Forecasting of the Traffic Situation in the Hannover Region
The main requirement of road traffic participants is to know the current traffic situation. Such data is typically obtained from routing services where the time of many different individual trips is taken into account.
In the context of Data4UrbanMobility tools were developed that allow to predict the traffic situation based on such time series data. The following figure presents an interface to visualize typical time series patterns as well as outliers present in the data:
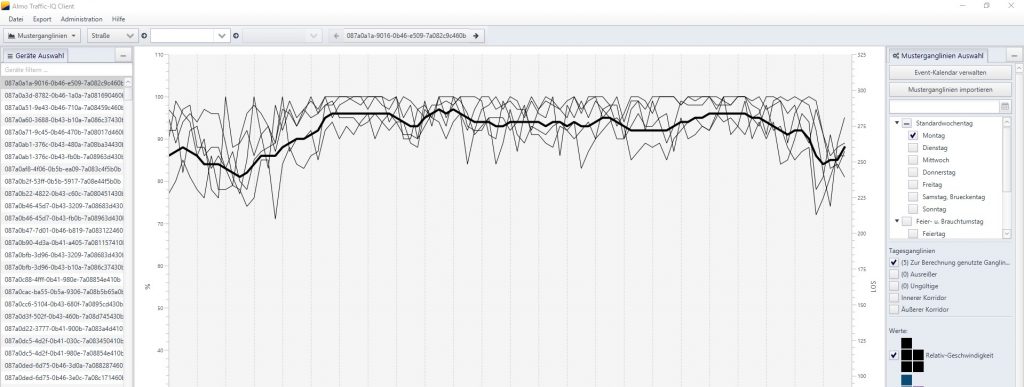
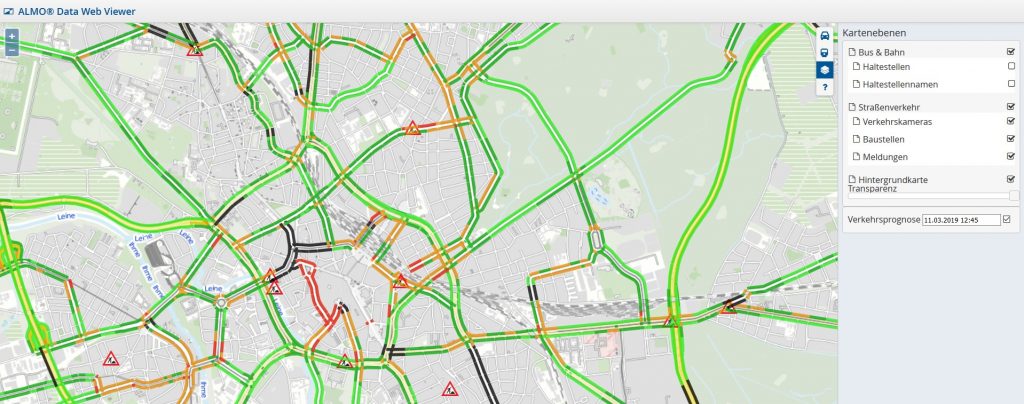
The prediction of the traffic situation is made available in the form of a map based interface for the end user:
Data4UrbanMobility Data Protection Regulation
The work on the Data4UrbanMobility data protection regulation is completed. The document is publicly available and can be found here.
First Version of MiC-App Available
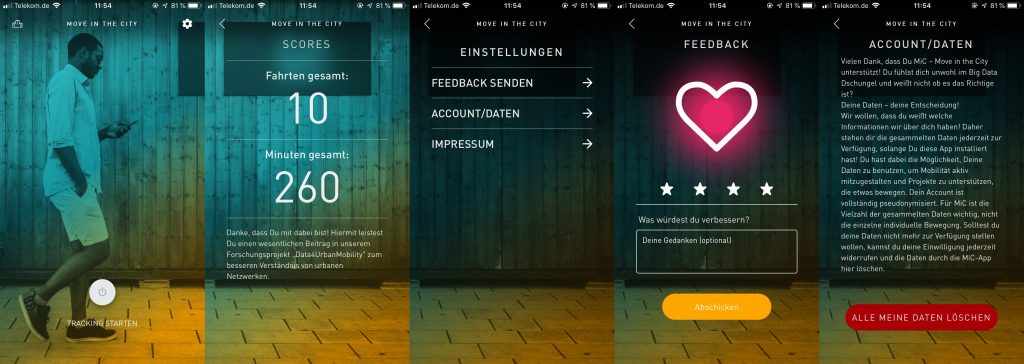
A first version of the novel MiC-App (Move in the City) App is now available for D4UM-associates as well as a protected group of public users. The mobile MiC-App is a tool to gather data.
MiC was developed by the Institute for Sustainable Urbanism at the University of Braunschweig and the Projektionisten GmbH. MiC links the growing awareness of digital citizen rights with the potential of evaluation big datasets. Therefore MiC gives the opportunity to citizen to actively participate in a citizen science project to take part in the development of the mobility of the feature.
MiC gathers data of the users movement, where the user has the about which data should be recorded. All data is pseudonymised such that the privacy of the contributing citizen is ensured.
Current Status:
In the first version of the app, the user can easily start and end the tracking of his/her movement. It is worth to point out, that the user decides when he is tracked and when not. A summary of his/her activity is available for the user as well as the opportunity to issue feedback or even delete all of his contributed data.
Updated System with Dashboard V2
With the new version of our system, the dashboard will provide even more insights into the impact of public events on the traffic situation.
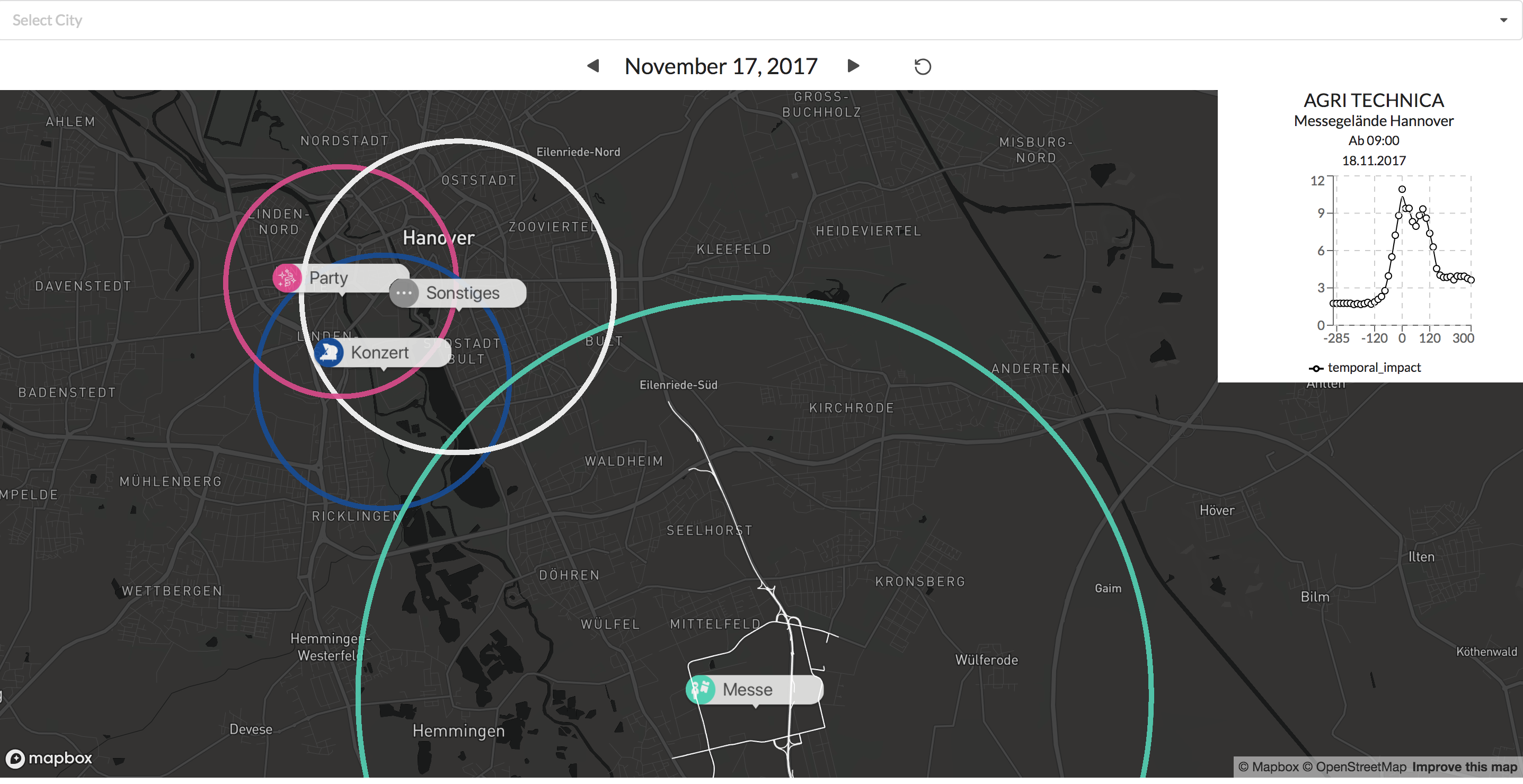
The coloring and labels let us easily distinguish between the different type of events. By clicking on the label we show the typically affected subgraph for that event type. This allows the user to check what specific routes are typically affected by an event at that location.
