4) 568–582.
- Naselja Bosne i Hercegovine kroz popise stanovništva u periodu 1879.-1991. Suljić, Alija (2024).
- The recurrent nova T CrB had prior eruptions observed near December 1787 and October 1217 AD. Schaefer, Bradley E (2023). 54(4) 436–455.
- A Systematic Review of Fairness, Accountability, Transparency and Ethics in Information Retrieval. Bernard, Nolwenn; Balog, Krisztian (2023).
- MG-ShopDial: A Multi-Goal Conversational Dataset for e-Commerce. Bernard, Nolwenn; Balog, Krisztian in SIGIR ’23 (2023). 2775–2785.
- On Correlated Stock Market Time Series Generation. Masi, Giuseppe; Prata, Matteo; Conti, Michele; Bartolini, Novella; Vyetrenko, Svitlana in ICAIF ’23 (2023). 524–532.
- Element abundance patterns in stars indicate fission of nuclei heavier than uranium. Roederer, Ian U; Vassh, Nicole; Holmbeck, Erika M; Mumpower, Matthew R; Surman, Rebecca; Cowan, John J; Beers, Timothy C; Ezzeddine, Rana; Frebel, Anna; Hansen, Terese T; Placco, Vinicius M; Sakari, Charli M (2023). 382(6675) 1177–1180.
- Refined Fuzzy Profile Matching. Rácz, Gábor; Sali, Attila; Schewe, Klaus-Dieter (2023). 26(2) 243–266.
- Outflows from the Youngest Stars are Mostly Molecular. Ray, T P; McCaughrean, M J; Caratti o Garatti, A; Kavanagh, P J; Justtanont, K; van Dishoeck, E F; Reitsma, M; Beuther, H; Francis, L; Gieser, C; Klaassen, P; Perotti, G; Tychoniec, L; van Gelder, M; Colina, L; Greve, Th R; Güdel, M; Henning, Th; Lagage, P O; Ãstlin, G; Vandenbussche, B; Waelkens, C; Wright, G (2023).
- Are Emergent Abilities of Large Language Models a Mirage?. Schaeffer, Rylan; Miranda, Brando; Koyejo, Sanmi (2023). 55565–55581.
- Can Transformers Learn to Solve Problems Recursively?. Zhang, Shizhuo Dylan; Tigges, Curt; Biderman, Stella; Raginsky, Maxim; Ringer, Talia (2023).
- In-Depth Analysis and Systematic Literature Review on Risk Based Access Control in Cloud. Sadia Hussain, M. Hasan Islam; Abbas, Haider (M. H. I. Sadia Hussain; H. Abbas, eds.) (2022). 12(9) 1–22.
- Beyond the Imitation Game: Quantifying and extrapolating the capabilities of language models. Srivastava, Aarohi; Rastogi, Abhinav; Rao, Abhishek; Shoeb, Abu Awal Md; Abid, Abubakar; Fisch, Adam; Brown, Adam R; Santoro, Adam; Gupta, Aditya; Garriga-Alonso, Adri�; Kluska, Agnieszka; Lewkowycz, Aitor; Agarwal, Akshat; Power, Alethea; Ray, Alex; Warstadt, Alex; Kocurek, Alexander W; Safaya, Ali; Tazarv, Ali; Xiang, Alice; Parrish, Alicia; Nie, Allen; Hussain, Aman; Askell, Amanda; Dsouza, Amanda; Slone, Ambrose; Rahane, Ameet; Iyer, Anantharaman