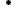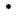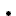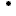
Forecasting of the Traffic Situation in the Hannover Region
The main requirement of road traffic participants is to know the current traffic situation. Such data is typically obtained from routing services where the time of many different individual trips is taken into account.
In the context of Data4UrbanMobility tools were developed that allow to predict the traffic situation based on such time series data. The following figure presents an interface to visualize typical time series patterns as well as outliers present in the data:
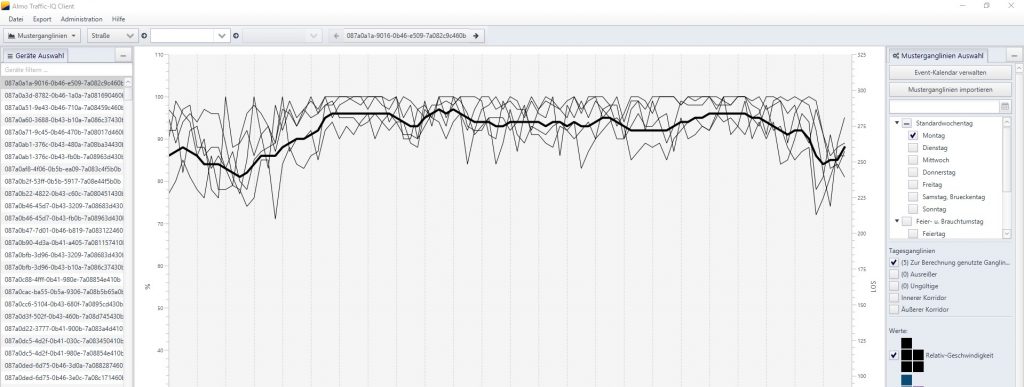
The prediction of the traffic situation is made available in the form of a map based interface for the end user:
Data4UrbanMobility Data Protection Regulation
The work on the Data4UrbanMobility data protection regulation is completed. The document is publicly available and can be found here.
First Version of MiC-App Available
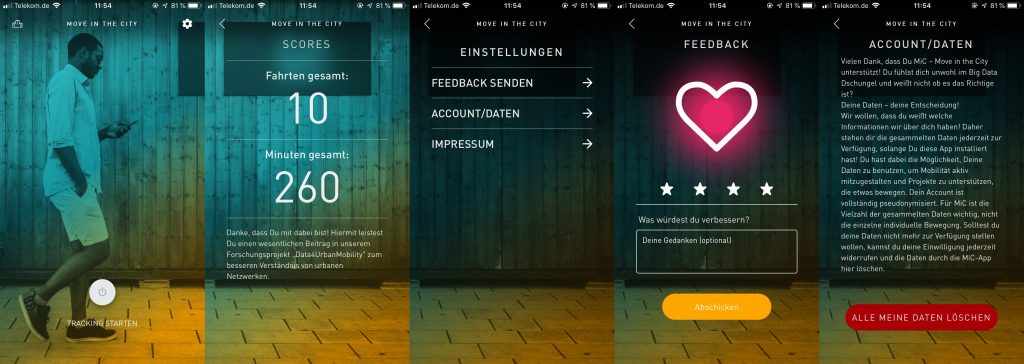
A first version of the novel MiC-App (Move in the City) App is now available for D4UM-associates as well as a protected group of public users. The mobile MiC-App is a tool to gather data.
MiC was developed by the Institute for Sustainable Urbanism at the University of Braunschweig and the Projektionisten GmbH. MiC links the growing awareness of digital citizen rights with the potential of evaluation big datasets. Therefore MiC gives the opportunity to citizen to actively participate in a citizen science project to take part in the development of the mobility of the feature.
MiC gathers data of the users movement, where the user has the about which data should be recorded. All data is pseudonymised such that the privacy of the contributing citizen is ensured.
Current Status:
In the first version of the app, the user can easily start and end the tracking of his/her movement. It is worth to point out, that the user decides when he is tracked and when not. A summary of his/her activity is available for the user as well as the opportunity to issue feedback or even delete all of his contributed data.
Updated System with Dashboard V2
With the new version of our system, the dashboard will provide even more insights into the impact of public events on the traffic situation.
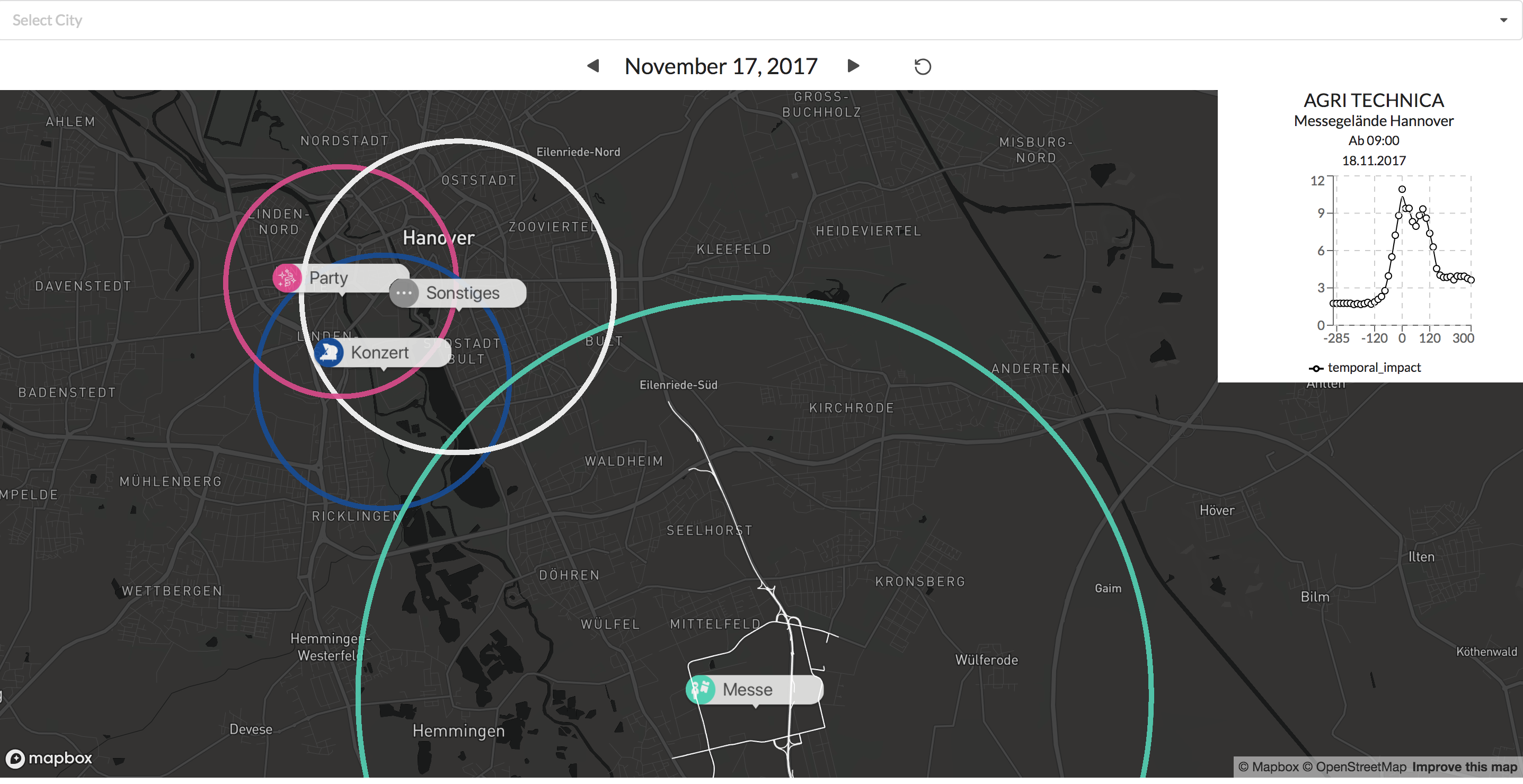
The coloring and labels let us easily distinguish between the different type of events. By clicking on the label we show the typically affected subgraph for that event type. This allows the user to check what specific routes are typically affected by an event at that location.