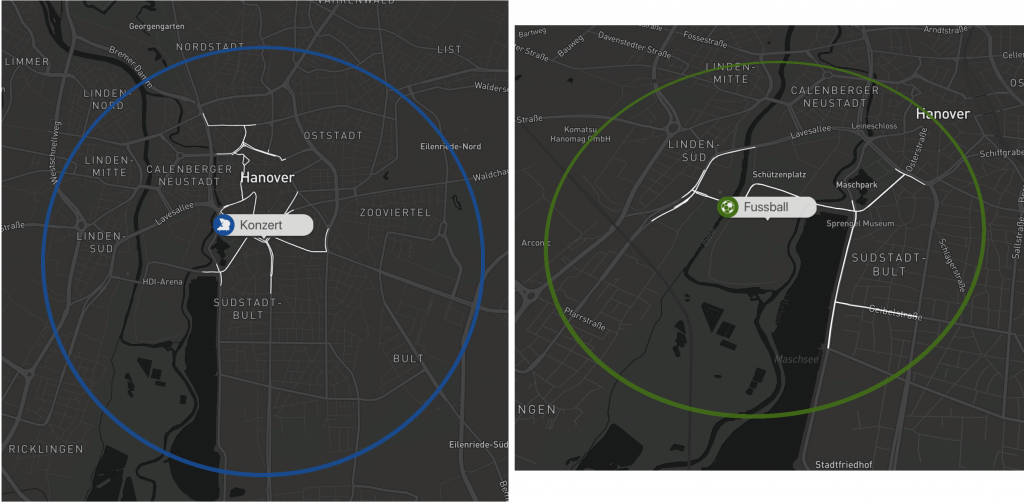
Examples: Visualisation of a concert and a football game.
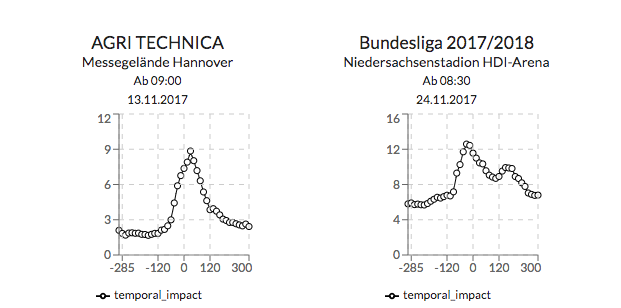
In addition, the graph at the top right gives additional information on how big the impact around the events start time tends to be.
{API}
We enriched the api endpoints with additional information from the data models that were developed as part of the research efforts.
D4UM App Version 1.0
We just released the first Version of the D4UM App. Every project member now has access to the application and can try out its features. Let’s quickly go over some of its main features.
The EFA integration (EFA is a routing engine covering Lower Saxony and Bremen ) allows for quick access to tip information using all available public transport options. Our focus, when designing the application, was on quick and easy navigation to provide a simple and easy to use trip planning tool.
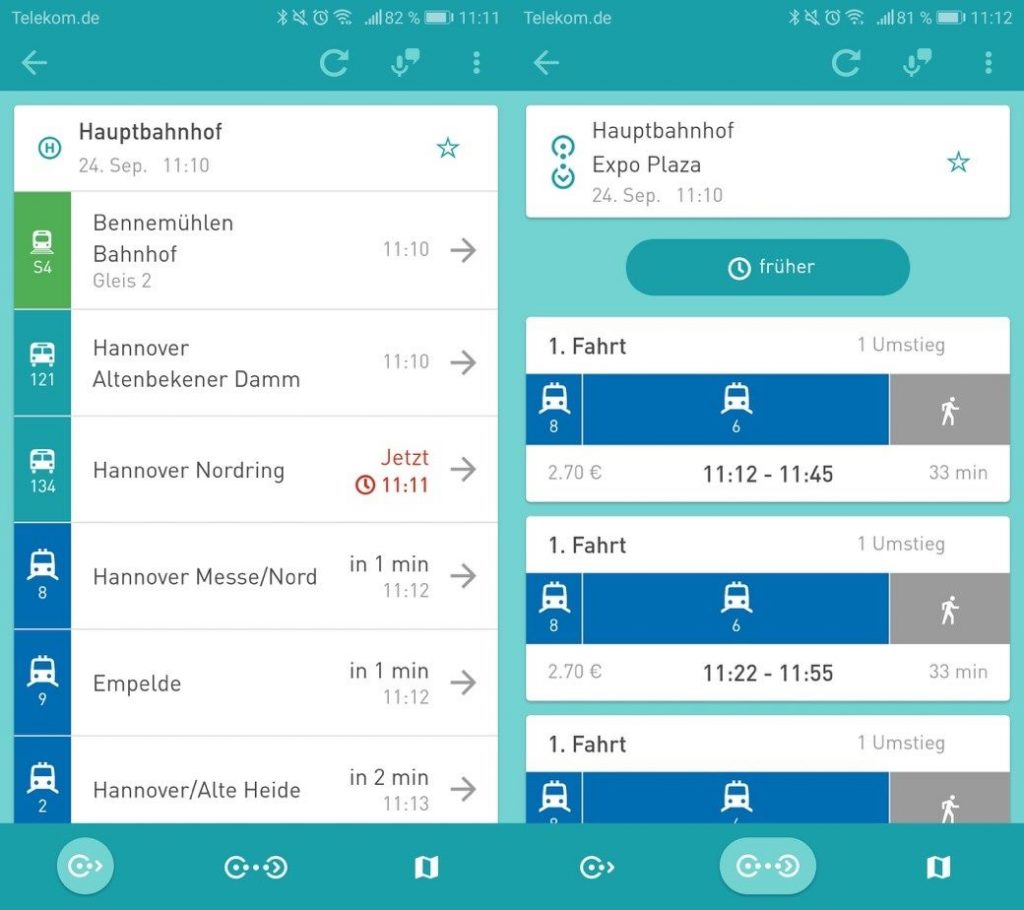
Departures and Connections
On the departure screen we show the user the closes stops for public transportation in his immediate vicinity. On the connection screen the user can fill in his desired starting location( either an address or an existing stop ) and destination and query for what connections are available to him. The provided information contains real time data , meaning we are able to visualized delays for any given connection.
Map
On the map screen you can see and or find all available stops of public transportation. This allows for providing the user with a great way to find out what stops are available in their city. By clicking on any of the shown stops will open the departure screen and provide you with the information mentioned above. To better visualize a selected connection, we show the route you plan to travel on the map.
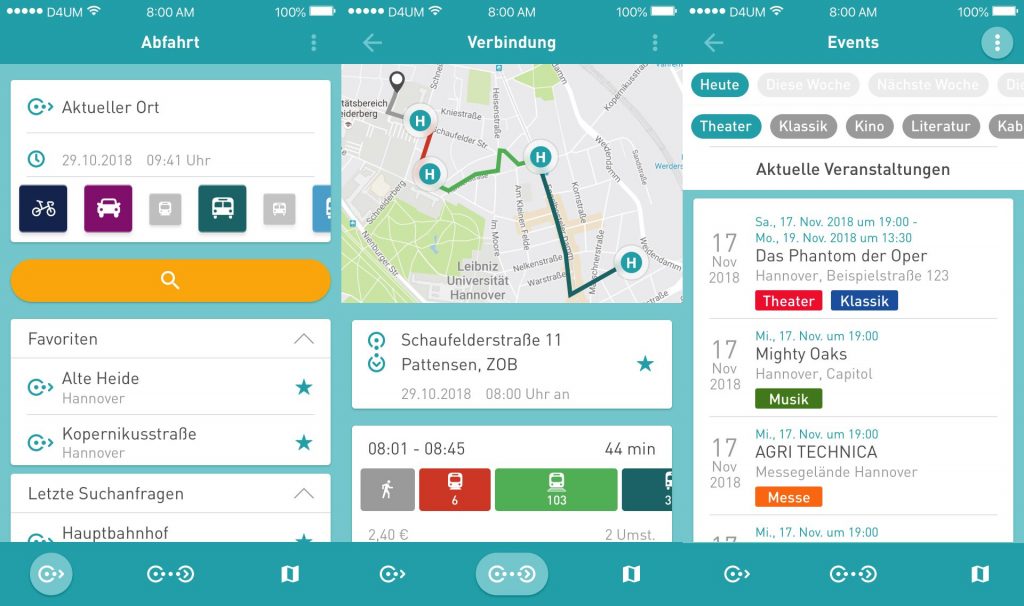
Menu / Settings
Additional features can be found in the settings menu of the application. Here you can find settings that allow you to customize your routing results for both the departures and connection screen. The best way to let us know what you think about the application is to use the feedback module. This can be found here as well. First click on the emoji that best describe how you feel about the app. And then put in any additional information or ideas or thoughts you may have. Now what is left is just to press send and you will send us an email.
We look forward to hearing from you.
Quantification and Prediction of Impact of Public Events
Current Data4UrbanMobility research results allow for measuring and prediction of spatial impact on road traffic of public events. Connected, affected street segments nearby public events are identified to measure the spatial impact. The approach is depicted in the following figure:
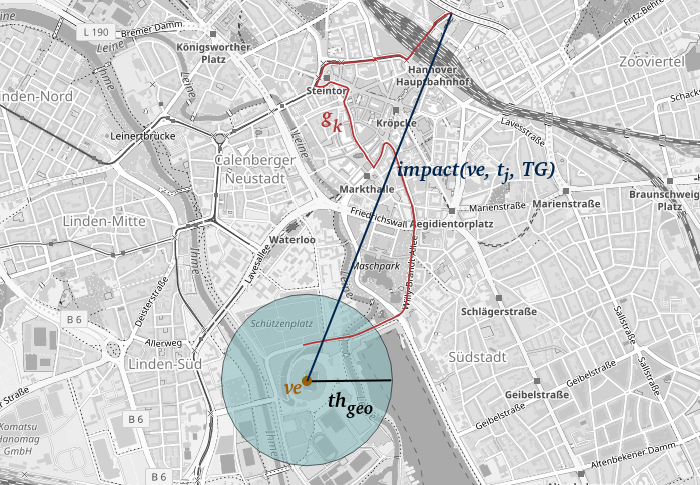
An event is marked as yellow dot, affected streets in red and the measured impact in dark blue. Moreover, an approach making use of machine learning algorithms was developed to predict the impact determined in this way, resulting an error-reduction of up to 40% when compared to existing state-of-the-art approaches.
D4UM – Platform V1 Released
The first version of the Data4UrbanMobiltiy platform has been released. The platform was designed and implemented following a 3-tier-architecture. The platform provides RESTfull Web services for mobility applications like dashboards or mobile apps. As a demonstration, an interactive map application has been developed that visualizes the spatial impact of public events. The following figure shows a screenshot of the application.