S; Andreassen, Anders; Madotto, Andrea; Santilli, Andrea; Stuhlmüller, Andreas; Dai, Andrew; La, Andrew; Lampinen, Andrew; Zou, Andy; Jiang, Angela; Chen, Angelica; Vuong, Anh; Gupta, Animesh; Gottardi, Anna; Norelli, Antonio; Venkatesh, Anu; Gholamidavoodi, Arash; Tabassum, Arfa; Menezes, Arul; Kirubarajan, Arun; Mullokandov, Asher; Sabharwal, Ashish; Herrick, Austin; Efrat, Avia; Erdem, Aykut; Karakaş, Ayla; Roberts, B Ryan; Loe, Bao Sheng; Zoph, Barret; Bojanowski, Bartłomiej; Özyurt, Batuhan; Hedayatnia, Behnam; Neyshabur, Behnam; Inden, Benjamin; Stein, Benno; Ekmekci, Berk; Lin, Bill Yuchen; Howald, Blake; Orinion, Bryan; Diao, Cameron; Dour, Cameron; Stinson, Catherine; Argueta, Cedrick; Ramírez, César Ferri; Singh, Chandan; Rathkopf, Charles; Meng, Chenlin; Baral, Chitta; Wu, Chiyu; Callison-Burch, Chris; Waites, Chris; Voigt, Christian; Manning, Christopher D; Potts, Christopher; Ramirez, Cindy; Rivera, Clara E; Siro, Clemencia; Raffel, Colin; Ashcraft, Courtney; Garbacea, Cristina; Sileo, Damien; Garrette, Dan; Hendrycks, Dan; Kilman, Dan; Roth, Dan; Freeman, Daniel; Khashabi, Daniel; Levy, Daniel; González, Daniel Moseguí; Perszyk, Danielle; Hernandez, Danny; Chen, Danqi; Ippolito, Daphne; Gilboa, Dar; Dohan, David; Drakard, David; Jurgens, David; Datta, Debajyoti; Ganguli, Deep; Emelin, Denis; Kleyko, Denis; Yuret, Deniz; Chen, Derek; Tam, Derek; Hupkes, Dieuwke; Misra, Diganta; Buzan, Dilyar; Mollo, Dimitri Coelho; Yang, Diyi; Lee, Dong-Ho; Schrader, Dylan; Shutova, Ekaterina; Cubuk, Ekin Dogus; Segal, Elad; Hagerman, Eleanor; Barnes, Elizabeth; Donoway, Elizabeth; Pavlick, Ellie; Rodola, Emanuele; Lam, Emma; Chu, Eric; Tang, Eric; Erdem, Erkut; Chang, Ernie; Chi, Ethan A; Dyer, Ethan; Jerzak, Ethan; Kim, Ethan; Manyasi, Eunice Engefu; Zheltonozhskii, Evgenii; Xia, Fanyue; Siar, Fatemeh; Martínez-Plumed, Fernando; Happé, Francesca; Chollet, Francois; Rong, Frieda; Mishra, Gaurav; Winata, Genta Indra; de Melo, Gerard; Kruszewski, Germán; Parascandolo, Giambattista; Mariani, Giorgio; Wang, Gloria; Jaimovitch-López, Gonzalo; Betz, Gregor; Gur-Ari, Guy; Galijasevic, Hana; Kim, Hannah; Rashkin, Hannah; Hajishirzi, Hannaneh; Mehta, Harsh; Bogar, Hayden; Shevlin, Henry; Schütze, Hinrich; Yakura, Hiromu; Zhang, Hongming; Wong, Hugh Mee; Ng, Ian; Noble, Isaac; Jumelet, Jaap; Geissinger, Jack; Kernion, Jackson; Hilton, Jacob; Lee, Jaehoon; Fisac, Jaime Fernández; Simon, James B; Koppel, James; Zheng, James; Zou, James; Kocoń, Jan; Thompson, Jana; Wingfield, Janelle; Kaplan, Jared; Radom, Jarema; Sohl-Dickstein, Jascha; Phang, Jason; Wei, Jason; Yosinski, Jason; Novikova, Jekaterina; Bosscher, Jelle; Marsh, Jennifer; Kim, Jeremy; Taal, Jeroen; Engel, Jesse; Alabi, Jesujoba; Xu, Jiacheng; Song, Jiaming; Tang, Jillian; Waweru, Joan; Burden, John; Miller, John; Balis, John