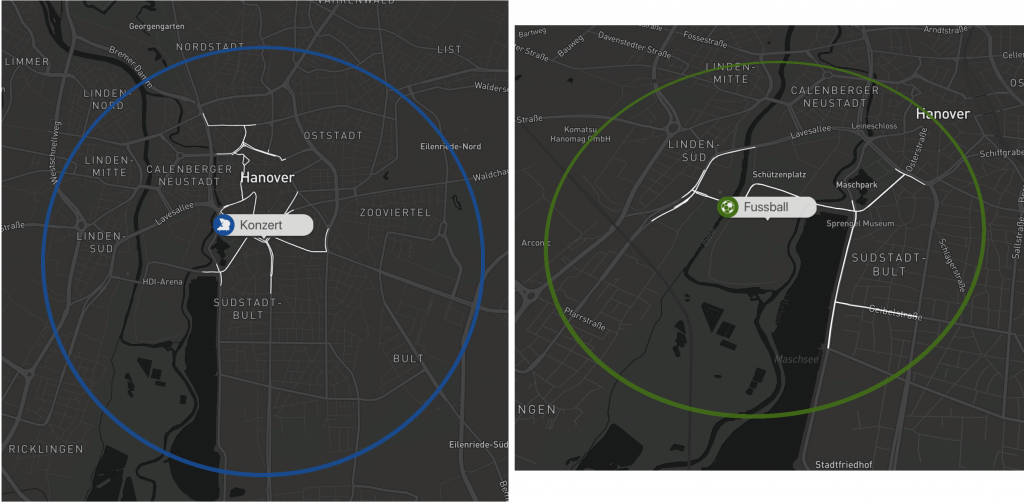
Examples: Visualisation of a concert and a football game.
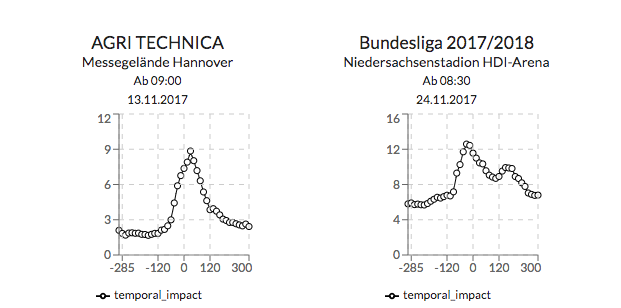
In addition, the graph at the top right gives additional information on how big the impact around the events start time tends to be.
{API}
We enriched the api endpoints with additional information from the data models that were developed as part of the research efforts.
D4UM App Version 1.0
We just released the first Version of the D4UM App. Every project member now has access to the application and can try out its features. Let’s quickly go over some of its main features.
The EFA integration (EFA is a routing engine covering Lower Saxony and Bremen ) allows for quick access to tip information using all available public transport options. Our focus, when designing the application, was on quick and easy navigation to provide a simple and easy to use trip planning tool.
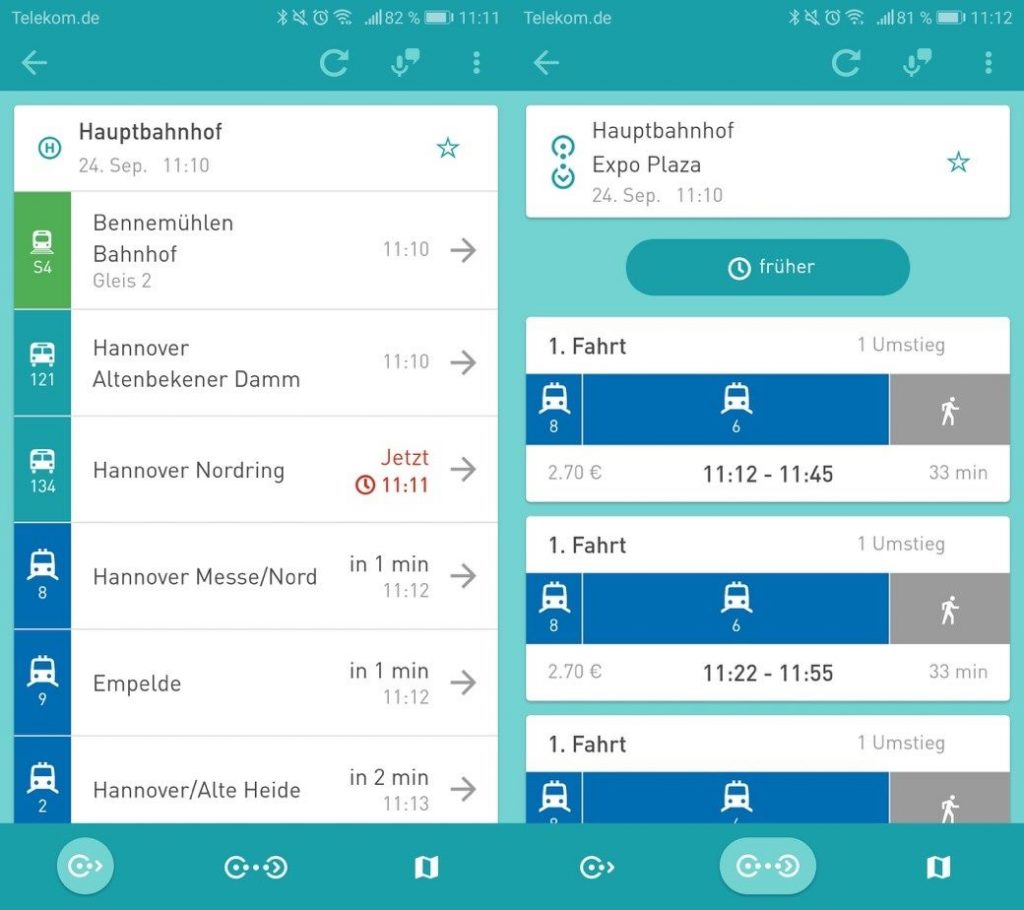
Departures and Connections
On the departure screen we show the user the closes stops for public transportation in his immediate vicinity. On the connection screen the user can fill in his desired starting location( either an address or an existing stop ) and destination and query for what connections are available to him. The provided information contains real time data , meaning we are able to visualized delays for any given connection.