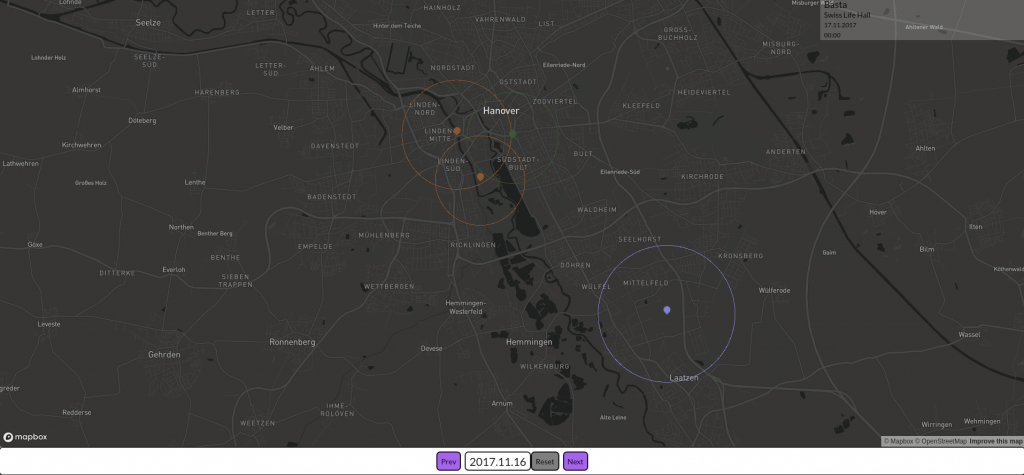
The figure shows 4 public events in the city of Hannover. The colors represent different types of public events (e.g. concerts, fairs, sport events). The circles visualize the spatial impact on road traffic caused by the public events.
Comprehensive Set of Requirements
The Data4UrbanMobility analysis of requirements includes requirements of the application partners Region Hannover (RH) and Wolfsburg AG (WAG) as well as non functional requirements. The requirements were collected by MOMA. The L3S derived research question for data analysis which are based on the requirements of RH and WAG. The research question address especially the information needs of end-users.
The current research questions particularly include
- Automated verification of traffic warnings and prediction of their impact
- Identification of events and prediction of their impact
- Investigation of correlation of road traffic data, public transportation query logs, traffic warnings and twitterfeeds
- Determination of optimal traveling timepoints
Growing Data Collection
ISU create a comprehensive data matrix containing potential source of mobility related data. The Data4UrbanMobility data model describes all project relevant data sets and sets them into context. This makes the data available in a unified manor for both analysis and applications. The selected data sources were transformed according to the Data4UrbanMobility data model by L3S. The data quality of selected data sources (i.e. public transportation query logs and road traffic data) was examined.
Tools for extracting the relevant information from the datasets were developed to enable the integration of the datasets.
- Street and graph extraction from OpenStreetMap
- Bulkloader for public transportation queries
- Integration of “Zentrales Haltestellen Verzeichniss” (central registry of public transportation stops)
The current collection (December 12th 2017) contians
EFA-Logs: 17 million public transportation queries
Road traffic data: 174 thousand street sements with a frequency of 15 minutes
GTFS-data: 90 thousand. public transportation stops, 2.6 thousand routes
Weather: Radolan “Regenraster” (rain grid)
Twitter: 2,5 Mio. Tweets starting at June 2017
OSM: 440 thousand streets
Events: 21 thousand public events (August 14th 2016-July 17th 2018)
Traffic warnings: 13 thousand warning (since June 2017)
Visualization of Public Transportation Information
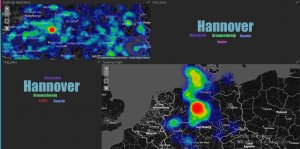
In order to allow intuitive analytics of public transportation information, the PROJEKTIONISTEN (PROJ) developed a dashboard web application. First prototypes visualize queries addressed to the regional timetable information system EFA (www.efa.de). The prototypes serve as foundations for exploration analyses as well as the implementation of future versions of the dashboard. The following figure shows an integrated visualization of the most frequent origins and destinations of the queries.
Analysen der EFA-Logs
Analysis of EFA Public Transportation Query Logs
Analyses regarding the impact of public events on public transportation are currently conducted to address early research questions. To this extend, explorative data analyses of the impact of major public events such as football games and medium sized events such as concerts were conducted. Visual analytics were used as a first step towards comprehensive analyses, which show start-like patterns for city center which identify mobility hubs of central importance.
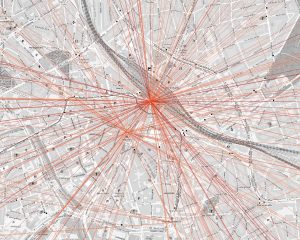
The figure shows the direct connection between origin and destination of public transportation queries. Darker colors correspond to more frequent queried trips. Star-like pattern identify the central train station and the central metro station.
Analyses of single stations reveal weekday dependent patterns.
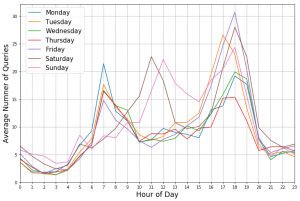
The figure depicts the average number of queries with the destination “Hannover Stadionbrücke”. Differences emerge between Weekends and workdays.
The impact of public events on the queries can be visualized as well.
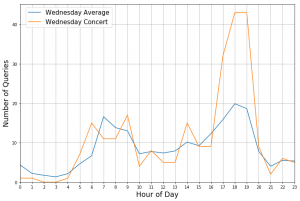
The figure shows the number of queries with the Destination “Hannover Stadionbrücke” for Wednesday, April 26th 2017 (orange) as well as the average number of queries on a Wednesday for the same destination. On this day a concert took place in venue nearby. The concert start at 8 pm. The significant deviations between 5 pm and 7 pm is highly likely to be caused by visitors of the concert. This shows that public transportation queries are a valuable information source to investigate the impact of public events on mobility infrastructure.
Decision Factors for the Selection of AI-based Decision Support Systems: The Case of Task Delegation in Prognostics. Heinrich, Kai; Krancher, Oliver; Stahmann, Philip; Wanner, Jonas; Zschech, Patrick (2025).
Unveiling the multifunctional use of ochre in the Middle Stone Age: Specialized ochre retouchers from Blombos Cave. Velliky, Elizabeth C.; d’Errico, Francesco; van Niekerk, Karen L.; Henshilwood, Christopher S. (2025). 11(26) eads2797.
Ochre, an iron-rich pigment, is widely associated with symbolic communication, but its functional applications in the Middle Stone Age (MSA) remain poorly understood. Experimental and ethnographic evidence suggests ochre being useful for hide tanning, hafting adhesives, and skin protection, although direct archeological evidence is scarce. We address this gap by presenting ochre tools from Blombos Cave, South Africa, found in Still Bay to pre–Still Bay layers dated 90 to 70,000 years ago. Seven ochre pieces were deliberately modified into lithic retouchers, showing clear use-wear patterns and evidence of intentional shaping. Targeted experiments confirm that some were used for pressure flaking and were rejuvenated to maintain function. These findings provide direct evidence of ochre being used to retouch lithic artifacts during the MSA, highlighting its role in technological systems of this period. The results emphasize the multifunctionality of ochre and suggest that such curated tools may have held personal, cultural, or technological significance within early modern human communities. Seven ochre artifacts from Blombos Cave show evidence of lithic retouching and pressure flaking, revealing specialized MSA tools.
Graphs With Polarities. Baez, John C.; Chaudhuri, Adittya (2025).
In fields ranging from business to systems biology, directed graphs with edges labeled by signs are used to model systems in a simple way: the nodes represent entities of some sort, and an edge indicates that one entity directly affects another either positively or negatively. Multiplying the signs along a directed path of edges lets us determine indirect positive or negative effects, and if the path is a loop we call this a positive or negative feedback loop. Here we generalize this to graphs with edges labeled by a monoid, whose elements represent `polarities' possibly more general than simply "positive" or "negative". We study three notions of morphism between graphs with labeled edges, each with its own distinctive application: to refine a simple graph into a complicated one, to transform a complicated graph into a simple one, and to find recurring patterns called "motifs". We construct three corresponding symmetric monoidal double categories of "open" graphs. We study feedback loops using a generalization of the homology of a graph to homology with coefficients in a commutative monoid. In particular, we describe the emergence of new feedback loops when we compose open graphs using a variant of the Mayer-Vietoris exact sequence for homology with coefficients in a commutative monoid.
Federated Generalised Variational Inference: A Robust Probabilistic Federated Learning Framework. Mildner, Terje; Hamelijnck, Oliver; Giampouras, Paris; Damoulas, Theodoros (2025).
We introduce FedGVI, a probabilistic Federated Learning (FL) framework that is robust to both prior and likelihood misspecification. FedGVI addresses limitations in both frequentist and Bayesian FL by providing unbiased predictions under model misspecification, with calibrated uncertainty quantification. Our approach generalises previous FL approaches, specifically Partitioned Variational Inference (Ashman et al., 2022), by allowing robust and conjugate updates, decreasing computational complexity at the clients. We offer theoretical analysis in terms of fixed-point convergence, optimality of the cavity distribution, and provable robustness to likelihood misspecification. Further, we empirically demonstrate the effectiveness of FedGVI in terms of improved robustness and predictive performance on multiple synthetic and real world classification data sets.
Detecting LLM-Generated Peer Reviews. Rao, Vishisht; Kumar, Aounon; Lakkaraju, Himabindu; Shah, Nihar B. (2025).
The integrity of peer review is fundamental to scientific progress, but the rise of large language models (LLMs) has introduced concerns that some reviewers may rely on these tools to generate reviews rather than writing them independently. Although some venues have banned LLM-assisted reviewing, enforcement remains difficult as existing detection tools cannot reliably distinguish between fully generated reviews and those merely polished with AI assistance. In this work, we address the challenge of detecting LLM-generated reviews. We consider the approach of performing indirect prompt injection via the paper's PDF, prompting the LLM to embed a covert watermark in the generated review, and subsequently testing for presence of the watermark in the review. We identify and address several pitfalls in naïve implementations of this approach. Our primary contribution is a rigorous watermarking and detection framework that offers strong statistical guarantees. Specifically, we introduce watermarking schemes and hypothesis tests that control the family-wise error rate across multiple reviews, achieving higher statistical power than standard corrections such as Bonferroni, while making no assumptions about the nature of human-written reviews. We explore multiple indirect prompt injection strategies--including font-based embedding and obfuscated prompts--and evaluate their effectiveness under various reviewer defense scenarios. Our experiments find high success rates in watermark embedding across various LLMs. We also empirically find that our approach is resilient to common reviewer defenses, and that the bounds on error rates in our statistical tests hold in practice. In contrast, we find that Bonferroni-style corrections are too conservative to be useful in this setting.