U; Batchelder, Jonathan; Berant, Jonathan; Frohberg, Jörg; Rozen, Jos; Hernandez-Orallo, Jose; Boudeman, Joseph; Guerr, Joseph; Jones, Joseph; Tenenbaum, Joshua B; Rule, Joshua S; Chua, Joyce; Kanclerz, Kamil; Livescu, Karen; Krauth, Karl; Gopalakrishnan, Karthik; Ignatyeva, Katerina; Markert, Katja; Dhole, Kaustubh D; Gimpel, Kevin; Omondi, Kevin; Mathewson, Kory; Chiafullo, Kristen; Shkaruta, Ksenia; Shridhar, Kumar; McDonell, Kyle; Richardson, Kyle; Reynolds, Laria; Gao, Leo; Zhang, Li; Dugan, Liam; Qin, Lianhui; Contreras-Ochando, Lidia; Morency, Louis-Philippe; Moschella, Luca; Lam, Lucas; Noble, Lucy; Schmidt, Ludwig; He, Luheng; Colón, Luis Oliveros; Metz, Luke; Şenel, Lütfi Kerem; Bosma, Maarten; Sap, Maarten; ter Hoeve, Maartje; Farooqi, Maheen; Faruqui, Manaal; Mazeika, Mantas; Baturan, Marco; Marelli, Marco; Maru, Marco; Quintana, Maria Jose Ramírez; Tolkiehn, Marie; Giulianelli, Mario; Lewis, Martha; Potthast, Martin; Leavitt, Matthew L; Hagen, Matthias; Schubert, Mátyás; Baitemirova, Medina Orduna; Arnaud, Melody; McElrath, Melvin; Yee, Michael A; Cohen, Michael; Gu, Michael; Ivanitskiy, Michael; Starritt, Michael; Strube, Michael; Swędrowski, Michał; Bevilacqua, Michele; Yasunaga, Michihiro; Kale, Mihir; Cain, Mike; Xu, Mimee; Suzgun, Mirac; Walker, Mitch; Tiwari, Mo; Bansal, Mohit; Aminnaseri, Moin; Geva, Mor; Gheini, Mozhdeh; T, Mukund Varma; Peng, Nanyun; Chi, Nathan A; Lee, Nayeon; Krakover, Neta Gur-Ari; Cameron, Nicholas; Roberts, Nicholas; Doiron, Nick; Martinez, Nicole; Nangia, Nikita; Deckers, Niklas; Muennighoff, Niklas; Keskar, Nitish Shirish; Iyer, Niveditha S; Constant, Noah; Fiedel, Noah; Wen, Nuan; Zhang, Oliver; Agha, Omar; Elbaghdadi, Omar; Levy, Omer; Evans, Owain; Casares, Pablo Antonio Moreno; Doshi, Parth; Fung, Pascale; Liang, Paul Pu; Vicol, Paul; Alipoormolabashi, Pegah; Liao, Peiyuan; Liang, Percy; Chang, Peter; Eckersley, Peter; Htut, Phu Mon; Hwang, Pinyu; Miłkowski, Piotr; Patil, Piyush; Pezeshkpour, Pouya; Oli, Priti; Mei, Qiaozhu; Lyu, Qing; Chen, Qinlang; Banjade, Rabin; Rudolph, Rachel Etta; Gabriel, Raefer; Habacker, Rahel; Risco, Ramon; Millière, Raphaël; Garg, Rhythm; Barnes, Richard; Saurous, Rif A; Arakawa, Riku; Raymaekers, Robbe; Frank, Robert; Sikand, Rohan; Novak, Roman; Sitelew, Roman; LeBras, Ronan; Liu, Rosanne; Jacobs, Rowan; Zhang, Rui; Salakhutdinov, Ruslan; Chi, Ryan; Lee, Ryan; Stovall, Ryan; Teehan, Ryan; Yang, Rylan; Singh, Sahib; Mohammad, Saif M; Anand, Sajant; Dillavou, Sam; Shleifer, Sam; Wiseman, Sam; Gruetter, Samuel; Bowman, Samuel R; Schoenholz, Samuel S; Han, Sanghyun; Kwatra, Sanjeev; Rous, Sarah