Map
On the map screen you can see and or find all available stops of public transportation. This allows for providing the user with a great way to find out what stops are available in their city. By clicking on any of the shown stops will open the departure screen and provide you with the information mentioned above. To better visualize a selected connection, we show the route you plan to travel on the map.
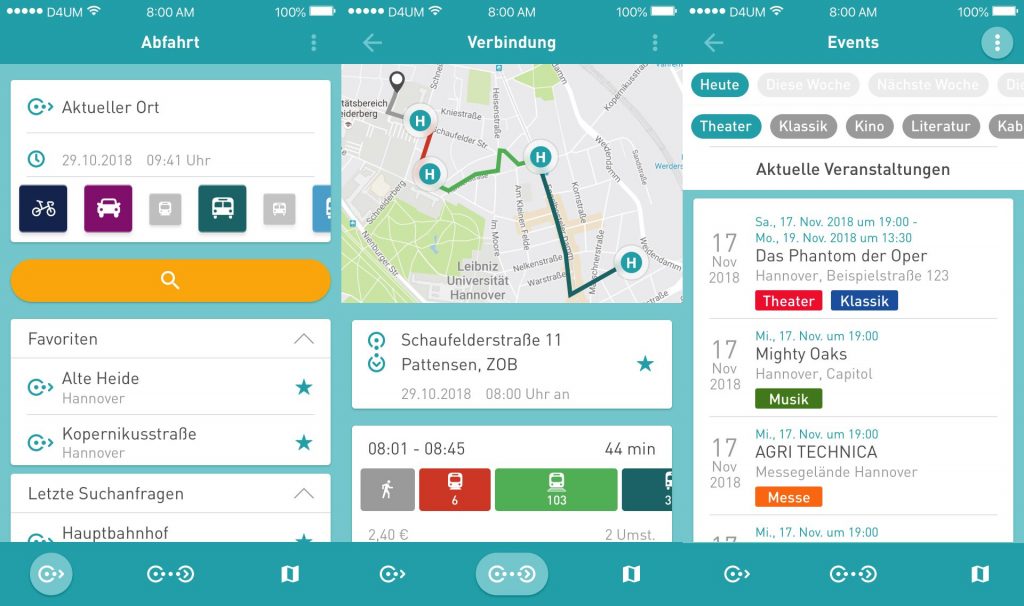
Menu / Settings
Additional features can be found in the settings menu of the application. Here you can find settings that allow you to customize your routing results for both the departures and connection screen. The best way to let us know what you think about the application is to use the feedback module. This can be found here as well. First click on the emoji that best describe how you feel about the app. And then put in any additional information or ideas or thoughts you may have. Now what is left is just to press send and you will send us an email.
We look forward to hearing from you.
Quantification and Prediction of Impact of Public Events
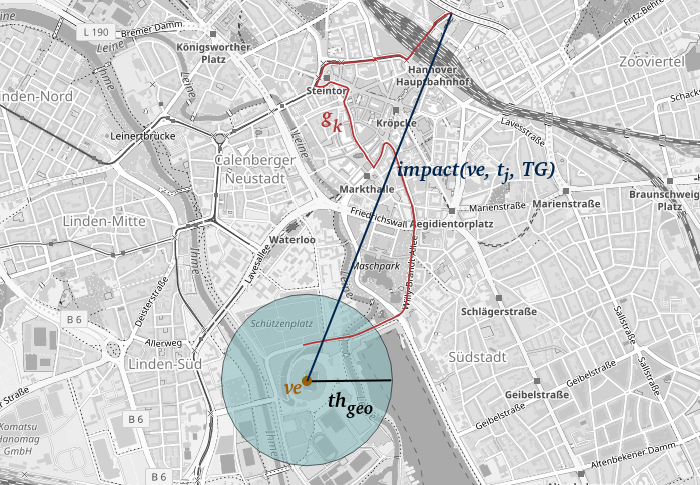
Current Data4UrbanMobility research results allow for measuring and prediction of spatial impact on road traffic of public events. Connected, affected street segments nearby public events are identified to measure the spatial impact. The approach is depicted in the following figure:
(Karte von https://www.openstreetmap.org)
An event is marked as yellow dot, affected streets in red and the measured impact in dark blue. Moreover, an approach making use of machine learning algorithms was developed to predict the impact determined in this way, resulting an error-reduction of up to 40% when compared to existing state-of-the-art approaches.
D4UM – Platform V1 Released
The first version of the Data4UrbanMobiltiy platform has been released. The platform was designed and implemented following a 3-tier-architecture. The platform provides RESTfull Web services for mobility applications like dashboards or mobile apps. As a demonstration, an interactive map application has been developed that visualizes the spatial impact of public events. The following figure shows a screenshot of the application.