Ready for VR? Assessing VR Competence and Exploring the Role of Human Abilities and Characteristics. Oberdörfer, Sebastian; Heinisch, Melina; Mühling, Tobias; Schreiner, Verena; König, Sarah; Latoschik, Marc Erich (2025).
The use of VR for educational purposes provides the opportunity for integrating VR applications into assessments or graded examinations. Interacting with an VR environment requires specific human abilities, thus suggesting the existence of a VR competence. With regard to the emerging field of VR-based examinations, this VR competence might influence a candidate's final grade and hence should be taken into account. In this paper, we proposed and developed a VR competence assessment application. The application features eight individual challenges that are based on generic 3D interaction techniques. In a pilot study, we measured the performance of 18 users. By identifying significant correlations between VR competence score, previous VR experience and theoretically-grounded contributing human abilities and characteristics, we provide first evidence that our VR competence assessment is effective. In addition, we provide first data that a specific VR competence exists. Our analyses further revealed that mainly spatial ability but also immersive tendency correlated with VR competence scores. These insights not only allow educators and researchers to assess and potentially equalize the VR competence level of their subjects, but also help designers to provide effective tutorials for first-time VR users.
Ready for VR? Assessing VR Competence and Exploring the Role of Human Abilities and Characteristics. Oberdörfer, Sebastian; Heinisch, Melina; Mühling, Tobias; Schreiner, Verena; König, Sarah; Latoschik, Marc Erich (2025).
The use of VR for educational purposes provides the opportunity for integrating VR applications into assessments or graded examinations. Interacting with an VR environment requires specific human abilities, thus suggesting the existence of a VR competence. With regard to the emerging field of VR-based examinations, this VR competence might influence a candidate's final grade and hence should be taken into account. In this paper, we proposed and developed a VR competence assessment application. The application features eight individual challenges that are based on generic 3D interaction techniques. In a pilot study, we measured the performance of 18 users. By identifying significant correlations between VR competence score, previous VR experience and theoretically-grounded contributing human abilities and characteristics, we provide first evidence that our VR competence assessment is effective. In addition, we provide first data that a specific VR competence exists. Our analyses further revealed that mainly spatial ability but also immersive tendency correlated with VR competence scores. These insights not only allow educators and researchers to assess and potentially equalize the VR competence level of their subjects, but also help designers to provide effective tutorials for first-time VR users.
Nonuniversality of inflammaging across human populations. Franck, Maximilien; Tanner, Kamaryn T.; Tennyson, Robert L.; Daunizeau, Camille; Ferrucci, Luigi; Bandinelli, Stefania; Trumble, Benjamin C.; Kaplan, Hillard S.; Aronoff, Jacob E.; Stieglitz, Jonathan; Kraft, Thomas S.; Lea, Amanda J.; Venkataraman, Vivek V.; Wallace, Ian J.; Lim, Yvonne A. L.; Ng, Kee Seong; Yeong, Joe Poh Sheng; Ho, Roger; Lim, Xinru; Mehrjerd, Ameneh; Charalambous, Eleftheria G.; Aiello, Allison E.; Pawelec, Graham; Franceschi, Claudio; Hertel, Johannes; Fülöp, Tamàs; Lemoine, Maël; Gurven, Michael; Cohen, Alan A. (2025).
Inflammaging, an age-associated increase in chronic inflammation, is considered a hallmark of aging. However, there is no consensus approach to measuring inflammaging based on circulating cytokines. Here we assessed whether an inflammaging axis detected in the Italian InCHIANTI dataset comprising 19 cytokines could be generalized to a different industrialized population (Singapore Longitudinal Aging Study) or to two indigenous, nonindustrialized populations: the Tsimane from the Bolivian Amazon and the Orang Asli from Peninsular Malaysia. We assessed cytokine axis structure similarity and whether the inflammaging axis replicating the InCHIANTI result increased with age or was associated with health outcomes. The Singapore Longitudinal Aging Study was similar to InCHIANTI except for IL-6 and IL-1RA. The Tsimane and Orang Asli showed markedly different axis structures with little to no association with age and no association with age-related diseases. Inflammaging, as measured in this manner in these cohorts, thus appears to be largely a byproduct of industrialized lifestyles, with major variation across environments and populations.
Leveraging AI to Improve the Discoverability and Classification of Linguistic Publications. Ho, Clara Wan Ching; Risse, Thomas; Vrdoljak, Ivana (2025).
Stretch to stretch, dust to dust: low-value local \($H_0$\) measurement from two-population modelling of type Ia supernovae. Wojtak, Radosław; Hjorth, Jens (2025).
Stretch to stretch, dust to dust: low-value local \($H_0$\) measurement from two-population modelling of type Ia supernovae. Wojtak, Radosław; Hjorth, Jens (2025).
Learning Theory from First Principles Bach, Francis (2025). The MIT Press.
Extreme synchronization transitions. Lee, Seungjae; Kuklinski, Lennart J.; Timme, Marc (2025). 16(1)
Semi-Supervised Learning with Noisy Labels Kober, Paula (2025).
Eye-to-Eye or Face-to-Face? Face and Head Substitution for Co-Located AR. Kullmann, Peter; Schell, Theresa; Botsch, Mario; Latoschik, Marc Erich (J. Saint-Aubert, ed.) (2025). 6
ANTS: Abstractive Entity Summarization in Knowledge Graphs. Firmansyah, Asep Fajar; Zahera, Hamada M.; Sherif, Mohamed Ahmed; and Moussallem, Diego; Ngonga Ngomo, Axel-Cyrille (2025).
On the role of AMOC weakening in shaping wintertime Euro-Atlantic atmospheric circulation. Vacca, Andrea Vito; Bellomo, Katinka; Fabiano, Federico; von Hardenberg, Jost (2025). 63(6) 273.
Climate change simulations project the slowdown of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) in the 21st century, though the rate and extent of the decline vary across models. In the Euro-Atlantic region, where the AMOC strongly influences sea surface temperature (SST) variability, climate projections also show significant uncertainty in the evolution of large-scale atmospheric circulation. We hypothesise that the decline of the AMOC and the uncertainty in Euro-Atlantic atmospheric circulation are interconnected. To test this, we analyse three coordinated experiments from the CMIP6 archive (SSP2\\($\$\)-\\($\$\)4.5, SSP5\\($\$\)-\\($\$\)8.5 and abrupt-4xCO2) adopting a storyline approach. In particular, we compare groups of models projecting a larger AMOC decline to groups of models projecting a smaller AMOC decline. Our results indicate that a stronger AMOC weakening is associated with an intensification of the North Atlantic storm track and jet stream, as well as an increased frequency of the NAO\\($\$\)+\\($\$\)weather regime. We link these atmospheric changes to the influence of a reduced warming of the subpolar North Atlantic, known as the North Atlantic Warming Hole (NAWH), associated with the AMOC weakening. To further support our findings, we conduct an additional experiment using the EC-Earth3 model, comparing an abrupt-4xCO2 experiment with one where the AMOC is fixed at preindustrial levels. This experiment corroborates the CMIP6 analysis and validates our hypothesis. We conclude that the AMOC plays a critical role in driving atmospheric changes over the Euro-Atlantic region. Improved monitoring and better constraints on future AMOC decline would help reduce uncertainty in predictions of atmospheric circulation and climate impacts over Europe.
On the O(frac√d. Li, Huan; Dong, Yiming; Lin, Zhouchen (2025).
Security and Privacy of Current and Emerging IoT Devices and Systems (Dagstuhl Seminar 2431). Crispo, Bruno; Dmitrienko, Alexandra; Tsudik, Gene; Xu, Wenyuan; Sendner, Christoph (2025).
Key components of effective non-pharmacological interventions for childhood obesity: a review considering social determinants of health. Zamanillo-Campos, R; Colom-Rossello, M; Rodríguez-Calero, M A; Martín, M I; Planas, T; Núñez-Jiménez, C; Ramos, M (2025). 184(7) 449–449.
Childhood obesity, driven by an obesogenic environment, remains a public health priority. To review the effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions for treating childhood obesity, with a focus on weight reduction and consideration of social determinants of health (SDOH). The review included randomized and quasi-experimental studies, published between August 2016 and December 2021, that evaluated the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing body weight in children aged 2 to 14 years with obesity. (PROSPERO ID: CRD42022301191). A total of 59 interventions were identified, showing wide variability in design, duration, components and settings. Most included physical activity (93%) and nutrition (81%), while fewer incorporated psychological support (46%) or digital tools (25%). Despite the diversity of approaches, 56% of the interventions were effective, particularly those implemented in healthcare or school settings, involving physical activity, and delivered by multidisciplinary teams. However, only six demonstrated sustained effects beyond 6 months. Risk of bias was high in over half of the studies, and only a small proportion (22%) reported participants' social characteristics such as family structure, race, or socioeconomic status. Importantly, very few interventions were designed or evaluated with explicit consideration of SDOH. CONCLUSION: Overall, effective interventions tended to target both children and parents, include multiple components-especially physical activity-and be delivered in accessible settings such as schools or primary care. Yet, the generalizability of findings is limited, as most studies involved children from relatively advantaged backgrounds. Future interventions should integrate SDOH in both design and evaluation to ensure equity and long-term effectiveness in diverse populations. WHAT IS KNOWN: • Childhood obesity remains a critical public health issue, heavily influenced by obesogenic environments and social determinants of health (SDOH). • Non-pharmacological interventions, particularly those incorporating physical activity and nutritional guidance, have been commonly used to address childhood obesity, though with varying degrees of success. WHAT IS NEW: • This review highlights that interventions delivered in healthcare or school settings by multidisciplinary teams, and involving both physical activity and parental engagement, show higher effectiveness in reducing childhood obesity. • The study identifies a significant gap in the integration of social determinants of health in both the design and evaluation of interventions, limiting their long-term impact and equity across diverse populations.