A; Ghazarian, Sarik; Ghosh, Sayan; Casey, Sean; Bischoff, Sebastian; Gehrmann, Sebastian; Schuster, Sebastian; Sadeghi, Sepideh; Hamdan, Shadi; Zhou, Sharon; Srivastava, Shashank; Shi, Sherry; Singh, Shikhar; Asaadi, Shima; Gu, Shixiang Shane; Pachchigar, Shubh; Toshniwal, Shubham; Upadhyay, Shyam; Shyamolima; Debnath; Shakeri, Siamak; Thormeyer, Simon; Melzi, Simone; Reddy, Siva; Makini, Sneha Priscilla; Lee, Soo-Hwan; Torene, Spencer; Hatwar, Sriharsha; Dehaene, Stanislas; Divic, Stefan; Ermon, Stefano; Biderman, Stella; Lin, Stephanie; Prasad, Stephen; Piantadosi, Steven T; Shieber, Stuart M; Misherghi, Summer; Kiritchenko, Svetlana; Mishra, Swaroop; Linzen, Tal; Schuster, Tal; Li, Tao; Yu, Tao; Ali, Tariq; Hashimoto, Tatsu; Wu, Te-Lin; Desbordes, Théo; Rothschild, Theodore; Phan, Thomas; Wang, Tianle; Nkinyili, Tiberius; Schick, Timo; Kornev, Timofei; Tunduny, Titus; Gerstenberg, Tobias; Chang, Trenton; Neeraj, Trishala; Khot, Tushar; Shultz, Tyler; Shaham, Uri; Misra, Vedant; Demberg, Vera; Nyamai, Victoria; Raunak, Vikas; Ramasesh, Vinay; Prabhu, Vinay Uday; Padmakumar, Vishakh; Srikumar, Vivek; Fedus, William; Saunders, William; Zhang, William; Vossen, Wout; Ren, Xiang; Tong, Xiaoyu; Zhao, Xinran; Wu, Xinyi; Shen, Xudong; Yaghoobzadeh, Yadollah; Lakretz, Yair; Song, Yangqiu; Bahri, Yasaman; Choi, Yejin; Yang, Yichi; Hao, Yiding; Chen, Yifu; Belinkov, Yonatan; Hou, Yu; Hou, Yufang; Bai, Yuntao; Seid, Zachary; Zhao, Zhuoye; Wang, Zijian; Wang, Zijie J; Wang, Zirui; Wu, Ziyi (2022).
- DAGFiNN: A Conversational Conference Assistant. Kostric, Ivica; Balog, Krisztian; Aresvik, Tollov Alexander; Bernard, Nolwenn; Dorheim, Eyvinn Thu; Hantula, Pholit; Havn-Sorensen, Sander; Henriksen, Rune; Hosseini, Hengameh; Khlybova, Ekaterina; Lajewska, Weronika; Mosand, Sindre Ekrheim; Orujova, Narmin in RecSys ’22 (2022). 628–631.
- A Gamified Approach To Automatically Detect Biased Wording And Train Critical Reading. Hinterreiter, Smi (2021).
- How to pretrain an efficient cross-disciplinary language model: The ScilitBERT use case. de la Broise, Jean-Baptiste; Bernard, Nolwenn; Dubuc, Jean-Philippe; Perlato, Andrea; Latard, Bastien in ICITR ’21 (2021). 1–6.
- Analytical, Statistical Approximate Solution of Dissipative and Nondissipative Binary-Single Stellar Encounters. Ginat, Yonadav Barry; Perets, Hagai B (2021). 11(3) 31020.
- Physical Properties of Trojan and Centaur Asteroids. Barueci, M A; Cruikshank, D P; Mottola, S; Lazzarin, M (2021).
- Moisture Sorption Isotherms and Isotherm Model Performance Evaluation for Food and Agricultural Products. Aviara, Ndubisi A. G. Kyzas, N. Lazaridis (eds.) (2020).