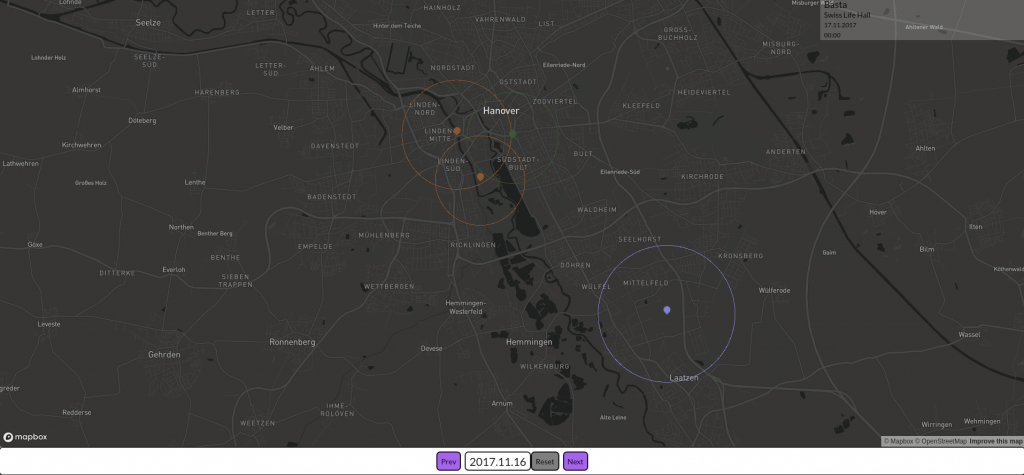
The figure shows 4 public events in the city of Hannover. The colors represent different types of public events (e.g. concerts, fairs, sport events). The circles visualize the spatial impact on road traffic caused by the public events.
Comprehensive Set of Requirements
The Data4UrbanMobility analysis of requirements includes requirements of the application partners Region Hannover (RH) and Wolfsburg AG (WAG) as well as non functional requirements. The requirements were collected by MOMA. The L3S derived research question for data analysis which are based on the requirements of RH and WAG. The research question address especially the information needs of end-users.
The current research questions particularly include
- Automated verification of traffic warnings and prediction of their impact
- Identification of events and prediction of their impact
- Investigation of correlation of road traffic data, public transportation query logs, traffic warnings and twitterfeeds
- Determination of optimal traveling timepoints
Growing Data Collection
ISU create a comprehensive data matrix containing potential source of mobility related data. The Data4UrbanMobility data model describes all project relevant data sets and sets them into context. This makes the data available in a unified manor for both analysis and applications. The selected data sources were transformed according to the Data4UrbanMobility data model by L3S. The data quality of selected data sources (i.e. public transportation query logs and road traffic data) was examined.
Tools for extracting the relevant information from the datasets were developed to enable the integration of the datasets.
- Street and graph extraction from OpenStreetMap
- Bulkloader for public transportation queries
- Integration of “Zentrales Haltestellen Verzeichniss” (central registry of public transportation stops)
The current collection (December 12th 2017) contians
EFA-Logs: 17 million public transportation queries
Road traffic data: 174 thousand street sements with a frequency of 15 minutes
GTFS-data: 90 thousand. public transportation stops, 2.6 thousand routes
Weather: Radolan “Regenraster” (rain grid)
Twitter: 2,5 Mio. Tweets starting at June 2017
OSM: 440 thousand streets
Events: 21 thousand public events (August 14th 2016-July 17th 2018)
Traffic warnings: 13 thousand warning (since June 2017)
Visualization of Public Transportation Information
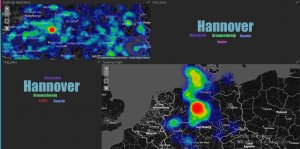
In order to allow intuitive analytics of public transportation information, the PROJEKTIONISTEN (PROJ) developed a dashboard web application. First prototypes visualize queries addressed to the regional timetable information system EFA (www.efa.de). The prototypes serve as foundations for exploration analyses as well as the implementation of future versions of the dashboard. The following figure shows an integrated visualization of the most frequent origins and destinations of the queries.
Analysen der EFA-Logs
Analysis of EFA Public Transportation Query Logs
Analyses regarding the impact of public events on public transportation are currently conducted to address early research questions. To this extend, explorative data analyses of the impact of major public events such as football games and medium sized events such as concerts were conducted. Visual analytics were used as a first step towards comprehensive analyses, which show start-like patterns for city center which identify mobility hubs of central importance.
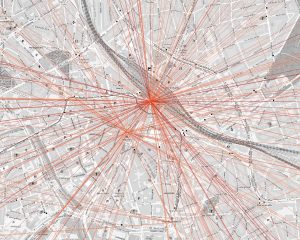
The figure shows the direct connection between origin and destination of public transportation queries. Darker colors correspond to more frequent queried trips. Star-like pattern identify the central train station and the central metro station.
Analyses of single stations reveal weekday dependent patterns.
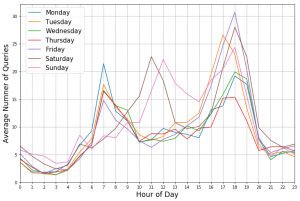
The figure depicts the average number of queries with the destination “Hannover Stadionbrücke”. Differences emerge between Weekends and workdays.
The impact of public events on the queries can be visualized as well.
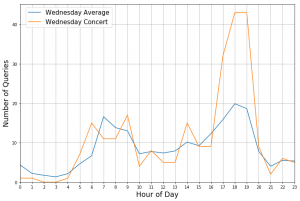
The figure shows the number of queries with the Destination “Hannover Stadionbrücke” for Wednesday, April 26th 2017 (orange) as well as the average number of queries on a Wednesday for the same destination. On this day a concert took place in venue nearby. The concert start at 8 pm. The significant deviations between 5 pm and 7 pm is highly likely to be caused by visitors of the concert. This shows that public transportation queries are a valuable information source to investigate the impact of public events on mobility infrastructure.
- HybridReg: Robust 3D Point Cloud Registration with Hybrid Motions. Du, Keyu; Xu, Hao; Li, Haipeng; Qu, Hong; Fu, Chi-Wing; Liu, Shuaicheng T. Walsh, J. Shah, Z. Kolter (eds.) (2025). 2789–2797.
- ‘I dropped a C-bomb into Tolstoy’: one man’s quest to translate War and Peace into ‘bogan Australian’ This article is more than 3 months old. Marsh, Walter (2025).