AI Narrative Breakdown. A Critical Assessment of Power and Promise. Rehak, Rainer in FAccT ’25 (2025). 1250–1260.
This article sets off for an exploration of the still evolving discourse surrounding artificial intelligence (AI) in the wake of the release of ChatGPT. It scrutinizes the pervasive narratives that are shaping the societal engagement with AI, spotlighting key themes such as agency and decision-making, autonomy, truthfulness, knowledge processing, prediction, general purpose, neutrality and objectivity, apolitical optimization, sustainability game-changer, democratization, mass unemployment, and the dualistic portrayal of AI as either a harbinger of societal utopia or dystopia. Those narratives are analysed critically based on insights from critical computer science, critical data and algorithm studies, from STS, data protection theory, as well as from the philosophy of mind and semiotics. To properly analyse the narratives presented, the article first delves into a historical and technical contextualisation of the AI discourse itself. The article then introduces the notion of "Zeitgeist AI" to critique the imprecise and misleading application of the term "AI" across various societal sectors. Then, by discussing common narratives with nuance, the article contextualises and challenges often assumed socio-political implications of AI, uncovering in detail and with examples the inherent political, power infused and value-laden decisions within all AI applications. Concluding with a call for a more grounded engagement with AI, the article carves out acute problems ignored by the narratives discussed and proposes new narratives recognizing AI as a human-directed tool necessarily subject to societal governance.
Inference Scaling for Long-Context Retrieval Augmented Generation. Yue, Zhenrui; Zhuang, Honglei; Bai, Aijun; Hui, Kai; Jagerman, Rolf; Zeng, Hansi; Qin, Zhen; Wang, Dong; Wang, Xuanhui; Bendersky, Michael (2025).
HyperPianist: Pianist with Linear-Time Prover and Logarithmic Communication Cost. Li, Chongrong; Zhu, Pengfei; Li, Yun; Hong, Cheng; Qu, Wenjie; Zhang, Jiaheng (2025). 3383–3401.
Prompt Inversion Attack Against Collaborative Inference of Large Language Models. Qu, Wenjie; Zhou, Yuguang; Wu, Yongji; Xiao, Tingsong; Yuan, Binhang; Li, Yiming; Zhang, Jiaheng (2025). 1695–1712.
Alternating Guided Training for Robust Adversarial Defense. Liu, Xinlei; Ma, Chunlai; Chen, Bo; Hu, Tao; Ma, Hailong; Yi, Peng; Jiang, Yiming; Hu, Yuxiang Z. (Mark) Zhang, E. Ricci, Y. Yan, L. Nie, V. Oria, L. Ballan (eds.) (2025). 2008–2012.
Generating Single Cell RNA-seq Data with Diffusion Models Fuchs, Felix (2025).
Sustainable visions: unsupervised machine learning insights on global development goals. García-Rodríguez, Alberto; Núñez, Matias; Pérez, Miguel Robles; Govezensky, Tzipe; Barrio, Rafael A; Gershenson, Carlos; Kaski, Kimmo K; Tagüeña, Julia (2025). 20(3)
Energy Efficient Virtual MIMO Communication Designed for Cluster based on Cooperative WSN using Oleach Protocol. Upreti, Shitiz; Naruka, Mahaveer Singh (N. Meghanathan, ed.) (2025). 17(3) 73–88.
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) use a vast number of sensor nodes to monitor physical states. The restricted energy supplies of sensor nodes is a significant issue in wireless communication systems. Virtual MIMO (vMIMO) is an implementation that can potentially optimize the energy efficiency in WSNs by sending or receiving data from a large number of nodes, improving the signal quality, and minimizing power. This research presents Energy-Efficient Virtual MIMO Communication (EE-VMC), a new solution to Wireless Sensor Networks' (WSNs) energy efficiency problem. EE-VMC provides a practicable solution to long-term cooperative cluster-based WSN deployments with communication via virtual Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO).In order to spread energy efficiency through effective communication and reduced energy use, the proposed approach uses an enhanced LEACH (OLEACH) protocol. The OLEACH method performs well for wireless sensor networks, according to simulation data. At a level of -10dB of SNR, OLEACH provides the best Packet Delivery Ratio (PDR), which demonstrates improved performance in low signal-to-noise ratio. Increasing antennas enhances the performance of data delivery of OLEACH. Compared to cutting-edge protocols (LEACH, HEED, BRICH, and B-LEACH), OLEACH consistently outperforms them as far as PDR, SNR values, and rounds of data transfer are concerned. Furthermore, OLEACH has greater residual energy levels, a sign of enhanced energy management and enhanced network lifetime. The conclusions are supported by the results to further ascertain that OLEACH is a prospective algorithm for optimizing energy usage, enhancing packet delivery, and enhancing general performance of networks within wireless sensor networks.
Hybrid Transformer-Based Classification for Web-Based Injection Attack Detection: A Novel Roberta-XLNet Approach. Seethawaka, Ranuja; Nambuwasam, Chathurya; Chandrasiri, D.K.W.G.G.T.; Kavithma, K.A.S.; Fernando, Harinda; Wijesooriya, Ayesha (D. S. Kumar, ed.) (2025). 1(4) 35–39.
In wind energy conversion system voltage control and reactive power compensation is the main problem. This paper presents vector oriented control of three-phase voltage source pulse width modulation (PWM) inverter which aims to control of active and reactive power injected into the grid. A wind driven Induction Generator in Self excited mode feed power to load through a ac-dc-ac converter. The modulation index of the inverter is adjusted using vector oriented control to enhance the active power export and reduce the reactive power requirement. The scheme is modeled in Matlab/Simulink and simulation is carried out to study the performance at varying wind speed.
Feasibility study of a mission to Sedna -- Nuclear propulsion and advanced solar sailing concepts. Ancona, Elena; Kezerashvili, Roman Ya.; Longo, Savino (2025).
Exploring the outer reaches of the Solar System presents significant propulsion and mission design challenges. This study assesses the feasibility of a mission to Sedna using two advanced propulsion concepts: the Direct Fusion Drive (DFD) rocket engine, based on D-3He thermonuclear fusion, and a solar sail utilizing thermal desorption of its coating for propulsion. Both are evaluated for a one-way Earth-to-Sedna mission; however, due to the different performances the DFD would enable orbit insertion, whereas for the solar sail a flyby is envisioned. The analysis evaluates key mission parameters, including delivered payload capacity, travel time, and potential science return. For the DFD, we assume a 1.6 MW system with constant thrust and specific impulse, while for the solar sail, we consider acceleration via thermal desorption and a gravity-assist maneuver around Jupiter. The mission analysis incorporates four key phases: departure, interplanetary acceleration, interplanetary coasting, and rendezvous. Sedna is expected to pass through the perihelion of its orbit in 2075--2076 and then move again away from the Sun. Considering the distances involved, a mission targeting the object would need to be launched "relatively" soon, especially if using conventional propulsion systems, which could require up to 30 years of deep-space travel. In our study, results indicate that the DFD could reach Sedna in approximately 10 years, with 1.5 years of thrusting, while the solar sail, assisted by Jupiter's gravity, could complete the journey in 7 years. The feasibility of science payload accommodation, power availability, and communication constraints is also considered. These findings provide a comparative foundation for future deep-space mission planning.
The role of insularity: Plants have few ornithophilous traits but are visited by morphologically more distinct hummingbirds in the Caribbean islands. Vollstädt, Maximillian G. R.; Jensen, Rasmus D.; Maruyama, Pietro K.; Schleuning, Matthias; Araújo‐Hoffmann, Francielle P.; Sazima, Marlies; Sonne, Jesper; Schrøder, Taia S. O.; Møller‐Stranges, Fredrik; Abrahamczyk, Stefan; Ramírez‐Burbano, Mónica B.; de Vasconcelos, Marcelo Ferreira; Tinoco, Boris A.; Maglianesi, María A.; Partida‐Lara, Ruth; Vázquez‐Pérez, José Raúl; Enríquez, Paula L.; Rech, André Rodrigo; Coelho, Aline G.; Gonçalves, Fernando; da Silva Neto, Edvaldo Nunes; Filho, Manoel Martins Dias; Reis, Matheus; Marín‐Gómez, Oscar H.; Ornelas, Juan Francisco; Cotton, Peter A.; Oliveira, Paulo Eugenio; Machado, Adriana Oliveira; Vizentin‐Bugoni, Jeferson; Bergamo, Pedro Joaquim; Lara, Carlos; Rocca, Márcia Alexandra; Sazima, Ivan; Gonzalez, Oscar; Fischer, Erich; Araujo, Andréa C.; Ortiz‐Pulido, Raúl; Patiño, Blanca; López, Rubén Pineda; Watts, Stella; Alarcon, Ruben; Machado, Caio Graco; Las‐Casas, Flor Maria G.; Simmons, Benno I.; Kaiser‐Bunbury, Christopher N.; Bilde, Trine; Dalsgaard, Bo (2025). 39 1678–1692.
Swarming rate and timing of unmanaged honeybee colonies (Apis mellifera carnica) in a forest environment. Rutschmann, B.; Kohl, P. L.; Steffan-Dewenter, I. (2025).
Investigating the life history of social insect colonies and the demography of their populations are important for their conservation, but data collection is challenging. There is a growing interest in understanding the population status of wild-living honeybee colonies across Europe, for which it is critical to collect data on survival and natality rates. Although survival rates can be investigated through regular inspections of wild nests, the accurate quantification of natality rates (i.e., the number of swarms produced per colony per year) remains a significant challenge. Using digital weight scales, we remotely monitored the natural swarming behavior of ten unmanaged Apis mellifera carnica colonies housed in static-volume hives (45 L) in a forest region of southern Germany. During the 2019 season, between mid-May and late June, we recorded 17 swarming events, averaging 1.7 swarms per colony. Our observations offer a reference point for the timing, frequency, and size of honeybee swarms that helps us understand the natural reproductive patterns of wild-living honeybees in a temperate forest environment.