- Knowledge-Based Categorization of Scientific Articles for Similarity Predictions. Bernard, Nolwenn; Weber, Jonathan; Forestier, Germain; Hassenforder, Michel; Latard, Bastien in TPDL ’20 (2020). 147–160.
- How runaway stars boost galactic outflows. Andersson, Eric P; Agertz, Oscar; Renaud, Florent (2020). 494(3) 3328–3341.
- In Search of Actionable Patterns of Lowest Cost - A Scalable Graph Method. Tzacheva, Angelina A. (2018). 10(6) 1–19.
- The prediction of moisture adsorption isotherm for commercial sodium bicarbonate powder. Clément, Yué Bi Yao; Djakalia, Bouatene; Clément, Akmel Djédjro; Kablan, Tano (2018). 9(3) 1829–1836.
- Large granulation cells on the surface of the giant star π1 Gruis. Paladini, C.; Baron, F.; Jorissen, A.; Le Bouquin, J.-B.; Freytag, B.; Van Eck, S.; Wittkowski, M.; Hron, J.; Chiavassa, A.; Berger, J.-P.; Siopis, C.; Mayer, A.; Sadowski, G.; Kravchenko, K.; Shetye, S.; Kerschbaum, F.; Kluska, J.; Ramstedt, S. (2018). 553(7688) 310–312.
- Global 3D radiation-hydrodynamics models of AGB stars: Effects of convection and radial pulsations on atmospheric structures. Freytag, B.; Liljegren, S.; Höfner, S. (2017). 600 A137.
- A Comparison of Four Series of CISCO Network Processors. Sadaf Abaei Senejani1, Hossein Karimi2 (2016).
- FLARES ON A-TYPE STARS: EVIDENCE FOR HEATING OF SOLAR CORONA BY NANOFLARES?. Švanda, Michal; Karlický, Marian (2016). 831(1) 9.
- Radial velocities of K–M dwarfs and local stellar kinematics. Sperauskas, J; Bartašiūtė, S; Boyle, R P; Deveikis, V; Raudeliūnas, S; Upgren, A R (2016). 596 A116-A116.
- Leksičke posebnosti Milićevićevih publikacija Budimir, Irina (2015).
- Sorption properties of sodium bicarbonate. Walawska, Barbara; Szymanek, Arkadiusz; Pajdak, Anna; Nowak, Marzena; Hala, Bożena (2012). (Vol. 66) 1169–1176.
- Effects of capillary condensation on the caking of bulk sucrose. Billings, S.W.; Bronlund, J.E.; Paterson, A.H.J. (2006). 77(4) 887–895.
- Water activity in concentrated sucrose solutions and its consequences for the availability of water in the film of syrup surrounding the sugar crystal. Starzak, Maciej; Mathlouthi, Mohamed (2002). 127 175–185.
- PISA 2000: Dokumentation der Erhebungsinstrumente Kunter, Mareike; Schümer, Gundel; Artelt, Cordula; Baumert, Jürgen; Klieme, Eckhard; Neubrand, Michael; Prenzel, Manfred; Schiefele, Ulrich; Schneider, Wolfgang; Stanat, Petra; Tillmann, Klaus-Jürgen; Weiß, Manfred (2002).
- The All-Variable Binary WR140 (HD 193793, WCT+O4, P=7.94 yr). Van Der Hucht, K.A; Williams, P.M; Pollock, A.M.T; Hidayat, B.; McCain, C.F; Spoelstra, T.A.Th; Wamsteker, W.M (1991). 143 251–251.
- Advanced Combinatorics Comtet, Louis (1974). Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht.
- Probability Breiman, Leo in Addison-Wesley Series in Statistics (1968). Addison-Wesley, Reading, Massachusetts.
- Differential thermal analysis of the decomposition of sodium bicarbonate and its simple double salts. Edward M. Barall, II; Rogers, L.B. (1966). 28(1) 41–51.
- Stellar Atmospheres; a Contribution to the Observational Study of High Temperature in the Reversing Layers of Stars. Payne, Cecilia Helena (1925).
- On the equilibrium of the Sun’s atmosphere. Schwarzschild, K. (1906). 195 41–53.