- Efficient Bearing Sensor Data Compression via an Asymmetrical Autoencoder with a Lifting Wavelet Transform Layer. Zhu, Xin; Çetin, Ahmet Enis (2025). 1–5.
- A Hybrid Framework for Predicting Citation Harm from Retracted Papers. Zhao, Jiahui; Li, Hao; Tang, Suqin (2025). 411–416.
- HoloDiT: Exploring 3D Diffusion Transformer Models Using 2D Images. Li, Hao; Zhao, Jiahui; Gu, Daixuan (2025). 7–11.
- Ladder: A Convergence-based Structured DAG Blockchain for High Throughput and Low Latency. Hu, Dengcheng; Wang, Jianrong; Liu, Xiulong; Xu, Hao; Wu, Xujing; Shahzad, Muhammad; Liu, Guyue; Li, Keqiu T. A. Benson, R. N. Mysore (eds.) (2025). 779–794.
- Mind the Location Leakage in LEO Direct-to-Cell Satellite Networks. Liu, Weisen; Lai, Zeqi; Wu, Qian; Li, Hewu; Weng, Yuxuan; Liu, Wei; Zhang, Qi; Li, Jihao; Li, Yuanjie; Liu, Jun M. Blanton, W. Enck, C. Nita-Rotaru (eds.) (2025). 1064–1080.
- BitsAI-CR: Automated Code Review via LLM in Practice. Sun, Tao; Xu, Jian; Li, Yuanpeng; Yan, Zhao; Zhang, Ge; Xie, Lintao; Geng, Lu; Wang, Zheng; Chen, Yueyan; Lin, Qin; Duan, Wenbo; Sui, Kaixin; Zhu, Yuanshuo L. Montecchi, J. Li, D. Poshyvanyk, D. Zhang (eds.) (2025). 274–285.
- Enhancing Code LLM Training with Programmer Attention. Zhang, Yifan; Huang, Chen; Karas, Zachary; Nguyen, Dung Thuy; Leach, Kevin; Huang, Yu L. Montecchi, J. Li, D. Poshyvanyk, D. Zhang (eds.) (2025). 616–620.
- Fast and Scalable Selective Retransmission for RDMA. Huang, Peihao; Chen, Guo; Zhang, Xin; Liu, Can; Wang, Hongyu; Shen, Huijun; Bian, Ying; Lu, Yuanwei; Ruan, Zhenyuan; Li, Bojie; Zhang, Jiansong; Liu, Yongfeng; Chen, Zhigang (2025). 1–10.
- AIGC-CM: An Efficient and Scalable Blockchain Solution for AIGC Copyright Management. Ma, Liyuan; Hu, Dengcheng; Liu, Xiulong; Xu, Hao; Wang, Jianrong; Li, Keqiu (2025). 1–10.
- Integrating the landscape scale supports SAR-based detection and assessment of the phenological development at the field level. Löw, Johannes; Hill, Steven; Otte, Insa; Friedrich, Christoph; Thiel, Michael; Ullmann, Tobias; Conrad, Christopher (2025). 6(161005) 17.
- Creative Through Constraints: How Old Mechanical Automata Fosters Innovation in Shadow Puppetry. Yao, Yuan; Li, Zhi; Ma, Ben N. Yamashita, V. Evers, K. Yatani, S. X. Ding (eds.) (2025). 159:1–159:7.
- Dedicated prostate DOI-TOF-PET based on the ProVision detection concept. Vo, Hong Phuc; Williams, Themistoklis; Doroud, Katayoun; Williams, Crispin; Rafecas, Magdalena (2025).
- BrokerAS: Towards Fault-tolerant Atomic Cross-chain Swaps. Shi, Gaowei; Liu, Xiulong; Wang, Huan; Li, Yuhan; Xu, Hao; Ma, Liyuan; Li, Keqiu (2025). 1–10.
- Beschäftigtenorientiertes People Analytics: ein kommentierter Foliensatz Köhne, Sonja; Richthofen, Georg von; Send, Hendrik; Buß, Nele; Klöpper, Miriam (2025, August).
- Poster: Jakiro: Spitting RDMA and TCP over Virtual Private Cloud. Liu, Yirui; Jiang, Lidong; Li, Deguo; Kang, Daxiang; Wei, Zhaoyang; Chai, Yuqi; Niu, Bin; Lin, Ke; Ding, Xiaoning; Pi, Jianwen; Luo, Hao V. Gopalakrishnan, J. Wang, I. A. Qazi, G. Tyson (eds.) (2024). 31–32.
- COSMO: A Large-Scale E-commerce Common Sense Knowledge Generation and Serving System at Amazon. Yu, Changlong; Liu, Xin; Maia, Jefferson; Li, Yang; Cao, Tianyu; Gao, Yifan; Song, Yangqiu; Goutam, Rahul; Zhang, Haiyang; Yin, Bing; Li, Zheng P. Barceló, N. Sánchez-Pi, A. Meliou, S. Sudarshan (eds.) (2024). 148–160.
- A One-Point-Trimmed 18.4 ppm/°C On-Chip Oscillator with Capacitively-Biased-Diode-based Quasi-Digital Temperature Compensation. Kuang, Yonghong; Chen, Yekan; Cai, Tianyi; Zhang, Qi; Cheng, Zipeng; Zhao, Bo; Luo, Yuxuan (2024). 1–5.
- Sleep No Mosquitoes: Compensating Distance-Aware Compression in a VR Audio Game. Li, Zhi; Yao, Yuan F. ’Floyd’ Mueller, P. Kyburz, J. R. Williamson, C. Sas (eds.) (2024). 293:1–293:6.
- SkyCastle: Taming LEO Mobility to Facilitate Seamless and Low-latency Satellite Internet Services. Li, Jihao; Li, Hewu; Lai, Zeqi; Wu, Qian; Liu, Weisen; Wang, Xiaomo; Li, Yuanjie; Liu, Jun; Zhang, Qi (2024). 541–550.
- In-Orbit Processing or Not? Sunlight-Aware Task Scheduling for Energy-Efficient Space Edge Computing Networks. Liu, Weisen; Lai, Zeqi; Wu, Qian; Li, Hewu; Zhang, Qi; Li, Zonglun; Li, Yuanjie; Liu, Jun (2024). 881–890.
- Service Satisfaction Evaluation from Gaits Using Local Low-level and Global Co-occurrence Features. Li, Hao; Huang, Lulu; Cheng, Wenzhuo; Wang, Xiaoyi; Wu, Chao (2024). 216–222.