Control of photoluminescence properties by tailored supramolecular matrices. Würthner, Frank; Hariharan, Mahesh (2025). 7(5) 208–224.
Photoluminescence (PL) is a property of great interest in science and technology. Here we review recent approaches for the control of fluorescence and phosphorescence by tailored supramolecular environments. Taking recent examples from solid-state materials as applied in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), supramolecular complexes, cyclophanes, foldamers, and protein–dye complexes, as well as DNA and RNA aptamers, we showcase how specific ‘smart’ matrices can modulate PL properties including brightness, quantum yield, wavelength, and lifetime. From the examples collected in this review it becomes evident that, by means of an advanced understanding of specific interactions of chromophores with the surrounding matrix, relevant processes in the excited state can be controlled in a desired way, leading to improved light-emitting materials.
RNN-GAN Integration for Enhanced Voice-Based Email Accessibility: A Comparative Study for Visually Impaired Users. Deepti, A R; K, Vivek; Basith, Farzeen; Manimekala, B (2025).
The Significance of Genetic Relatedness and Nest Sharing on the Worker‐Worker Similarity of Gut Bacterial Microbiome and Cuticular Hydrocarbon Profile in a Sweat Bee. Ronchetti, Federico; Schmitt, Thomas; Keller, Alexander; García‐Reina, Andrés; De la Rua, Pilar; Steffan‐Dewenter, Ingolf; Polidori, Carlo (2025). 15(6) e71519.
The Gulf Stream: Its History and Links to Coastal Impacts and Climate Change. Ezer, Tal (2025).
The Gulf Stream (GS) is possibly the world's most widely recognized oceanic feature—from encounters by Spanish sailors in the 1500s, to Benjamin Franklin's charts in the 1700s, to early observations by Stommel and other in the 1900s. Today, modern undersea observations, satellite data, and computer models have revealed the GS's complex nature, though some challenges remain. This review provides an overview of past and recent studies of the GS, with a focus on links between the GS, extreme weather events, climate change, and coastal impacts. Examples of those links include a potential slowdown of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) and the GS that could increase coastal flooding, and hurricanes that disrupt the flow of the GS and cause posthurricane coastal sea level rise. A better understanding of the role of the GS in the Earth's system will help in the prediction of future climate change.
SDNet: Noise-Robust Bandwidth Extension under Flexible Sampling Rates. Yang, Junkang; Liu, Hongqing; Gan, Lu; Zhou, Yi; Li, Xing; Jia, Jie; Yao, Jinzhuo (2024). 1–6.
Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model for Realistic Financial Correlation Matrices. Kubiak, Szymon; Weyde, Tillman; Galkin, Oleksandr; Philps, Daniel; Gopal, Ram (2024). 1–9.
A 0.04 μJ/ Classification High-Accuracy Energy-Efficient ECG Processor with SNN On-Chip Backpropagation and Adaptive Threshold Encoding. Fan, Haodong; Zhou, Junlu; Guo, Zilong; Chang, Zhiyuan; Yang, Xi; Hu, Zhicheng; Zeng, Jiahao; Lin, Shuisheng; Zhou, Liang; Zhou, Jun; Zhang, Li; Huang, Jinxi; Su, Jianlei; Gao, Wei; Wu, Qiang; Chang, Liang (2024). 1–3.
A 28nm 118.26TOPS/W Multi-Dimensional Fault-Tolerant Al Processor Enabling Voltage-Frequency Scaling Below Point-of-First-Failure. Wang, Yang; Yang, Xiaolong; Qin, Yubin; Zhao, Zhiren; Guo, Ruiqi; Yue, Zhiheng; Wei, Shaojun; Hu, Yang; Yin, Shouyi (2024). 1–3.
Time Series Diffusion in the Frequency Domain. Crabbé, Jonathan; Huynh, Nicolas; Stanczuk, Jan Pawel; Van Der Schaar, Mihaela in Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, R. Salakhutdinov, Z. Kolter, K. Heller, A. Weller, N. Oliver, J. Scarlett, F. Berkenkamp (eds.) (2024). (Vol. 235) 9407–9438.
Fourier analysis has been an instrumental tool in the development of signal processing. This leads us to wonder whether this framework could similarly benefit generative modelling. In this paper, we explore this question through the scope of time series diffusion models. More specifically, we analyze whether representing time series in the frequency domain is a useful inductive bias for score-based diffusion models. By starting from the canonical SDE formulation of diffusion in the time domain, we show that a dual diffusion process occurs in the frequency domain with an important nuance: Brownian motions are replaced by what we call mirrored Brownian motions, characterized by mirror symmetries among their components. Building on this insight, we show how to adapt the denoising score matching approach to implement diffusion models in the frequency domain. This results in frequency diffusion models, which we compare to canonical time diffusion models. Our empirical evaluation on real-world datasets, covering various domains like healthcare and finance, shows that frequency diffusion models better capture the training distribution than time diffusion models. We explain this observation by showing that time series from these datasets tend to be more localized in the frequency domain than in the time domain, which makes them easier to model in the former case. All our observations point towards impactful synergies between Fourier analysis and diffusion models.
Knowledge Generation for Zero-shot Knowledge-based VQA. Cao, Rui; Jiang, Jing Y. Graham, M. Purver (eds.) (2024). 533–549.
HPL-ESS: Hybrid Pseudo-Labeling for Unsupervised Event-based Semantic Segmentation. Jing, Linglin; Ding, Yiming; Gao, Yunpeng; Wang, Zhigang; Yan, Xu; Wang, Dong; Schaefer, Gerald; Fang, Hui; Zhao, Bin; Li, Xuelong (2024). 23128–23137.
A 28nm 76.25TOPS/W RRAM/SRAM-Collaborative CIM Fine-Tuning Accelerator with RRAM-Endurance/Latency-Aware Weight Allocation for CNN and Transformer. Mu, Chen; Huang, Zhirui; Jiang, Hao; Liao, Jie; Jiao, Bo; Zhou, Yuliang; Zhu, Haozhe; Yang, Jianguo; Liu, Qi; Chen, Chixiao (2024). 1–3.
A 75.6Gb/S 22-Bit Floating-Point Reconfigurable DSP Accelerator Embedding 2048×256-Point Complex FFT and 26K-Point 1-D Signal Processing. Xu, Xuanzhe; Liu, Xianjun; Wei, Siyuan; Yu, Shuangming; Dou, Runjiang; Yang, Xu; Wang, Zhe; Liu, Jian; Wu, Nanjian; Liu, Liyuan (2024). 1–3.
A 64-channel SPAD-based LiDAR sensor with Compact Coincidence Detection Circuit and Inter-frame Correlation-based Nonlinear Partial Histogram Builder. Hu, Jin; Li, Dong; Wang, Xiayu; Ma, Rui; Liu, Yang; Zhu, Zhangming (2024). 1–3.
A 28-nm 323 TOPS/mm2/b and 2007 TOPS/W/b Ternary Latch Based Sparsity-Aware CIM Macro With Double-Sampling Ternary ADC. Kim, Myoung; Jeong, Hoichang; Kim, Woo-Seok; Jeong, Yesong; Choi, Young-Eun; Park, Junyoung; Ryu, Min Woo; Lee, Yong Kyu; Lee, Kyuho Jason; Kim, Kyung Rok (2024). 1–3.
A reduced complexity MLSD-based adaptive Duo-PAM4 detector in 28-nm CMOS for 56-Gb/s wireline receiver. Xu, Chaolong; Lv, Fangxu; Lai, Mingche; Luo, Zhang; Qi, Xingyun; Xu, Jiaqing; Wang, Qiang; Xiao, Liquan; Liu, Cewen; Xu, Hua (2024). 1–3.
RMMIC: A 40 μW Reconfigurable Multi-modal Multi-channel Interface Circuit System for Bio-signals Monitoring. Zhou, Ting; Huang, Jiajie; Wang, Chao; Hao, Yuzhi; Ji, Yuxin; Gu, Zhiwen; Gao, Zhuo; Yang, Feng; Zhang, Yuhang; Zhao, Yang; Zhao, Jian; Liu, Yan; Chen, Mingyi; Wang, Guoxing; Lian, Yong; Li, Yongfu (2024). 1–3.
A Wireless Battery-Free Cerebral-Oxygen-Monitoring Micro-System Featuring 0.028% Sensing Resolution. Wang, Weixiao; Zhu, Boyu; Xuan, Yangfan; Shen, Yili; Xiao, Qijing; Wang, Zhiyu; Luo, Yuxuan; Pan, Gang; Su, Bin; Zhao, Bo (2024). 1–3.
A 13.75-14.75-GHz 32.1-fsRMS Jitter -100.6-dBc Reference Spur -261.4-dB FoM Sub-Sampling PLL Using a KPD-Doubled Isolated Sub-Sampling Phase Detector for Reliable Spur-Jitter-Joint Optimization. Xu, Yiqing; Li, Yixi; Zhang, Zhao; Qi, Nan; Liu, Jian; Wu, Nanjian; Liu, Liyuan (2024). 1–3.
ANVMP: A 28nm 52.6 μW 1.25pJ/SOP Asynchronous Non- Volatile-Memory-based Computing-In-Memory Neuromorphic Processor for Edge-Al Applications. Zhang, Jilin; Wei, Qiumeng; Huo, Dexuan; Li, Tao; Gao, Bin; Qian, He; Wu, Huaqiang; Tang, Kea-Tiong; Chen, Hong (2024). 1–3.
A 0.0006-mm2 0.13-pJ/bit 9-21-Gb/s Sampling CDR with Inverter-Based Frequency Multiplier and Embedded 1: 3 DEMUX in 65-nm CMOS. Dong, Zhicheng; Zhao, Xiaoteng; Yang, Zekai; Su, Xianting; Han, Haolin; Bu, Feng; Zhou, Rong; Sun, Depeng; Chen, Yong; Liu, Shubin; Ding, Ruixue; Zhu, Zhangming (2024). 1–3.