- Trace-agnostic and Adversarial Training-resilient Website Fingerprinting Defense. Qiao, Litao; Wu, Bang; Li, Heng; Gao, Cuiying; Yuan, Wei; Luo, Xiapu (2024). 211–220.
- Your Mega-Constellations Can Be Slim: A Cost-Effective Approach for Constructing Survivable and Performant LEO Satellite Networks. Lai, Zeqi; Wang, Yibo; Li, Hewu; Wu, Qian; Zhang, Qi; Hou, Yunan; Liu, Jun; Li, Yuanjie (2024). 521–530.
- Brief Analysis of False Data Injection Attacks Based on Two Data Modalities in IoTs-based Solar Insecticidal Lamps. Su, Qin; Shu, Lei; Zhao, Qingsong; Yang, Xing; Jiang, Zitian; Fang, Jiarui; Chin, Huihsin (2024). 1–6.
- AlN Sputtering Parameter Estimation Using A Multichannel Parallel DCT Neural Network. Luo, Yingyi; Khan, Talha M.; Hamdan, Emadeldeen; Zhu, Xin; Pan, Hongyi; Ozevin, Didem; Çetin, A. Enis (2024). 1–5.
- Online GNN Evaluation Under Test-time Graph Distribution Shifts. Zheng, Xin; Song, Dongjin; Wen, Qingsong; Du, Bo; Pan, Shirui (2024).
- Radical Basis Neural Network Based Anti-swing Control for 5-DOF Ship-Mounted Crane. Li, Zhi; Chuanjing, Hou; Liu, Can in Communications in Computer and Information Science, H. Zhang, X. Li, T. Hao, W. Meng, Z. Wu, Q. He (eds.) (2024). (Vol. 2181) 18–29.
- Motif-Based Linearizing Graph Transformer for Web API Recommendation. Zheng, Xin; Wang, Guiling; Zhang, Yuqi; Han, Boyang; Yu, Jian in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, W. Gaaloul, M. Sheng, Q. Yu, S. Yangui (eds.) (2024). (Vol. 15405) 138–145.
- Optimized Method for Dynamic Allocation of Driving Rights and Trajectory Tracking under Human-Machine Co-driving. Li, Hao; An, Yisheng; Li, Ting; Li, Nandong; Zhang, Yukun; Yang, Peng; Gao, Zhengge X. Chen, J. Fang (eds.) (2024). 127–132.
- Adaptive Cooperative Ant Colony Optimization: A Task Scheduling Method on Heterogeneous Multi-Core Processors. Li, Nandong; An, Yisheng; Li, Ting; Li, Hao; Zhang, Yukun; Yang, Peng; Gao, Zhengge X. Chen, J. Fang (eds.) (2024). 519–525.
- Multi-feature Electric Load Forecasting Based on AVMD-LSTM-Informer Model. Zhang, Yukun; An, Yisheng; Li, Ting; Li, Nandong; Li, Hao; Yang, Peng; Gao, Zhengge X. Chen, J. Fang (eds.) (2024). 491–496.
- Uncovering and Mitigating the Impact of Code Obfuscation on Dataset Annotation with Antivirus Engines. Gao, Cuiying; Wu, Yueming; Li, Heng; Yuan, Wei; Jiang, Haoyu; He, Qidan; Liu, Yang M. Christakis, M. Pradel (eds.) (2024). 553–565.
- A 2T P-Channel Logic Flash Cell for Reconfigurable Interconnection in Chiplet-Based Computing-In-Memory Accelerators. Li, Weizeng; Wang, Linfang; Li, Zhi; Ye, Wang; Zhou, Zhidao; Zhou, Haiyang; Gao, Hanghang; Yue, Jinshan; Hu, Hongyang; Liu, Fengman; Luo, Qing; Dou, Chunmeng (2024). 1–4.
- Debunking Fake News in Online Social Networks Without Text Analysis. Su, Xing; Yang, Jian; Wu, Jia; Qiu, Zitai E. Baralis, K. Zhang, E. Damiani, M. Debbah, P. Kalnis, X. Wu (eds.) (2024). 450–459.
- SiMA-Hand: Boosting 3D Hand-Mesh Reconstruction by Single-to-Multi-View Adaptation. Wang, Yinqiao; Xu, Hao; Heng, Pheng-Ann; Fu, Chi-Wing M. J. Wooldridge, J. G. Dy, S. Natarajan (eds.) (2024). 5704–5712.
- Tuning Spatial Distributions of Selection Pressure to Suppress Emergence of Resistance. Tunstall, Thomas; Madgwick, Philip G.; Kanitz, Ricardo; Möbius, Wolfram (2024).
- DiffMoCa: Diffusion Model Based Multi-modality Cut and Paste. Zhang, Junjie; Wu, Shaojin; Gao, Junbin; Yu, Fusheng; Xu, Hao; Zeng, Zhigang in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, X. Le, Z. Zhang (eds.) (2024). (Vol. 14827) 153–162.
- Reflecting Intelligent Surface Aided Downlink Transmission in Ultra-Dense LEO Satellite Networks. Zhang, Xin; Ma, Ting; Qin, Xiaohan; Wang, Yilei; Zhou, Haibo (2023). 1123–1128.
- Applications of Deep Learning in Satellite Communication: A Survey. He, Yuanzhi; Sheng, Biao; Li, Yuan; Wang, Changxu; Chen, Xiang; Liu, Jinchao in Communications in Computer and Information Science, Q. Yu (ed.) (2023). (Vol. 2057) 17–33.
- IDMUNet : An effective network for liver tumor segmentation. Wu, Caihong; Song, Changming; Cheng, Dongxu; Ren, Siyv; Li, Zenghui; Chen, Kang; Li, Hao (2023). 49–56.
- On the Minimum Depth of Circuits with Linear Number of Wires Encoding Good Codes. Drucker, Andrew; Li, Yuan in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, W. Wu, G. Tong (eds.) (2023). (Vol. 14423) 392–403.
- Analysis of Co-Frequency Interference Avoidance Effect of Downlink Between Giant NGSO Constellations Based on MESINR Satellite Selection. Li, Yuan; He, Yuanzhi (2023). 1214–1218.
- Sum-Rate Capacity Scaling Law in Massive MIMO With Antenna Selection. Ouyang, Chongjun; Xu, Hao; Zang, Xujie; Yang, Hongwen (2023). 1–6.
- AoI-Minimal Power and Trajectory Optimization for UAV-Assisted Wireless Networks. Zhang, Xin; Hu, Yun; Chang, Zheng; Min, Geyong (2023). 1–6.
- Characterize and Optimize Dense Linear Solver on Multi-core CPUs. Fu, Xiao; Su, Xing; Dong, Dezun; Yang, Weiling (2023). 1833–1842.
- Characterization of flow-blurring atomization with Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH). Ates, Cihan; Gundogdu, Cansu; Okraschevski, Max; Bürkle, Niklas; Koch, Rainer; Bauer, Hans-Jörg (2023). 164 104442-.
- A Novel Classification Model for Automatic Multi-Label ICD Coding via BERT-LSTM. Wen, Luhan; Zhou, Dongmei; Luo, Hao; Cheng, Yongjian (2023). 1–7.
- Simulations of the insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway with randomly sampled parameters. Yan, Yan; Zhang, Xinan; Tian, Tianhai X. Jiang, H. Wang, R. Alhajj, X. Hu, F. Engel, M. Mahmud, N. Pisanti, X. Cui, H. Song (eds.) (2023). 3848–3854.
- Exploiting Lens Antenna Arrays in Uplink mmWave MU-MIMO Networks: Joint Beamforming Optimization. Ouyang, Chongjun; Xu, Hao; Zang, Xujie; Yang, Hongwen (2022). 1–6.
- Joint Subchannel Allocation and Beamforming for Multicast in Ultra-Dense LEO Backbone Network. Ma, Ting; Qian, Bo; Qin, Xiaohan; Zhang, Xin; Cheng, Nan; Zhou, Haibo (2022). 1625–1630.
- SFC Enabled Data Delivery for Ultra-Dense LEO Satellite-Terrestrial Integrated Network. Qin, Xiaohan; Ma, Ting; Tang, Zhixuan; Zhang, Xin; Liu, Xiaoyu; Zhou, Haibo (2022). 668–673.
- Distributed Massive MIMO Cooperation With Low-Dimensional CSI Exchange. He, Zhenyao; Xu, Wei; Shen, Hong; Sun, Yan; You, Xiaohu; Fu, Jiewei (2022). 699–704.
- Image Description Generation Method Based on X-Linear Attention Mechanism. Qiao, Pingan; Li, Yuan; Shen, Ruixue (2022). 581–586.
- Review of Flow Blurring Atomization: Advances and Perspectives. Kourmatzis, Agisilaos; Jaber, Othman J.; Singh, Gajendra; Masri, Assaad R. (2022). 36(8) 4224–4233.
- Research on Image Description Generation Method Based on G-AoANet. Qiao, Pingan; Shen, Ruixue; Li, Yuan (2022). 631–636.
- Trajectory Optimization and Resource Allocation for Time Minimization in the UAV-Enabled MEC System. Zhang, Xin; Chang, Zheng; Zhang, Guopeng; Li, Ming; Hu, Yulin (2022). 333–338.
- lncRNAMalat1and miR-26 cooperate in the regulation of neuronal progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation. Was, Nina; Sauer, Mark; Fischer, Utz; Becker, Matthias (2022). 29(1) 69–81.
- Research Hotspots and Evolution Trend of Virtual Power Plant in China: An Empirical Analysis Based on Big Data. Zhang, Yan; Liu, Pengcheng; Xu, Hao; Wang, Mulan in Communications in Computer and Information Science, Y. Tian, T. Ma, Q. Jiang, Q. Liu, M. K. Khan (eds.) (2022). (Vol. 1796) 105–121.
- Ratgeber berufsbegleitende Promotion : Eine Entscheidungshilfe Staab, Thomas; Matusiewicz, David in UTB (2022). (Vol. 5845) Budrich.
- A Double Full Diversity Unitary Space Time Precoded V2V MIMO Communication System. Deng, Tao; Zhang, Lin; Feng, Yan; Jiang, Yuan (2022). 99–104.
- QoS-Centric Handover for Civil Aviation Aircraft Access in Ultra-Dense LEO Satellite Networks. Wang, Yilei; Qin, Xiaohan; Tang, Zhixuan; Ma, Ting; Zhang, Xin; Zhou, Haibo (2022). 1085–1089.
- Joint Mode Selection and Dynamic Pricing in Ultra Dense LEO Integrated Satellite-Terrestrial Networks. Zhang, Xin; Qin, Xiaohan; Qian, Bo; Ma, Ting; Zhou, Haibo (2022). 1090–1094.
- Social-Computing Based Long-Term Task Offloading in D2D-Enhanced MEC Networks. Long, Hao; Xu, Chen; Zhang, Zhanpeng; Li, Zewu (2021). 934–939.
- A 98.1-dB SNDR 188-dB FoMS Noise-Shaping SAR ADC Using Series Connection Capacitors. Jing, Xixin; Lan, Zhechong; Zhang, Bing; Dong, Li; Xin, Youze; Guo, Zhuoqi; Xue, Zhongming; Geng, Li (2021). 10–13.
- A Bayesian framework for inferring heterogeneity of cellular processes using single-cell data. He, Wenlong; Xia, Peng; Zhang, Xinan; Tian, Tianhai Y. Huang, L. A. Kurgan, F. Luo, X. Hu, Y. Chen, E. R. Dougherty, A. Kloczkowski, Y. Li (eds.) (2021). 2142–2146.
- Service Caching Based Task Offloading and Resource Allocation in Multi-UAV Assisted MEC Networks. Zheng, Guangyuan; Xu, Chen; Long, Hao; Sheng, Yun (2021). 1024–1029.
- Optimisation for the product configuration system of Renault: towards an integration of symmetries. Xu, Hao; Baarir, Souheib; Ziadi, Tewfik; Hillah, Lom-Messan; Essodaigui, Siham; Bossu, Yves M. R. Mousavi, P.-Y. Schobbens (eds.) (2021). 86–90.
- MEC in NOMA-HetNets: A Joint Task Offloading and Resource Allocation Approach. Zheng, Guangyuan; Xu, Chen; Long, Hao; Zhao, Xiongwen (2021). 1–6.
- Progress in the Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Method to Simulate and Post-process Numerical Simulations of Annular Airblast Atomizers. Chaussonnet, G.; Dauch, T.; Keller, M.; Okraschevski, M.; Ates, C.; Schwitzke, C.; Koch, R.; Bauer, H.-J. (2020). 105(4) 1119–1147.