A 32×32 SPAD LiDAR Sensor with In-pixel Spatial-temporal Coincidence and Per-SPAD Pulse Delay for Resolution-lossless Imaging. Chen, Bu; Huang, Zhangcheng; Wang, Jingyi; Shang, Hongyang; Lv, Hankun; Liu, Qi; Liu, Ming (2024). 1–3.
Ant-Search Algorithm for Distributed Knowledge Graphs. Chepizhko, Oleksandr; Forgács, Péter; Schranz, Melanie (2024).
Plants and Bee Visitors in the Eastern Afromontane Biodiversity Hotspot of Kenya, East Africa. Dzekashu, Fairo F.; Peters, Marcell K.; Steffan‐Dewenter, Ingolf; Macharia, Jayne M.; Matheka, Kennedy W.; Yusuf, Abdullahi A.; Pirk, Christian W. W.; Lattorff, H. Michael G. (2024). 106(1) e02211.
The Two-Bridge Ant Experiment as an Interactive Netlogo Library Model. Umlauft, Martina; Schranz, Melanie (2024).
Efficient self-organization of informal public transport networks. Mittal, Kush Mohan; Timme, Marc; Schröder, Malte (2024). 15(1)
RePreM: Representation Pre-training with Masked Model for Reinforcement Learning. Cai, Yuanying; Zhang, Chuheng; Shen, Wei; Zhang, Xuyun; Ruan, Wenjie; Huang, Longbo B. Williams, Y. Chen, J. Neville (eds.) (2023). 6879–6887.
Citizen scientists report global rapid reductions in the visibility of stars from 2011 to 2022. Kyba, Christopher C. M.; Altıntaş, Yiğit Öner; Walker, Constance E.; Newhouse, Mark (2023). 379(6629) 265–268.
The artificial glow of the night sky is a form of light pollution; its global change over time is not well known. Developments in lighting technology complicate any measurement because of changes in lighting practice and emission spectra. We investigated the change in global sky brightness from 2011 to 2022 using 51,351 citizen scientist observations of naked-eye stellar visibility. The number of visible stars decreased by an amount that can be explained by an increase in sky brightness of 7 to 10% per year in the human visible band. This increase is faster than emissions changes indicated by satellite observations. We ascribe this difference to spectral changes in light emission and to the average angle of light emissions. Artificial lighting that escapes into the sky causes it to glow, preventing humans and animals from seeing the stars. Satellites can measure the light emitted upward, but they are not sensitive to all wavelengths produced by LED lighting or to light emitted horizontally. Kyba et al. used data from citizen scientists to measure how light pollution is affecting human views of the stars worldwide (see the Perspective by Falchi and Bará). Participants were shown maps of the sky at different levels of light pollution and asked which most closely matched their view. Trends in the data showed that the average night sky got brighter by 9.6% per year from 2011 to 2022, which is equivalent to doubling the sky brightness every 8 years. —KTS Observations of the night sky by citizen scientists show that it is rapidly getting brighter due to light pollution.
Hierarchical Relational Learning for Few-Shot Knowledge Graph Completion. Wu, Han; Yin, Jie; Rajaratnam, Bala; Guo, Jianyuan (2023).
Imitation Learning to Outperform Demonstrators by Directly Extrapolating Demonstrations. Cai, Yuanying; Zhang, Chuheng; Shen, Wei; He, Xiaonan; Zhang, Xuyun; Huang, Longbo M. A. Hasan, L. Xiong (eds.) (2022). 128–137.
Dynamics of ranking. I~niguez, Gerardo; Pineda, Carlos; Gershenson, Carlos; Barabási, Albert-László (2022). 13(1)
TD3 with Reverse KL Regularizer for Offline Reinforcement Learning from Mixed Datasets. Cai, Yuanying; Zhang, Chuheng; Zhao, Li; Shen, Wei; Zhang, Xuyun; Song, Lei; Bian, Jiang; Qin, Tao; Liu, Tieyan X. Zhu, S. Ranka, M. T. Thai, T. Washio, X. Wu (eds.) (2022). 21–30.
A Transformer-Based User Satisfaction Prediction for Proactive Interaction Mechanism in DuerOS. Shen, Wei; He, Xiaonan; Zhang, Chuheng; Zhang, Xuyun; Xie, Jian M. A. Hasan, L. Xiong (eds.) (2022). 1777–1786.
Experimental Characterization Techniques for Solid-Liquid Slurry Flows in Pipelines: A Review. Silva, Rui C. (2022). 10(3)
In industrial environments, having instrumentation able to attain fast, accurate, and autonomous measurements is pivotal to understanding the dynamics of liquid and particles during transport. Ideally, these instruments, consisting of either probes or sensors, should be robust, fast, and unintrusive, i.e., not cause interference on the very flows being monitored, and require minimal maintenance. Beyond monitoring, the process knowledge gained through real time inspection allows teams to make informed technical decisions based on particle behavior, i.e., settling of particles causing pipe wear and clustering or blockages that can damage the unit or cause shutdowns, both of which with economical drawbacks. The purpose of this review is to examine experimental measurement techniques used to characterize physical properties and operational parameters of solid-liquid slurry flows, focusing on non-ionizing radiation methods. With this text the intent is not to provide an exhaustive examination of each individual technique but rather an overview on the most pertinent types of instrumentation, which will be presented, in addition to application examples from the literature, while directing the reader for pertinent seminal and review papers for a more in-depth analysis.
COVID-19 in South Africa: outbreak despite interventions. Schröder, Malte; Bossert, Andreas; Kersting, Moritz; Aeffner, Sebastian; Coetzee, Justin; Timme, Marc; Schlüter, Jan (2021). 11(1)
Incentive-driven transition to high ride-sharing adoption. Storch, David-Maximilian; Timme, Marc; Schröder, Malte (2021). 12(1)
Feldmessgeräte: 1. AgriSens FELDTAG „Einsatz von Fernerkundungstechnologien in der Landwirtschaft“. Truckenbrodt, Sina; Ahmadian, Nima; Borg, Erik; Gerighausen, Heike; Böttcher, Falk; Conrad, Christopher; Dahms, Thorsten; Harfenmeister, Katharina; Hüttich, Christian; Dhillon, Maninder Singh; Spengler, Daniel; Thürkow, Detlef; Thiel, Michael (2021).
cCorrGAN: Conditional Correlation GAN for Learning Empirical Conditional Distributions in the Elliptope. Marti, Gautier; Goubet, Victor; Nielsen, Frank in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, F. Nielsen, F. Barbaresco (eds.) (2021). (Vol. 12829) 613–620.
The Busy Beaver Frontier. Aaronson, Scott (2020). 51(3) 32–54.
The Busy Beaver function, with its incomprehensibly rapid growth, has captivated generations of computer scientists, mathematicians, and hobbyists. In this survey, I o er a personal view of the BB function 58 years after its introduction, emphasizing lesser-known insights, recent progress, and especially favorite open problems. Examples of such problems include: when does the BB function rst exceed the Ackermann function? Is the value of BB(20) independent of set theory? Can we prove that BB(n + 1) > 2BB(n) for large enough n? Given BB(n), how many advice bits are needed to compute BB(n + 1)? Do all Busy Beavers halt on all inputs, not just the 0 input? Is it decidable, given n, whether BB(n) is even or odd?
CORRGAN: Sampling Realistic Financial Correlation Matrices Using Generative Adversarial Networks. Marti, Gautier (2020). 8459–8463.
Comparing the performance of crop growth models using synthetic remote sensing data at DEMMIN, Germany. Dhillon, Maninder Singh; Dahms, Thorsten; Kuebert-Flock, Carina; Conrad, Christopher (2019).
This research has been conducted on a main agricultural production region of the NorthEast Germany over the time frame of 2015. Five widely used crop growth models, namely, WOFOST, Aqua Crop, Ceres Wheat, CropSyst and Light Use Efficiency (LUE), are compared to predict the biomass of winter wheat. To obtain the higher spatial and temporal coverage, this study explains the usage of a fusion model in which both Landsat (30m) and Modis (500m) were combined to generate the synthetic remote sensing time series for the accurate evaluation of vegetation on a daily basis.
Thermodynamics of NaHCO3 decomposition during Na2CO3-based CO2 capture. Toan, Sam; O’Dell, William; Russell, Christopher K.; Zhao, Sun; Lai, Qinghua; Song, Huiping; Zhao, Ying; Fan, Maohong (2019). 78 74–80.
Amine-basedcarbon-capture technologies have been shown to be energetically expensive and to cause significant environmental and epidemiological impacts due to their volatility. Bicarbonate formation from carbon dioxide's reaction with water has been suggested as an effective alternative for capturing CO2; however, the thermodynamics of this reaction are not well understood. This study experimentally determined the equilibrium constant of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) decomposition to sodium, water, and carbon dioxide; the study also compared the equilibrium constant to theoretical calculations. Using a combination of experimentation and thermodynamic relationships, the unitless equilibrium constants of the forward and reverse reactions were calculated accurately (error <±9% and <±4%, respectively). Equilibrium data were calculated using enthalpy and entropy values of each component of NaHCO3 decomposition at temperatures ranging from 25 to 155°C respectively. These results offer more data essential to optimizing NaHCO3 use in environmentally friendly next-generation CO2-capture technologies.
An Analysis of Surface and Growth Differences in Plants of Different Stages Using Image Processing. Rashid, Faizur; Delesa, Tamirat (F. Rashid; T. Delesa, eds.) (2019). 9(4) 1–7.
Genomes are main reason for growth and surface differences in the plants. All plants grow on basis of their different surrounding like soil, water, breed of seed, and climatic session. This paper attempts to find stem growth from birth to maturity level of selected plant using image processing technique. Few reasons have been observed commonly by the researchers that some plants could not grow sufficiently as to the other plants of similar breed and age. Images were taken of different stage of bean plant and images of some other plant samples were also included for better assessment. Researchers are trying to understand through their calculative analysis by image processing emulator in MATLAB to view its reasons. Suitable comparison technique is applied to detect their period of growth. Image processing methods like Restoration, stem or leaves spots, filtering, and plant comparison have applied in MATLAB. Those effects that are not supporting to grow the plants of their similar age group are matter to calculate scientifically later in the future. The observation would help for further support in medicinal science or agricultural science of plant and Bio-chemical.