- Evaluation of Phenotyping Errors on Polygenic Risk Score Predictions. Li, Ruowang; Tong, Jiayi; Duan, Rui; Chen, Yong; Moore, Jason H. E. D. Maria, A. Fred, H. Gamboa (eds.) (2020). 123–130.
- How Autonomy is Used in Information Systems Research: Status Quo and Prospective Opportunities. Weber, Sebastian; Klesel, Michael; Oschinsky, Frederike Marie; Niehaves, Björn (2020). 1–9.
- A Novel Pose Estimation Method of Object in Robotic Manipulation Using Vision-Based Tactile Sensor. Zhao, Dan; Sun, Fuchun; Zhou, Quan; Wang, Zongtao in Communications in Computer and Information Science, F. Sun, H. Liu, B. Fang (eds.) (2020). (Vol. 1397) 266–275.
- Location Aided Intelligent Deep Learning Channel Estimation for Millimeter Wave Communications. Lin, Xintong; Zhang, Lin; Jiang, Yuan (2020). 489–494.
- Robust-ODAL: Learning from Heterogeneous Health Systems Without Sharing Patient-LevelData. Tong, Jiayi; Duan, Rui; Li, Ruowang; Scheuemie, Martijn J.; Moore, Jason H.; Chen, Yong (2020). 695–706.
- A combined experimental and computational study of flow-blurring atomization in a twin-fluid atomizer. Murugan, Raju; Kolhe, Pankaj S.; Sahu, Kirti Chandra (2020). 84 528–541.
- Malware Detection on Highly Imbalanced Data through Sequence Modeling. Oak, Rajvardhan; Du, Min; Yan, David; Takawale, Harshvardhan C.; Amit, Idan L. Cavallaro, J. Kinder, S. Afroz, B. Biggio, N. Carlini, Y. Elovici, A. Shabtai (eds.) (2019). 37–48.
- Fast Sparse Coding Inference with Historical Information. Zhang, Zhenchang; Jiang, Fei; Shen, Ruimin J. Wang, K. Shim, X. Wu (eds.) (2019). 1462–1467.
- Perry’s Chemical Engineers’ Handbook Green, Don W.; Southard, Marylee Z. (2019). (Ninth ) McGraw-Hill Education, New York.
- ODAL: A one-shot distributed algorithm to perform logistic regressions on electronic health records data from multiple clinical sites. Duan, Rui; Boland, Mary Regina; Moore, Jason H.; Chen, Yong R. B. Altman, A. K. Dunker, L. Hunter, M. D. Ritchie, T. E. Klein (eds.) (2019). 30–41.
- The Quantum Shor Algorithm Simulated on FPGA. Zhang, Xin; Zhao, Yaqian; Li, RenGang; Li, Xuelei; Guo, Zhenhua; Zhu, XiaoMin; Dong, Gang (2019). 542–546.
- Making data-driven porting decisions with Tuscan. Khazem, Kareem; Barr, Earl T.; Hosek, Petr F. Tip, E. Bodden (eds.) (2018). 276–286.
- Comparing adverse effects of Hepatitis C drugs using FAERS data. Huang, Jing; Zhang, Xinyuan; Tong, Jiayi; Du, Jingcheng; Duan, Rui; Yang, Liu; Moore, Jason H.; Chen, Yong; Tao, Cui H. J. Zheng, Z. Callejas, D. Griol, H. Wang, X. Hu, H. H. H. W. Schmidt, J. Baumbach, J. Dickerson, L. Zhang (eds.) (2018). 1653–1656.
- Comparing Pharmacovigilance Outcomes Between FAERS and EMR Data for Acute Mania Patients. Zhang, Xinyuan; Duan, Rui; Du, Jingcheng; Huang, Jing; Chen, Yong; Tao, Cui (2018). 57–59.
- Performance analysis of quad-LED complex spatial modulation in visible light communication system. Zhang, Qi; Bai, Zhiquan; Zhang, Na; Sun, Shangqian; Han, Tao; Kwak, Kyung Sup (2018). 1–5.
- Atomization and Sprays Lefebvre, Arthur H.; McDonell, Vincent G. in Combustion (2017). Taylor & Francis, CRC Press, Boca Raton.
- vCFI: Visible Control Flow Integrity for Cloud Tenants. Li, Yuan; Zhang, Chao; Luo, Xiapu (2017). 6:1–6:2.
- Fallstudien in der Organisationsforschung. Pflüger, Jessica; Pongratz, Hans J.; Trinczek, Rainer (2017). 389–413.
- An improved algorithm for symbol segmentation of mathematical formula images. Wang, Haiyan; Wang, Yu; Lu, Liying; Liu, Jianhang; Li, Shibao; Zhang, Yang (2016). 461–464.
- Extended Sunflower Hidden Markov Models for the recognition of homotypic cis-regulatory modules. Lemnian, Ioana M.; Eggeling, Ralf; Grosse, Ivo (2013).
- New analytical framework for the products of independent RVs with wireless applications. Chen, Yunfei; Karagiannidis, George K.; Lu, Hao; Cao, Ning (2012). 103–108.
- Handbook of Atomization and Sprays : Theory and Applications Ashgriz, N. (2011). Springer, New York.
- Genealogies and Geography. Barton, N H; Wilson, I P. H. Harvey, A. J. Leigh Brown, J. Maynard Smith (eds.) (1995).
- Liquid–Gas Systems. Fair, J. R.; Steinmeyer, D. E.; Penney, W. R.; Crocker, B. B. R. H. Perry, D. W. Green, J. O. Maloney (eds.) (1984). (Sixth )
- Spray Drying Handbook Masters, K. (1979). (Third ) G. Godwin ; Halsted Press, London, New York.
- Spray Drying. Dombrowski, N.; Munday, G. N. Blakegrough (ed.) (1968). (Vol. 2) 209–320.
- The Phenomena of Fluid Motions. Brodkey, Robert S. (1967).
- The phenomena of fluid motions Brodkey, Robert S. in Addison-Wesley series in chemical engineering (1967). (Fourth ) Addison-Wesley, Reading, Massachusetts.
- Atomization and Spray Drying Marshall, Jr. in Chemical Engineering Progress Monograph Series (1954). (Vol. 50) American Institute of Chemical Engineers, New York.