Light Use Efficiency Model to Estimate Biomass and YIELD with and Without Vapour Pressure Deficit Dhillon, Maninder Singh; Dahms, Thorsten; Nill, Leon (2018). University of Würzburg.
Evaluation Criteria for Selecting NoSQL Databases in a Single Box Environment. Ryan D. L. Engle, Brent T. Langhals; Hodson, Douglas D. (2018). 10(4) 01–12.
In recent years, NoSQL database systems have become increasingly popular, especially for big data, commercial applications. These systems were designed to overcome the scaling and flexibility limitations plaguing traditional relational database management systems (RDBMSs). Given NoSQL database systems have been typically implemented in large-scale distributed environments serving large numbers of simultaneous users across potentially thousands of geographically separated devices, little consideration has been given to evaluating their value within single-box environments. It is postulated some of the inherent traits of each NoSQL database type may be useful, perhaps even preferable, regardless of scale. Thus, this paper proposes criteria conceived to evaluate the usefulness of NoSQL systems in small-scale single-box environments. Specifically, key value, document, column family, and graph database are discussed with respect to the ability of each to provide CRUD transactions in a single-box environment.
Experience in the implementation of projects in professional environment in a 1st cycle of studies of Civil Engineering. Ribeiro, Diogo; Neto, Teresa; Santos, Ricardo; de Fátima Portela, Maria F. J. García-Peñalvo (ed.) (2018). 93–99.
Toponimi u Desnama: rodnome selu fra Jeronima Šetke. Vidović, Domagoj (2016).
Metodologija izrade toponimijskoga (anojkonimijskoga) rječnika (primijenjena na toponimiju ludbreške Podravine). Horvat, Joža (2016). 25 75–142.
Joint Modeling of Users’ Interests and Mobility Patterns for Point-of-Interest Recommendation. Yin, Hongzhi; Cui, Bin; Huang, Zi; Wang, Weiqing; Wu, Xian; Zhou, Xiaofang X. Zhou, A. F. Smeaton, Q. Tian, D. C. A. Bulterman, H. T. Shen, K. Mayer-Patel, S. Yan (eds.) (2015). 819–822.
Unifying Local and Global Agreement and Disagreement Classification in Online Debates. Yin, Jie; Narang, Nalin; Thomas, Paul; Paris, Cécile A. Balahur, A. Montoyo, P. Martínez-Barco, E. Boldrini (eds.) (2012). 61–69.
Doing Bayesian data analysis. A tutorial introduction with R and BUGS Kruschke, John (2011). (First ) Academic Press, Amsterdam.
Discripti in decurias (Plin. Nat. hist. 3, 142-143): uređenje osvojenih područja pod Augustom. Čače, Slobodan (2010). 57–81.
Etnička, konfesionalna i regionalna imena i nadimci u Hercegovini XV–XIX st. Dodig, Radoslav (2009).
Ivan Babić: Studenački rječnik, Župni red Studenci, Studenci, 2008., 556 str. Dodig, Radoslav (2009). (23) 293–296.
Addressing the out-of-vocabulary problem for large-scale Chinese spoken term detection. Meng, Sha; Shao, Jian; Yu, Roger Peng; Liu, Jia; Seide, Frank (2008). 2146–2149.
Toponimija hrvatskoga Jadranskog prostora Šimunović, Petar (2005). (Vol. 2) 319-. Golden marketing, Zagreb.
Abrasive Flow Polishing of Micro Bores. Yin, Ling; Ramesh, Kuppuswamy; Wan, Stephen; Liu, Xiang Dong; Huang, Han; Liu, Yu Chan (2004). 19(2) 187–207.
Micro bore finishing for metal and ceramic materials has been a challenge in the manufacturing industry. Unfortunately, little is understood about how to polish a micro bore and how to assess its inner wall quality because it is difficult to access the micro bore for either polishing or measurement. This article reports on a feasibility study of the abrasive flow polishing of micro bores of 260 ˜ 500-µm diameters and 25 ˜ 50 length/diameter ratios for both metal and ceramic materials. An abrasive flow polishing machine was designed and built with turbulent flow characteristics. Polishing of steel S45C bores of 400- and 500-µm diameters, stainless steel 304 bores of 500-µm diameter, and zirconia bores of 260-µm diameter was conducted. Surface roughness and topography of the polished inner walls of micro bores were characterized using profilometry and optical interferometry from the three-dimensional point of view. Significant reduction in surface roughness of the micro bore inner walls has been made in the polishing processes. The results indicate that it is feasible to apply the abrasive flow polishing technology for metal and ceramic micro bores of diameters of 260 µm or larger and the length/diameter ratios of 25 or higher. It is found that surface roughness of the polished micro bore inner walls decreases with an increase of the abrasive flow passes.
Slurry systems handbook Abulnaga, Baha E. in McGraw-Hill Handbooks (2002). McGraw-Hill, New York.
Development of high speed slurry flow finishing of the inner wall of stainless steel capillary: Polishing and gas flow characteristics of various size of capillaries. Kurobe, T.; Yamada, Y.; Yamamoto, K. (2001). 25(2) 100–106.
A new finishing method for inner wall of capillaries has been developed, in which the polishing is performed by letting the slurry flow through the capillary at high speed. With the increasing number of slurry passes, the surface roughness of as-received capillaries decreases rapidly in the early stage of the low number of slurry passes, and then tends to saturate to a certain level depending on the diameter of the capillaries. It is also found that the decreasing surface roughness of the inner wall results in the increasing conductance of gas flow through the capillary. Accounting for the effect of the capillary diameter D on the differential pressure which is measured in nitrogen gas flow through the capillary at a constant flow rate, an empirical equation is found between the differential pressure P and the surface roughness Ra, logP · D4 = 0.362 + logRa1/6.
A simple model of seasonal open ocean convection. Kuhlbrodt, Till; Titz, Sven; Feudel, Ulrike; Rahmstorf, Stefan (2001). 52(1) 36–49.
enspaceAspects of open ocean deep convection variability are explored with a two-box model. In order to place the model in a region of parameter space relevant to the real ocean, it is fitted to observational data from the Labrador Sea. A systematic fit to OWS Bravo data allows us to determine the model parameters and to locate the position of the Labrador Sea on a stability diagram. The model suggests that the Labrador Sea is in a bistable regime where winter convection can be either ``on'' or ``off '', with both these possibilities being stable climate states. When shifting the surface buoyancy forcing slightly to warmer or fresher conditions, the only steady solution is one without winter convection. emspaceWe then introduce short-term variability by adding a noise term to the surface temperature forcing, turning the box model into a stochastic climate model. The surface forcing anomalies generated in this way induce jumps between the two model states. These state transitions occur on the interannual to decadal time scale. Changing the average surface forcing towards more buoyant conditions lowers the frequency of convection. However, convection becomes more frequent with stronger variability in the surface forcing. As part of the natural variability, there is a non-negligible probability for decadal interruptions of convection. The results highlight the role of surface forcing variability for the persistence of convection in the ocean.
Polyphilo, or, The dark forest revisited : an erotic epiphany of architecture Pérez Gómez Alberto; Colonna, Francesco (1992). MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
An inverse of the evaluation functional for typed Lambda-calculus. Berger, Ulrich; Schwichtenberg, Helmut R. Vermuri (ed.) (1991). 203–211.
In any model of typed \($\lambda$\)-calculus conianing some basic arithmetic, a functional p - * (procedure--* expression) will be defined which inverts the evaluation functional for typed X-terms, Combined with the evaluation functional, p-e yields an efficient normalization algorithm. The method is extended to X-calculi with constants and is used to normalize (the X-representations of) natural deduction proofs of (higher order) arithmetic. A consequence of theoretical interest is a strong completeness theorem for \($\beta$\)\($\eta$\)-reduction, generalizing results of Friedman [1] and Statman [31: If two Xterms have the same value in some model containing representations of the primitive recursive functions (of level 1) then they are provably equal in the \($\beta$\)\($\eta$\)- calculus.
Krug što skamenjuje Šegedin, Petar in Biblioteka Globus (1988). 556-. Globus, Zagreb.
Thermal decomposition of sodium bicarbonate. Keener, Timothy C.; Frazier, George C.; Davis, Wayne T. (1985). 33(1-4) 93–105.
The thermal decomposition of sodium bicarbonate, a candidate material for flue gas desulfurization, has been investigated over the temperature range of 225-350°F (380-450K) and over the particle size range of 51 -140 μm. The shrinking core model, with chemical reaction as the rate controlling step, provides a good fit to the data in the temperature range investigated. However, caution should be exercised in extrapolating these results into the range of about 600°F (about 590K) where sintering of this material is reported to occur. The activation energy of the decomposition reaction is 20.5 kcal/mol (85.7 kj/mol).
Activity coefficient of aqueous sodium bicarbonate. Pitzer, Kenneth S.; Peiper, J. Christopher (1980). 84(19) 2396–2398.
The determination of the activity coefficient and related properties of sodium bicarbonate presents special problems because of the appreciable vapor pressure of CO&sub2; above such solutions. With the development of reliable equations for the thermodynamic properties of mixed electrolytes, it is possible to determine the parameters for NaHCO&sub3; from cell measurements or NaCl-NaHCO&sub2; mixtgures. Literature data are analyzed to illustrate the method and provide interim values, but it is noted that further measurements over a wider range of concentrations would yield more definitive results. An estimate is also given for the activity coefficient of KHCO&sub3;.
Heuristische Bezugsrahmen und heuristisch angelegte Forschungsdesigns als Elemente einer Konstruktionsstrategie empirischer Forschung. Kubicek, Herbert R. Köhler (ed.) (1977). 3–36.
Humidity fixed points of binary saturated aqueous solutions. Greenspan, Lewis (1977). 81A(1) 89–96.
Relative humidity-temperature relationships of some saturated salt solutions in the temperature range 0℃ to 50℃. Wexler, Arnold; Hasegawa, Saburo (1954). 53(1) 19–26.
The relative humidity-temperature relationships have been determined in air in equilibration with saturated salt solutions of lithium chloride, ...